 |
PDBsum entry 1ee2

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ee2
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
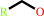 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
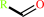 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
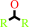 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
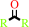 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:12885-12897
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for substrate specificity differences of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes.
|
|
H.W.Adolph,
P.Zwart,
R.Meijers,
I.Hubatsch,
M.Kiefer,
V.Lamzin,
E.Cedergren-Zeppezauer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A structure determination in combination with a kinetic study of the steroid
converting isozyme of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase, SS-ADH, is presented.
Kinetic parameters for the substrates, 5beta-androstane-3beta,17beta-ol,
5beta-androstane-17beta-ol-3-one, ethanol, and various secondary alcohols and
the corresponding ketones are compared for the SS- and EE-isozymes which differ
by nine amino acid substitutions and one deletion. Differences in substrate
specificity and stereoselectivity are explained on the basis of individual
kinetic rate constants for the underlying ordered bi-bi mechanism. SS-ADH was
crystallized in complex with 3alpha,7alpha,12alpha-trihydroxy-5beta-cholan
-24-acid (cholic acid) and NAD(+), but microspectrophotometric analysis of
single crystals proved it to be a mixed complex containing 60-70% NAD(+) and
30-40% NADH. The crystals belong to the space group P2(1) with cell dimensions a
= 55.0 A, b = 73.2 A, c = 92.5 A, and beta = 102.5 degrees. A 98% complete data
set to 1.54-A resolution was collected at 100 K using synchrotron radiation. The
structure was solved by the molecular replacement method utilizing EE-ADH as the
search model. The major structural difference between the isozymes is a widening
of the substrate channel. The largest shifts in C(alpha) carbon positions (about
5 A) are observed in the loop region, in which a deletion of Asp115 is found in
the SS isozyme. SS-ADH easily accommodates cholic acid, whereas steroid
substrates of similar bulkiness would not fit into the EE-ADH substrate site. In
the ternary complex with NAD(+)/NADH, we find that the carboxyl group of cholic
acid ligates to the active site zinc ion, which probably contributes to the
strong binding in the ternary NAD(+) complex.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Barzegar,
A.A.Moosavi-Movahedi,
A.Kyani,
B.Goliaei,
S.Ahmadian,
and
N.Sheibani
(2010).
New model for polymerization of oligomeric alcohol dehydrogenases into nanoaggregates.
|
| |
Appl Biochem Biotechnol,
160,
1188-1205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.V.Plapp
(2010).
Conformational changes and catalysis by alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
493,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.N.Marino-Marmolejo,
A.De León-Rodríguez,
A.P.de la Rosa,
and
L.Santos
(2009).
Heterologous Expression and Characterization of an Alcohol Dehydrogenase from the Archeon Thermoplasma acidophilum.
|
| |
Mol Biotechnol,
42,
61-67.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Lertwattanasakul,
K.Sootsuwan,
S.Limtong,
P.Thanonkeo,
and
M.Yamada
(2007).
Comparison of the gene expression patterns of alcohol dehydrogenase isozymes in the thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus and their physiological functions.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
71,
1170-1182.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Aishima,
D.S.Russel,
L.J.Guibas,
P.D.Adams,
and
A.T.Brunger
(2005).
Automated crystallographic ligand building using the medial axis transform of an electron-density isosurface.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1354-1363.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Heinz,
M.Kiefer,
A.Tholey,
and
H.W.Adolph
(2005).
On the competition for available zinc.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
3197-3207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Hirakawa,
N.Kamiya,
Y.Kawarabayashi,
and
T.Nagamune
(2004).
Properties of an alcohol dehydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix K1.
|
| |
J Biosci Bioeng,
97,
202-206.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Bidlack,
and
P.M.Silverman
(2004).
An active type IV secretion system encoded by the F plasmid sensitizes Escherichia coli to bile salts.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
5202-5209.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.H.Zwart,
G.G.Langer,
and
V.S.Lamzin
(2004).
Modelling bound ligands in protein crystal structures.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
2230-2239.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Valencia,
A.Rosell,
C.Larroy,
J.Farrés,
J.A.Biosca,
I.Fita,
X.Parés,
and
W.F.Ochoa
(2003).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of NADP(H)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Rana perezi.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
334-337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Bottoms,
P.E.Smith,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2002).
A structurally conserved water molecule in Rossmann dinucleotide-binding domains.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
2125-2137.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.F.Chou,
C.L.Lai,
Y.C.Chang,
G.Duester,
and
S.J.Yin
(2002).
Kinetic mechanism of human class IV alcohol dehydrogenase functioning as retinol dehydrogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
25209-25216.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

