 |
PDBsum entry 1dhs

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.46
- deoxyhypusine synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
EC 2.5.1.46
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[eIF5A protein]-L-lysine + spermidine = [eIF5A protein]-deoxyhypusine + propane-1,3-diamine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[eIF5A protein]-L-lysine
|
+
|
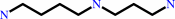 spermidine
spermidine
|
=
|
[eIF5A protein]-deoxyhypusine
|
+
|
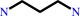 propane-1,3-diamine
propane-1,3-diamine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
NAD(+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
NAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
6:23-32
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the NAD complex of human deoxyhypusine synthase: an enzyme with a ball-and-chain mechanism for blocking the active site.
|
|
D.I.Liao,
E.C.Wolff,
M.H.Park,
D.R.Davies.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (elF-5A) contains an unusual amino
acid, hypusine [N epsilon-(4-aminobutyl-2-hydroxy)lysine]. The first step in the
post-translational formation of hypusine is catalysed by the enzyme
deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS). The modified version of elF-5A, and DHS, are
required for eukaryotic cell proliferation. Knowledge of the three-dimensional
structure of this key enzyme should permit the design of specific inhibitors
that may be useful as anti-proliferative agents. RESULTS: The crystal structure
of human DHS with bound NAD cofactor has been determined and refined at 2.2 A
resolution. The enzyme is a tetramer of four identical subunits arranged with
222 symmetry; each subunit contains a nucleotide-binding (or Rossmann) fold. The
tetramer comprises two tightly associated dimers and contains four active sites,
two in each dimer interface. The catalytic portion of each active site is
located in one subunit while the NAD-binding site is located in the other. The
entrance to the active-site cavity is blocked by a two-turn alpha helix, part of
a third subunit, to which it is joined by an extended loop. CONCLUSIONS: The
active site of DHS is a cavity buried below the surface of the enzyme at the
interface between two subunits. In the conformation observed here, the
substrate-binding site is inaccessible and we propose that the reaction steps
carried out by the enzyme must be accompanied by significant conformational
changes, the least of which would be the displacement of the two-turn alpha
helix.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. A ball-and-stick model of the DHS active-site
structure. The N-terminal helix from a third monomer that covers
the pocket entrance is in pale yellow. The orientation and color
scheme of this figure are the same as in Figure 2. For clarity,
only the nicotinamide ring and its adjacent ribose of NAD are
shown. The hydrogen bonds between water molecules and sidechains
of the protein residues are indicated by gray dotted lines;
atoms are shown in standard colours. The N-terminal helix from
the third monomer blocks the access to the active site.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1998,
6,
23-32)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Chawla,
A.Jhingran,
S.Singh,
N.Tyagi,
M.H.Park,
N.Srinivasan,
S.C.Roberts,
and
R.Madhubala
(2010).
Identification and characterization of a novel deoxyhypusine synthase in Leishmania donovani.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
453-463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kerscher,
E.Nzukou,
and
A.Kaiser
(2010).
Assessment of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase as a putative, novel drug target.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
38,
471-477.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Blavid,
P.Kusch,
J.Hauber,
U.Eschweiler,
S.R.Sarite,
S.Specht,
S.Deininger,
A.Hoerauf,
and
A.Kaiser
(2010).
Down-regulation of hypusine biosynthesis in plasmodium by inhibition of S-adenosyl-methionine-decarboxylase.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
38,
461-469.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Huang,
Y.Cui,
C.H.Chen,
D.Clampitt,
C.T.Lin,
and
L.Wen
(2007).
Molecular cloning and functional expression of bovine deoxyhypusine hydroxylase cDNA and homologs.
|
| |
Protein Expr Purif,
54,
126-133.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Shirai,
Y.Mokrab,
and
K.Mizuguchi
(2006).
The guanidino-group modifying enzymes: structural basis for their diversity and commonality.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
1010-1023.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.T.Njuguna,
M.Nassar,
A.Hoerauf,
and
A.E.Kaiser
(2006).
Cloning, expression and functional activity of deoxyhypusine synthase from Plasmodium vivax.
|
| |
BMC Microbiol,
6,
91.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Park
(2006).
The post-translational synthesis of a polyamine-derived amino acid, hypusine, in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A).
|
| |
J Biochem,
139,
161-169.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Davies,
and
D.Davies
(2005).
A quiet life with proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
34,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Umland,
E.C.Wolff,
M.H.Park,
and
D.R.Davies
(2004).
A new crystal structure of deoxyhypusine synthase reveals the configuration of the active enzyme and of an enzyme.NAD.inhibitor ternary complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
28697-28705.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ober,
R.Harms,
L.Witte,
and
T.Hartmann
(2003).
Molecular evolution by change of function. Alkaloid-specific homospermidine synthase retained all properties of deoxyhypusine synthase except binding the eIF5A precursor protein.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
12805-12812.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Park,
E.C.Wolff,
J.E.Folk,
and
M.H.Park
(2003).
Reversal of the deoxyhypusine synthesis reaction. Generation of spermidine or homospermidine from deoxyhypusine by deoxyhypusine synthase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
32683-32691.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Binda,
R.Angelini,
R.Federico,
P.Ascenzi,
and
A.Mattevi
(2001).
Structural bases for inhibitor binding and catalysis in polyamine oxidase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
2766-2776.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Wolff,
J.Wolff,
and
M.H.Park
(2000).
Deoxyhypusine synthase generates and uses bound NADH in a transient hydride transfer mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
9170-9177.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kaiser
(1999).
Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding homospermidine synthase from Senecio vulgaris (Asteraceae) in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Plant J,
19,
195-201.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Binda,
A.Coda,
R.Angelini,
R.Federico,
P.Ascenzi,
and
A.Mattevi
(1999).
A 30-angstrom-long U-shaped catalytic tunnel in the crystal structure of polyamine oxidase.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
265-276.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ober,
and
T.Hartmann
(1999).
Deoxyhypusine synthase from tobacco. cDNA isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of an enzyme with extended substrate specificity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
32040-32047.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Wolff,
and
M.H.Park
(1999).
Identification of lysine350 of yeast deoxyhypusine synthase as the site of enzyme intermediate formation.
|
| |
Yeast,
15,
43-50.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Aliverti,
Z.Deng,
D.Ravasi,
L.Piubelli,
P.A.Karplus,
and
G.Zanetti
(1998).
Probing the function of the invariant glutamyl residue 312 in spinach ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
34008-34015.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Peat,
J.Newman,
G.S.Waldo,
J.Berendzen,
and
T.C.Terwilliger
(1998).
Structure of translation initiation factor 5A from Pyrobaculum aerophilum at 1.75 A resolution.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
1207-1214.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

