 |
PDBsum entry 1c9h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Immune system
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1c9h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
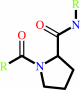 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
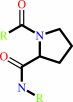 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
56:266-271
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of FKBP12.6 in complex with rapamycin.
|
|
C.C.Deivanayagam,
M.Carson,
A.Thotakura,
S.V.Narayana,
R.S.Chodavarapu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
FKBP12.6 is a novel isoform of FKBP12, which selectively binds to the cardiac
ryanodine receptor (RyR2). The crystal structure of FKBP12.6 in complex with
rapamycin has now been determined at 2.0 A resolution. The structures of
FKBP12.6 and FKBP12 are nearly identical, except for a displacement observed in
the helical region of FKBP12.6 toward the hydrophobic pocket. This displacement
was not predicted by homology modeling studies. Analyses of the residues that
are likely to confer the RyR2-binding specificity are presented.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 Stereo diagrams of the protein surfaces of rapamycin
complexes of FKBP12.6 and FKBP12. The rapamycin is shown in
ball-and-stick format, colored white, red and blue for carbon,
oxygen and nitrogen, respectively. The protein surfaces are
colored by chemical property: white is hydrophobic, red is
negatively charged, blue is positively charged, orange is a
hydrogen-bond acceptor, cyan is a hydrogen-bond donor and
magenta can both accept and donate hydrogen bonds. Exposed
surfaces of non-identical residues are textured with a mesh and
labeled. The orientation is as in Fig. 1-(b), only 90% smaller.
Above, FKBP12.6; below, FKBP12.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4 Stereo diagrams of the hydrophobic binding pockets of
FKBP12.6 and FKBP12. All residues and surfaces within 4 Å of
rapamycin are shown. Ribbons and carbon are white in FKBP12.6
and gray in FKBP12. O atoms and N atoms are red and blue,
respectively, in both. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed black
lines.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2000,
56,
266-271)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Song,
J.G.Lee,
H.S.Youn,
S.H.Eom,
and
d.o. .H.Kim
(2011).
Ryanodine receptor assembly: A novel systems biology approach to 3D mapping.
|
| |
Prog Biophys Mol Biol,
105,
145-161.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.S.Woo,
J.H.Hwang,
J.K.Ko,
d.o. .H.Kim,
J.Ma,
and
E.H.Lee
(2009).
Glutamate at position 227 of junctophilin-2 is involved in binding to TRPC3.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biochem,
328,
25-32.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Huang,
J.Shan,
S.Reiken,
X.H.Wehrens,
and
A.R.Marks
(2006).
Analysis of calstabin2 (FKBP12.6)-ryanodine receptor interactions: rescue of heart failure by calstabin2 in mice.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
3456-3461.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Sharma,
L.H.Jeyakumar,
S.Fleischer,
and
T.Wagenknecht
(2006).
Three-dimensional visualization of FKBP12.6 binding to an open conformation of cardiac ryanodine receptor.
|
| |
Biophys J,
90,
164-172.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.H.Lee,
S.H.Rho,
S.J.Kwon,
S.H.Eom,
P.D.Allen,
and
d.o. .H.Kim
(2004).
N-terminal region of FKBP12 is essential for binding to the skeletal ryanodine receptor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
26481-26488.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.J.Pereira,
M.C.Vega,
E.González-Rey,
R.Fernández-Carazo,
S.Macedo-Ribeiro,
F.X.Gomis-Rüth,
A.González,
and
M.Coll
(2002).
Trypanosoma cruzi macrophage infectivity potentiator has a rotamase core and a highly exposed alpha-helix.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
3,
88-94.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

