
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain R:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 GTP
GTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
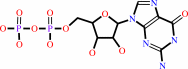 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nature
394:337-343
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structural basis of the activation of Ras by Sos.
|
|
P.A.Boriack-Sjodin,
S.M.Margarit,
D.Bar-Sagi,
J.Kuriyan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of human H-Ras complexed with the Ras
guanine-nucleotide-exchange-factor region of the Son of sevenless (Sos) protein
has been determined at 2.8 A resolution. The normally tight interaction of
nucleotides with Ras is disrupted by Sos in two ways. First, the insertion into
Ras of an alpha-helix from Sos results in the displacement of the Switch 1
region of Ras, opening up the nucleotide-binding site. Second, side chains
presented by this helix and by a distorted conformation of the Switch 2 region
of Ras alter the chemical environment of the binding site for the phosphate
groups of the nucleotide and the associated magnesium ion, so that their binding
is no longer favoured. Sos does not impede the binding sites for the base and
the ribose of GTP or GDP, so the Ras-Sos complex adopts a structure that allows
nucleotide release and rebinding.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 The complex of human H-Ras with the exchange-factor
region of human Sos1. a, The N-domain of Sos (residues 568-741)
is shown blue; the catalytic domain (residues 752-1044) is
green; the Switch 1 and Switch 2 segments and the P-loop region
of Ras (as defined here) are orange and red, respectively;
conserved regions (SCRs) among Ras-family exchange factors are
cyan2,17. Disordered residues of Sos are shown as dotted lines.
This and all other ribbon diagrams were generated using
RIBBONS44. b, The Ras-Sos complex is shown with the catalytic
domain of Sos depicted as a molecular surface. Conserved
residues Ile 956 and Phe 958 in the catalytic domain that form a
hydrophobic interface with the N-domain are labelled. This and
all other figures with molecular surfaces were generated using
GRASP45.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3 Interface surfaces of the Ras-Sos complex. a,
Residues of Ras that form direct interactions with Sos are shown
as red spheres; additional residues at the interface are orange
spheres. The nucleotide is shown for reference only and is not
present in the structure. b, The interface surface of Ras; the
orientation is the same as in a. The surface is coloured using a
gradient: bright orange indicates atoms <4 ? from Sos, white
indicates atoms >7 ? from Sos, lighter shades of orange indicate
intermediate distances. Sos (N-domain deleted) is shown as a
green ribbon. c, The primary sequence of Ras.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nature
(1998,
394,
337-343)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Fernández-Medarde,
and
E.Santos
(2011).
The RasGrf family of mammalian guanine nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1815,
170-188.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Chung,
and
M.Kondo
(2011).
Role of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling in physiological hematopoiesis and leukemia development.
|
| |
Immunol Res,
49,
248-268.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Gremer,
T.Merbitz-Zahradnik,
R.Dvorsky,
I.C.Cirstea,
C.P.Kratz,
M.Zenker,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
M.R.Ahmadian
(2011).
Germline KRAS mutations cause aberrant biochemical and physical properties leading to developmental disorders.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
32,
33-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Rawat,
and
P.Biswas
(2011).
Shape, flexibility and packing of proteins and nucleic acids in complexes.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
13,
9632-9643.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Mace,
Y.Wallez,
M.K.Dobaczewska,
J.J.Lee,
H.Robinson,
E.B.Pasquale,
and
S.J.Riedl
(2011).
NSP-Cas protein structures reveal a promiscuous interaction module in cell signaling.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
18,
1381-1387.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Radha,
A.Mitra,
K.Dayma,
and
K.Sasikumar
(2011).
Signalling to actin: role of C3G, a multitasking guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor.
|
| |
Biosci Rep,
31,
231-244.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Naruo,
T.Nagashima,
R.Ushikoshi-Nakayama,
Y.Saeki,
T.Nakakuki,
T.Naka,
H.Tanaka,
S.F.Tsai,
and
M.Okada-Hatakeyama
(2011).
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in combination with expression of MIG6 alters gefitinib sensitivity.
|
| |
BMC Syst Biol,
5,
29.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Abankwa,
A.A.Gorfe,
K.Inder,
and
J.F.Hancock
(2010).
Ras membrane orientation and nanodomain localization generate isoform diversity.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
1130-1135.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Vigil,
J.Cherfils,
K.L.Rossman,
and
C.J.Der
(2010).
Ras superfamily GEFs and GAPs: validated and tractable targets for cancer therapy?
|
| |
Nat Rev Cancer,
10,
842-857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Buhrman,
G.Holzapfel,
S.Fetics,
and
C.Mattos
(2010).
Allosteric modulation of Ras positions Q61 for a direct role in catalysis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
4931-4936.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gureasko,
O.Kuchment,
D.L.Makino,
H.Sondermann,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2010).
Role of the histone domain in the autoinhibition and activation of the Ras activator Son of Sevenless.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
3430-3435.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Lebbink,
A.Fish,
A.Reumer,
G.Natrajan,
H.H.Winterwerp,
and
T.K.Sixma
(2010).
Magnesium coordination controls the molecular switch function of DNA mismatch repair protein MutS.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
13131-13141.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Gremer,
A.De Luca,
T.Merbitz-Zahradnik,
B.Dallapiccola,
S.Morlot,
M.Tartaglia,
K.Kutsche,
M.R.Ahmadian,
and
G.Rosenberger
(2010).
Duplication of Glu37 in the switch I region of HRAS impairs effector/GAP binding and underlies Costello syndrome by promoting enhanced growth factor-dependent MAPK and AKT activation.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
19,
790-802.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Nassar,
K.Singh,
and
M.Garcia-Diaz
(2010).
Structure of the dominant negative S17N mutant of Ras.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
49,
1970-1974.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Niault,
and
M.Baccarini
(2010).
Targets of Raf in tumorigenesis.
|
| |
Carcinogenesis,
31,
1165-1174.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.A.Andrade,
A.M.Silva,
V.S.Alves,
A.P.Salgado,
M.B.Melo,
H.M.Andrade,
F.V.Dall'Orto,
S.A.Garcia,
T.N.Silveira,
and
R.T.Gazzinelli
(2010).
Early endosome localization and activity of RasGEF1b, a toll-like receptor-inducible Ras guanine-nucleotide exchange factor.
|
| |
Genes Immun,
11,
447-457.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Thomas,
I.Fricke,
M.Weyand,
and
A.Berken
(2009).
3D structure of a binary ROP-PRONE complex: the final intermediate for a complete set of molecular snapshots of the RopGEF reaction.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
390,
427-435.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Tu,
X.Zhou,
J.E.Tropea,
B.P.Austin,
D.S.Waugh,
D.L.Court,
and
X.Ji
(2009).
Structure of ERA in complex with the 3' end of 16S rRNA: implications for ribosome biogenesis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
14843-14848.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Yaman,
R.Gasper,
C.Koerner,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
U.H.Tazebay
(2009).
RasGEF1A and RasGEF1B are guanine nucleotide exchange factors that discriminate between Rap GTP-binding proteins and mediate Rap2-specific nucleotide exchange.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
4607-4616.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.F.Chin,
Y.Cai,
S.Menon,
S.Ferro-Novick,
K.M.Reinisch,
and
E.M.De La Cruz
(2009).
Kinetic analysis of the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of TRAPP, a multimeric Ypt1p exchange factor.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
389,
275-288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Raaijmakers,
and
J.L.Bos
(2009).
Specificity in ras and rap signaling.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
10995-10999.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yang,
Z.Zhang,
S.M.Roe,
C.J.Marshall,
and
D.Barford
(2009).
Activation of Rho GTPases by DOCK exchange factors is mediated by a nucleotide sensor.
|
| |
Science,
325,
1398-1402.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Kim,
J.Song,
and
C.Park
(2009).
Determining protein stability in cell lysates by pulse proteolysis and Western blotting.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
1051-1059.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Freedman,
H.Sondermann,
O.Kuchment,
G.D.Friedland,
T.Kortemme,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2009).
Differences in flexibility underlie functional differences in the Ras activators son of sevenless and Ras guanine nucleotide releasing factor 1.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
41-53.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Dong,
B.Yang,
Y.Li,
C.Zhong,
and
J.Ding
(2009).
Molecular basis of the acceleration of the GDP-GTP exchange of human ras homolog enriched in brain by human translationally controlled tumor protein.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
23754-23764.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Karnoub,
and
R.A.Weinberg
(2008).
Ras oncogenes: split personalities.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
9,
517-531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lopez-Alcalá,
B.Alvarez-Moya,
P.Villalonga,
M.Calvo,
O.Bachs,
and
N.Agell
(2008).
Identification of essential interacting elements in K-Ras/calmodulin binding and its role in K-Ras localization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
10621-10631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rehmann,
E.Arias-Palomo,
M.A.Hadders,
F.Schwede,
O.Llorca,
and
J.L.Bos
(2008).
Structure of Epac2 in complex with a cyclic AMP analogue and RAP1B.
|
| |
Nature,
455,
124-127.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gureasko,
W.J.Galush,
S.Boykevisch,
H.Sondermann,
D.Bar-Sagi,
J.T.Groves,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2008).
Membrane-dependent signal integration by the Ras activator Son of sevenless.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
15,
452-461.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Adler,
W.Bowne,
I.Kamran,
J.Michl,
F.K.Friedman,
E.Chin,
M.Zenilman,
and
M.R.Pincus
(2008).
Two peptides derived from ras-p21 induce either phenotypic reversion or tumor cell necrosis of ras-transformed human cancer cells.
|
| |
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,
62,
491-498.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cai,
H.F.Chin,
D.Lazarova,
S.Menon,
C.Fu,
H.Cai,
A.Sclafani,
D.W.Rodgers,
E.M.De La Cruz,
S.Ferro-Novick,
and
K.M.Reinisch
(2008).
The structural basis for activation of the Rab Ypt1p by the TRAPP membrane-tethering complexes.
|
| |
Cell,
133,
1202-1213.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kintses,
M.Gyimesi,
D.S.Pearson,
M.A.Geeves,
W.Zeng,
C.R.Bagshaw,
and
A.Málnási-Csizmadia
(2007).
Reversible movement of switch 1 loop of myosin determines actin interaction.
|
| |
EMBO J,
26,
265-274.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Thomas,
I.Fricke,
A.Scrima,
A.Berken,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2007).
Structural evidence for a common intermediate in small G protein-GEF reactions.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
25,
141-149.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Dong,
M.Medkova,
P.Novick,
and
K.M.Reinisch
(2007).
A catalytic coiled coil: structural insights into the activation of the Rab GTPase Sec4p by Sec2p.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
25,
455-462.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Kae,
A.Kortholt,
H.Rehmann,
R.H.Insall,
P.J.Van Haastert,
G.B.Spiegelman,
and
G.Weeks
(2007).
Cyclic AMP signalling in Dictyostelium: G-proteins activate separate Ras pathways using specific RasGEFs.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
8,
477-482.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rehmann,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
J.L.Bos
(2007).
Capturing cyclic nucleotides in action: snapshots from crystallographic studies.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
8,
63-73.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Bos,
H.Rehmann,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2007).
GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins.
|
| |
Cell,
129,
865-877.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Modzelewska,
M.G.Elgort,
J.Huang,
G.Jongeward,
A.Lauritzen,
C.H.Yoon,
P.W.Sternberg,
and
N.Moghal
(2007).
An activating mutation in sos-1 identifies its Dbl domain as a critical inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway during Caenorhabditis elegans vulval development.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
27,
3695-3707.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Xie,
Y.Jiang,
P.Ouyang,
J.Chen,
H.Doan,
B.Herndon,
J.E.Sylvester,
K.Zhang,
A.Molteni,
M.Reichle,
R.Zhang,
M.D.Haub,
R.C.Baybutt,
and
W.Wang
(2007).
Effects of dietary calorie restriction or exercise on the PI3K and Ras signaling pathways in the skin of mice.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
28025-28035.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sethuraman,
N.Clavreul,
H.Huang,
M.E.McComb,
C.E.Costello,
and
R.A.Cohen
(2007).
Quantification of oxidative posttranslational modifications of cysteine thiols of p21ras associated with redox modulation of activity using isotope-coded affinity tags and mass spectrometry.
|
| |
Free Radic Biol Med,
42,
823-829.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Zenker,
D.Horn,
D.Wieczorek,
J.Allanson,
S.Pauli,
I.van der Burgt,
H.G.Doerr,
H.Gaspar,
M.Hofbeck,
G.Gillessen-Kaesbach,
A.Koch,
P.Meinecke,
S.Mundlos,
A.Nowka,
A.Rauch,
S.Reif,
C.von Schnakenburg,
H.Seidel,
L.E.Wehner,
C.Zweier,
S.Bauhuber,
V.Matejas,
C.P.Kratz,
C.Thomas,
and
K.Kutsche
(2007).
SOS1 is the second most common Noonan gene but plays no major role in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome.
|
| |
J Med Genet,
44,
651-656.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Schubbert,
K.Shannon,
and
G.Bollag
(2007).
Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer.
|
| |
Nat Rev Cancer,
7,
295-308.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.J.Belden,
L.F.Larrondo,
A.C.Froehlich,
M.Shi,
C.H.Chen,
J.J.Loros,
and
J.C.Dunlap
(2007).
The band mutation in Neurospora crassa is a dominant allele of ras-1 implicating RAS signaling in circadian output.
|
| |
Genes Dev,
21,
1494-1505.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Sato,
R.Shirakawa,
H.Horiuchi,
N.Dohmae,
S.Fukai,
and
O.Nureki
(2007).
Asymmetric coiled-coil structure with Guanine nucleotide exchange activity.
|
| |
Structure,
15,
245-252.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Itzen,
O.Pylypenko,
R.S.Goody,
K.Alexandrov,
and
A.Rak
(2006).
Nucleotide exchange via local protein unfolding--structure of Rab8 in complex with MSS4.
|
| |
EMBO J,
25,
1445-1455.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Ford,
V.Hornak,
H.Kleinman,
and
N.Nassar
(2006).
Structure of a transient intermediate for GTP hydrolysis by ras.
|
| |
Structure,
14,
427-436.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Gottlieb,
C.Grunwald,
C.Nowak,
J.Kuhlmann,
and
H.Waldmann
(2006).
Intein-mediated in vitro synthesis of lipidated Ras proteins.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
260-262.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rehmann,
J.Das,
P.Knipscheer,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
J.L.Bos
(2006).
Structure of the cyclic-AMP-responsive exchange factor Epac2 in its auto-inhibited state.
|
| |
Nature,
439,
625-628.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Bos
(2006).
Epac proteins: multi-purpose cAMP targets.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
31,
680-686.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Zarich,
J.L.Oliva,
N.Martínez,
R.Jorge,
A.Ballester,
S.Gutiérrez-Eisman,
S.García-Vargas,
and
J.M.Rojas
(2006).
Grb2 is a negative modulator of the intrinsic Ras-GEF activity of hSos1.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
17,
3591-3597.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Aloy,
and
R.B.Russell
(2006).
Structural systems biology: modelling protein interactions.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
7,
188-197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Boykevisch,
C.Zhao,
H.Sondermann,
P.Philippidou,
S.Halegoua,
J.Kuriyan,
and
D.Bar-Sagi
(2006).
Regulation of ras signaling dynamics by Sos-mediated positive feedback.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
16,
2173-2179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Freedman,
H.Sondermann,
G.D.Friedland,
T.Kortemme,
D.Bar-Sagi,
S.Marqusee,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2006).
A Ras-induced conformational switch in the Ras activator Son of sevenless.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
16692-16697.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Dupuy,
S.L'Hoste,
J.Cherfils,
J.Camonis,
G.Gaudriault,
and
J.de Gunzburg
(2005).
Novel Rap1 dominant-negative mutants interfere selectively with C3G and Epac.
|
| |
Oncogene,
24,
4509-4520.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Wilkins,
K.Szafranski,
D.J.Fraser,
D.Bakthavatsalam,
R.Müller,
P.R.Fisher,
G.Glöckner,
L.Eichinger,
A.A.Noegel,
and
R.H.Insall
(2005).
The Dictyostelium genome encodes numerous RasGEFs with multiple biological roles.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
6,
R68.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.B.Friday,
and
A.A.Adjei
(2005).
K-ras as a target for cancer therapy.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1756,
127-144.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Ford,
K.Skowronek,
S.Boykevisch,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
N.Nassar
(2005).
Structure of the G60A mutant of Ras: implications for the dominant negative effect.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
25697-25705.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Sondermann,
B.Nagar,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2005).
Computational docking and solution x-ray scattering predict a membrane-interacting role for the histone domain of the Ras activator son of sevenless.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
16632-16637.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Heo,
and
S.L.Campbell
(2005).
Superoxide anion radical modulates the activity of Ras and Ras-related GTPases by a radical-based mechanism similar to that of nitric oxide.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
12438-12445.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Rossman,
C.J.Der,
and
J.Sondek
(2005).
GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors.
|
| |
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,
6,
167-180.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Rossman,
and
J.Sondek
(2005).
Larger than Dbl: new structural insights into RhoA activation.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
30,
163-165.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Jeppesen,
T.Navratil,
L.L.Spremulli,
and
J.Nyborg
(2005).
Crystal structure of the bovine mitochondrial elongation factor Tu.Ts complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
5071-5081.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Mishra,
S.K.Gara,
S.Mishra,
and
B.Prakash
(2005).
Analysis of GTPases carrying hydrophobic amino acid substitutions in lieu of the catalytic glutamine: implications for GTP hydrolysis.
|
| |
Proteins,
59,
332-338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Pereira,
and
R.A.Cerione
(2005).
A switch 3 point mutation in the alpha subunit of transducin yields a unique dominant-negative inhibitor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
35696-35703.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Smith,
M.Hyde,
and
M.R.Pincus
(2005).
Comparison of the predicted structures of loops in the ras-SOS protein bound to a single ras-p21 protein with the crystallographically determined structures in SOS bound to two ras-p21 proteins.
|
| |
Protein J,
24,
391-398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Delprato,
E.Merithew,
and
D.G.Lambright
(2004).
Structure, exchange determinants, and family-wide rab specificity of the tandem helical bundle and Vps9 domains of Rabex-5.
|
| |
Cell,
118,
607-617.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Ponsioen,
J.Zhao,
J.Riedl,
F.Zwartkruis,
G.van der Krogt,
M.Zaccolo,
W.H.Moolenaar,
J.L.Bos,
and
K.Jalink
(2004).
Detecting cAMP-induced Epac activation by fluorescence resonance energy transfer: Epac as a novel cAMP indicator.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
5,
1176-1180.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Helmreich
(2004).
Structural flexibility of small GTPases. Can it explain their functional versatility?
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
1121-1136.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.W.Becker
(2004).
Relevance of the kinetic equilibrium of forces to the control of the cell cycle by Ras proteins.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
41-47.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Sondermann,
S.M.Soisson,
S.Boykevisch,
S.S.Yang,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2004).
Structural analysis of autoinhibition in the Ras activator Son of sevenless.
|
| |
Cell,
119,
393-405.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Dail,
M.S.Kalo,
J.A.Seddon,
J.F.Côté,
K.Vuori,
and
E.B.Pasquale
(2004).
SHEP1 function in cell migration is impaired by a single amino acid mutation that disrupts association with the scaffolding protein cas but not with Ras GTPases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
41892-41902.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Kristelly,
G.Gao,
and
J.J.Tesmer
(2004).
Structural determinants of RhoA binding and nucleotide exchange in leukemia-associated Rho guanine-nucleotide exchange factor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
47352-47362.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Silver,
F.Chen,
L.Doyon,
A.W.Zink,
and
I.Rebay
(2004).
New class of Son-of-sevenless (Sos) alleles highlights the complexities of Sos function.
|
| |
Genesis,
39,
263-272.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Boesen,
S.S.Mohammad,
G.D.Pavitt,
and
G.R.Andersen
(2004).
Structure of the catalytic fragment of translation initiation factor 2B and identification of a critically important catalytic residue.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
10584-10592.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Cai,
J.Pei,
and
N.V.Grishin
(2004).
Reconstruction of ancestral protein sequences and its applications.
|
| |
BMC Evol Biol,
4,
33.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Tabancay,
C.L.Gau,
I.M.Machado,
E.J.Uhlmann,
D.H.Gutmann,
L.Guo,
and
F.Tamanoi
(2003).
Identification of dominant negative mutants of Rheb GTPase and their use to implicate the involvement of human Rheb in the activation of p70S6K.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
39921-39930.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Rak,
O.Pylypenko,
T.Durek,
A.Watzke,
S.Kushnir,
L.Brunsveld,
H.Waldmann,
R.S.Goody,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2003).
Structure of Rab GDP-dissociation inhibitor in complex with prenylated YPT1 GTPase.
|
| |
Science,
302,
646-650.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Hochbaum,
T.Tanos,
F.Ribeiro-Neto,
D.Altschuler,
and
O.A.Coso
(2003).
Activation of JNK by Epac is independent of its activity as a Rap guanine nucleotide exchanger.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
33738-33746.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Matallanas,
I.Arozarena,
M.T.Berciano,
D.S.Aaronson,
A.Pellicer,
M.Lafarga,
and
P.Crespo
(2003).
Differences on the inhibitory specificities of H-Ras, K-Ras, and N-Ras (N17) dominant negative mutants are related to their membrane microlocalization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
4572-4581.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Mossessova,
R.A.Corpina,
and
J.Goldberg
(2003).
Crystal structure of ARF1*Sec7 complexed with Brefeldin A and its implications for the guanine nucleotide exchange mechanism.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
12,
1403-1411.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rehmann,
A.Rueppel,
J.L.Bos,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2003).
Communication between the regulatory and the catalytic region of the cAMP-responsive guanine nucleotide exchange factor Epac.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
23508-23514.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Rehmann,
F.Schwede,
S.O.Døskeland,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
J.L.Bos
(2003).
Ligand-mediated activation of the cAMP-responsive guanine nucleotide exchange factor Epac.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
38548-38556.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Sondermann,
S.M.Soisson,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2003).
Tandem histone folds in the structure of the N-terminal segment of the ras activator Son of Sevenless.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
1583-1593.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cherfils,
and
M.Chabre
(2003).
Activation of G-protein Galpha subunits by receptors through Galpha-Gbeta and Galpha-Ggamma interactions.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
28,
13-17.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Renault,
B.Guibert,
and
J.Cherfils
(2003).
Structural snapshots of the mechanism and inhibition of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor.
|
| |
Nature,
426,
525-530.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Caloca,
J.L.Zugaza,
and
X.R.Bustelo
(2003).
Exchange factors of the RasGRP family mediate Ras activation in the Golgi.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
33465-33473.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Malumbres,
and
M.Barbacid
(2003).
RAS oncogenes: the first 30 years.
|
| |
Nat Rev Cancer,
3,
459-465.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Wing,
J.T.Snyder,
J.Sondek,
and
T.K.Harden
(2003).
Direct activation of phospholipase C-epsilon by Rho.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
41253-41258.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Naber,
S.Rice,
M.Matuska,
R.D.Vale,
R.Cooke,
and
E.Pate
(2003).
EPR spectroscopy shows a microtubule-dependent conformational change in the kinesin switch 1 domain.
|
| |
Biophys J,
84,
3190-3196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Uthaiah,
G.J.Praefcke,
J.C.Howard,
and
C.Herrmann
(2003).
IIGP1, an interferon-gamma-inducible 47-kDa GTPase of the mouse, showing cooperative enzymatic activity and GTP-dependent multimerization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
29336-29343.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Consonni,
I.Arosio,
T.Recca,
R.Longhi,
G.Colombo,
and
M.Vanoni
(2003).
Structure determination and dynamics of peptides overlapping the catalytic hairpin of the Ras-specific GEF Cdc25(Mm).
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
12154-12162.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Goody
(2003).
The missing link in the muscle cross-bridge cycle.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
773-775.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Margarit,
H.Sondermann,
B.E.Hall,
B.Nagar,
A.Hoelz,
M.Pirruccello,
D.Bar-Sagi,
and
J.Kuriyan
(2003).
Structural evidence for feedback activation by Ras.GTP of the Ras-specific nucleotide exchange factor SOS.
|
| |
Cell,
112,
685-695.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Rocheleau,
R.M.Howard,
A.P.Goldman,
M.L.Volk,
L.J.Girard,
and
M.V.Sundaram
(2002).
A lin-45 raf enhancer screen identifies eor-1, eor-2 and unusual alleles of Ras pathway genes in Caenorhabditis elegans.
|
| |
Genetics,
161,
121-131.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Prober,
and
B.A.Edgar
(2002).
Interactions between Ras1, dMyc, and dPI3K signaling in the developing Drosophila wing.
|
| |
Genes Dev,
16,
2286-2299.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Buchwald,
A.Friebel,
J.E.Galán,
W.D.Hardt,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
K.Scheffzek
(2002).
Structural basis for the reversible activation of a Rho protein by the bacterial toxin SopE.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
3286-3295.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Wieden,
K.Gromadski,
D.Rodnin,
and
M.V.Rodnina
(2002).
Mechanism of elongation factor (EF)-Ts-catalyzed nucleotide exchange in EF-Tu. Contribution of contacts at the guanine base.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
6032-6036.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Zhu,
Y.Qin,
M.Zhao,
L.Van Aelst,
and
R.Malinow
(2002).
Ras and Rap control AMPA receptor trafficking during synaptic plasticity.
|
| |
Cell,
110,
443-455.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Goldberg,
L.Bosgraaf,
P.J.Van Haastert,
and
J.L.Smith
(2002).
Identification of four candidate cGMP targets in Dictyostelium.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
6749-6754.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Rossman,
D.K.Worthylake,
J.T.Snyder,
D.P.Siderovski,
S.L.Campbell,
and
J.Sondek
(2002).
A crystallographic view of interactions between Dbs and Cdc42: PH domain-assisted guanine nucleotide exchange.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
1315-1326.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Rossman,
D.K.Worthylake,
J.T.Snyder,
L.Cheng,
I.P.Whitehead,
and
J.Sondek
(2002).
Functional analysis of cdc42 residues required for Guanine nucleotide exchange.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
50893-50898.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Macaluso,
G.Russo,
C.Cinti,
V.Bazan,
N.Gebbia,
and
A.Russo
(2002).
Ras family genes: an interesting link between cell cycle and cancer.
|
| |
J Cell Physiol,
192,
125-130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Papadaki,
V.Pizon,
B.Onken,
and
E.C.Chang
(2002).
Two ras pathways in fission yeast are differentially regulated by two ras guanine nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
22,
4598-4606.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Jorge,
N.Zarich,
J.L.Oliva,
M.Azañedo,
N.Martínez,
X.de la Cruz,
and
J.M.Rojas
(2002).
HSos1 contains a new amino-terminal regulatory motif with specific binding affinity for its pleckstrin homology domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
44171-44179.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.I.Gringhuis,
E.A.Papendrecht-van der Voort,
A.Leow,
E.W.Nivine Levarht,
F.C.Breedveld,
and
C.L.Verweij
(2002).
Effect of redox balance alterations on cellular localization of LAT and downstream T-cell receptor signaling pathways.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
22,
400-411.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Brinkmann,
O.Daumke,
U.Herbrand,
D.Kühlmann,
P.Stege,
M.R.Ahmadian,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2002).
Rap-specific GTPase activating protein follows an alternative mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
12525-12531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Tian,
G.Rusanescu,
W.Hou,
B.Schaffhausen,
and
L.A.Feig
(2002).
PDK1 mediates growth factor-induced Ral-GEF activation by a kinase-independent mechanism.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
1327-1338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yang,
L.Li,
G.W.Wong,
S.A.Krilis,
M.S.Madhusudhan,
A.Sali,
and
R.L.Stevens
(2002).
RasGRP4, a new mast cell-restricted Ras guanine nucleotide-releasing protein with calcium- and diacylglycerol-binding motifs. Identification of defective variants of this signaling protein in asthma, mastocytosis, and mast cell leukemia patients and demonstration of the importance of RasGRP4 in mast cell development and function.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
25756-25774.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.de Hoog,
J.A.Koehler,
M.D.Goldstein,
P.Taylor,
D.Figeys,
and
M.F.Moran
(2001).
Ras binding triggers ubiquitination of the Ras exchange factor Ras-GRF2.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
21,
2107-2117.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Bi,
B.Debreceni,
K.Zhu,
B.Salani,
A.Eva,
and
Y.Zheng
(2001).
Autoinhibition mechanism of proto-Dbl.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
21,
1463-1474.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Rusanescu,
T.Gotoh,
X.Tian,
and
L.A.Feig
(2001).
Regulation of Ras signaling specificity by protein kinase C.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
21,
2650-2658.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Sondermann,
C.Scheufler,
C.Schneider,
J.Hohfeld,
F.U.Hartl,
and
I.Moarefi
(2001).
Structure of a Bag/Hsc70 complex: convergent functional evolution of Hsp70 nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
Science,
291,
1553-1557.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.R.Vetter,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2001).
The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions.
|
| |
Science,
294,
1299-1304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.D.Corbett,
and
T.Alber
(2001).
The many faces of Ras: recognition of small GTP-binding proteins.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
26,
710-716.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Zhu,
B.Debreceni,
F.Bi,
and
Y.Zheng
(2001).
Oligomerization of DH domain is essential for Dbl-induced transformation.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
21,
425-437.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Renault,
J.Kuhlmann,
A.Henkel,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(2001).
Structural basis for guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the regulator of chromosome condensation (RCC1).
|
| |
Cell,
105,
245-255.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Tsuda
(2001).
[Molecular science of the living organism: the case of G-proteins]
|
| |
Yakugaku Zasshi,
121,
523-534.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Rondard,
T.Iiri,
S.Srinivasan,
E.Meng,
T.Fujita,
and
H.R.Bourne
(2001).
Mutant G protein alpha subunit activated by Gbeta gamma: a model for receptor activation?
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
6150-6155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rudoni,
S.Colombo,
P.Coccetti,
and
E.Martegani
(2001).
Role of guanine nucleotides in the regulation of the Ras/cAMP pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1538,
181-189.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Tian,
and
L.A.Feig
(2001).
Basis for signaling specificity difference between Sos and Ras-GRF guanine nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
47248-47256.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Gao,
J.Xing,
M.Streuli,
T.L.Leto,
and
Y.Zheng
(2001).
Trp(56) of rac1 specifies interaction with a subset of guanine nucleotide exchange factors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
47530-47541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Song,
A.Marx,
J.Müller,
G.Woehlke,
M.Schliwa,
A.Krebs,
A.Hoenger,
and
E.Mandelkow
(2001).
Structure of a fast kinesin: implications for ATPase mechanism and interactions with microtubules.
|
| |
EMBO J,
20,
6213-6225.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhu,
J.J.Dumas,
S.E.Lietzke,
and
D.G.Lambright
(2001).
A helical turn motif in Mss4 is a critical determinant of Rab binding and nucleotide release.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3027-3036.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kobe,
and
A.V.Kajava
(2000).
When protein folding is simplified to protein coiling: the continuum of solenoid protein structures.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
25,
509-515.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Prakash,
G.J.Praefcke,
L.Renault,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
C.Herrmann
(2000).
Structure of human guanylate-binding protein 1 representing a unique class of GTP-binding proteins.
|
| |
Nature,
403,
567-571.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Ye,
D.Liao,
X.Zhang,
P.Zhang,
H.Dong,
and
R.L.Huganir
(2000).
GRASP-1: a neuronal RasGEF associated with the AMPA receptor/GRIP complex.
|
| |
Neuron,
26,
603-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Yoon,
C.Chang,
N.A.Hopper,
G.M.Lesa,
and
P.W.Sternberg
(2000).
Requirements of multiple domains of SLI-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans homologue of c-Cbl, and an inhibitory tyrosine in LET-23 in regulating vulval differentiation.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
11,
4019-4031.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.de Hoog,
W.T.Fan,
M.D.Goldstein,
M.F.Moran,
and
C.A.Koch
(2000).
Calmodulin-independent coordination of Ras and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation by Ras-GRF2.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
20,
2727-2733.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.R.Andersen,
L.Pedersen,
L.Valente,
I.Chatterjee,
T.G.Kinzy,
M.Kjeldgaard,
and
J.Nyborg
(2000).
Structural basis for nucleotide exchange and competition with tRNA in the yeast elongation factor complex eEF1A:eEF1Balpha.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
6,
1261-1266.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.R.Hoffman,
N.Nassar,
and
R.A.Cerione
(2000).
Structure of the Rho family GTP-binding protein Cdc42 in complex with the multifunctional regulator RhoGDI.
|
| |
Cell,
100,
345-356.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Scita,
P.Tenca,
E.Frittoli,
A.Tocchetti,
M.Innocenti,
G.Giardina,
and
P.P.Di Fiore
(2000).
Signaling from Ras to Rac and beyond: not just a matter of GEFs.
|
| |
EMBO J,
19,
2393-2398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Hutchinson,
and
J.F.Eccleston
(2000).
Mechanism of nucleotide release from Rho by the GDP dissociation stimulator protein.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
11348-11359.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Aravind
(2000).
Exploring histones and their relatives with the Histone Sequence Database.
|
| |
Trends Genet,
16,
517-518.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Pincus,
P.W.Brandt-Rauf,
J.Michl,
R.P.Carty,
and
F.K.Friedman
(2000).
ras-p21-induced cell transformation: unique signal transduction pathways and implications for the design of new chemotherapeutic agents.
|
| |
Cancer Invest,
18,
39-50.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Pham,
I.Cheglakov,
C.A.Koch,
C.L.de Hoog,
M.F.Moran,
and
D.Rotin
(2000).
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor CNrasGEF activates ras in response to cAMP and cGMP.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
10,
555-558.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Chen,
T.Michaeli,
L.Van Aelst,
and
R.Ballester
(2000).
A role for the noncatalytic N terminus in the function of Cdc25, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ras-guanine nucleotide exchange factor.
|
| |
Genetics,
154,
1473-1484.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Abseher,
and
M.Nilges
(2000).
Efficient sampling in collective coordinate space.
|
| |
Proteins,
39,
82-88.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Lin,
C.H.Hsu,
J.H.Tsai,
J.Y.Wang,
T.J.Hsieh,
and
C.H.Wu
(2000).
Decreased GTPase activity of K-ras mutants deriving from human functional adrenocortical tumours.
|
| |
Br J Cancer,
82,
1035-1040.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Robineau,
M.Chabre,
and
B.Antonny
(2000).
Binding site of brefeldin A at the interface between the small G protein ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1) and the nucleotide-exchange factor Sec7 domain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
9913-9918.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Ganesan,
L.Mende-Mueller,
J.Selzer,
and
J.T.Barbieri
(1999).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S, a double ADP-ribosyltransferase, resembles vertebrate mono-ADP-ribosyltransferases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
9503-9508.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Ganesan,
T.S.Vincent,
J.C.Olson,
and
J.T.Barbieri
(1999).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S disrupts Ras-mediated signal transduction by inhibiting guanine nucleotide exchange factor-catalyzed nucleotide exchange.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
21823-21829.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.P.Ponting,
P.Bork,
J.Schultz,
and
L.Aravind
(1999).
No Sec7-homology domain in guanine-nucleotide-exchange factors that act on Ras and Rho.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
24,
177-178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cherfils,
and
P.Chardin
(1999).
GEFs: structural basis for their activation of small GTP-binding proteins.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
24,
306-311.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Buolamwini
(1999).
Novel anticancer drug discovery.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
3,
500-509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Ménétrey,
and
J.Cherfils
(1999).
Structure of the small G protein Rap2 in a non-catalytic complex with GTP.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
465-473.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Pérez,
G.Siegal,
J.Kriek,
K.Hård,
J.Dijk,
G.W.Canters,
and
W.Möller
(1999).
The solution structure of the guanine nucleotide exchange domain of human elongation factor 1beta reveals a striking resemblance to that of EF-Ts from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
217-226.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.de Rooij,
N.M.Boenink,
M.van Triest,
R.H.Cool,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
J.L.Bos
(1999).
PDZ-GEF1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor specific for Rap1 and Rap2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
38125-38130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.A.Quilliam,
A.F.Castro,
K.S.Rogers-Graham,
C.B.Martin,
C.J.Der,
and
C.Bi
(1999).
M-Ras/R-Ras3, a transforming ras protein regulated by Sos1, GRF1, and p120 Ras GTPase-activating protein, interacts with the putative Ras effector AF6.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
23850-23857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Geeves,
and
K.C.Holmes
(1999).
Structural mechanism of muscle contraction.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
68,
687-728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Chiadmi,
A.Navaza,
M.Miginiac-Maslow,
J.P.Jacquot,
and
J.Cherfils
(1999).
Redox signalling in the chloroplast: structure of oxidized pea fructose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
18,
6809-6815.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Floer,
and
G.Blobel
(1999).
Putative reaction intermediates in Crm1-mediated nuclear protein export.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
16279-16286.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Rudolph,
C.Weise,
S.Mirold,
B.Hillenbrand,
B.Bader,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
W.D.Hardt
(1999).
Biochemical analysis of SopE from Salmonella typhimurium, a highly efficient guanosine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoGTPases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
30501-30509.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Seidel,
M.Klinger,
M.Freissmuth,
and
C.Höller
(1999).
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by the A(2A)-adenosine receptor via a rap1-dependent and via a p21(ras)-dependent pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
25833-25841.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Vanoni,
R.Bertini,
E.Sacco,
L.Fontanella,
M.Rieppi,
S.Colombo,
E.Martegani,
V.Carrera,
A.Moroni,
C.Bizzarri,
V.Sabbatini,
M.Cattozzo,
A.Colagrande,
and
L.Alberghina
(1999).
Characterization and properties of dominant-negative mutants of the ras-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor CDC25(Mm).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
36656-36662.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.van den Berghe,
R.H.Cool,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(1999).
Discriminatory residues in Ras and Rap for guanine nucleotide exchange factor recognition.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
11078-11085.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Chardin,
and
F.McCormick
(1999).
Brefeldin A: the advantage of being uncompetitive.
|
| |
Cell,
97,
153-155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Meyer,
J.Janin,
and
S.Baudet-Nessler
(1999).
p55-hGRF, a short natural form of the Ras-GDP exchange factor high yield production and characterization.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
263,
806-816.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Hillig,
L.Renault,
I.R.Vetter,
T.Drell,
A.Wittinghofer,
and
J.Becker
(1999).
The crystal structure of rna1p: a new fold for a GTPase-activating protein.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
3,
781-791.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.H.Cool,
G.Schmidt,
C.U.Lenzen,
H.Prinz,
D.Vogt,
and
A.Wittinghofer
(1999).
The Ras mutant D119N is both dominant negative and activated.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
19,
6297-6305.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Müller,
C.von Eichel-Streiber,
and
M.Moos
(1999).
Impact of amino acids 22-27 of Rho-subfamily GTPases on glucosylation by the large clostridial cytotoxins TcsL-1522, TcdB-1470 and TcdB-8864.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
266,
1073-1080.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Benard,
G.M.Bokoch,
and
B.A.Diebold
(1999).
Potential drug targets: small GTPases that regulate leukocyte function.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
20,
365-370.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.C.Dodelet,
C.Pazzagli,
A.H.Zisch,
C.A.Hauser,
and
E.B.Pasquale
(1999).
A novel signaling intermediate, SHEP1, directly couples Eph receptors to R-Ras and Rap1A.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
31941-31946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Liao,
K.Kariya,
C.D.Hu,
M.Shibatohge,
M.Goshima,
T.Okada,
Y.Watari,
X.Gao,
T.G.Jin,
Y.Yamawaki-Kataoka,
and
T.Kataoka
(1999).
RA-GEF, a novel Rap1A guanine nucleotide exchange factor containing a Ras/Rap1A-associating domain, is conserved between nematode and humans.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
37815-37820.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Aghazadeh,
K.Zhu,
T.J.Kubiseski,
G.A.Liu,
T.Pawson,
Y.Zheng,
and
M.K.Rosen
(1998).
Structure and mutagenesis of the Dbl homology domain.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
5,
1098-1107.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Giglione,
and
A.Parmeggiani
(1998).
Raf-1 is involved in the regulation of the interaction between guanine nucleotide exchange factor and Ha-ras. Evidences for a function of Raf-1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase upstream to Ras.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
34737-34744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.J.Day,
R.D.Mosteller,
and
D.Broek
(1998).
Distinct subclasses of small GTPases interact with guanine nucleotide exchange factors in a similar manner.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
18,
7444-7454.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Goldberg
(1998).
Structural basis for activation of ARF GTPase: mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and GTP-myristoyl switching.
|
| |
Cell,
95,
237-248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Bos
(1998).
All in the family? New insights and questions regarding interconnectivity of Ras, Rap1 and Ral.
|
| |
EMBO J,
17,
6776-6782.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Sprang,
and
D.E.Coleman
(1998).
Invasion of the nucleotide snatchers: structural insights into the mechanism of G protein GEFs.
|
| |
Cell,
95,
155-158.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.W.Schwartz,
and
A.P.IJzerman
(1998).
Principles of agonism: undressing efficacy.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
19,
433-436.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Liu,
H.Wang,
M.Eberstadt,
A.Schnuchel,
E.T.Olejniczak,
R.P.Meadows,
J.M.Schkeryantz,
D.A.Janowick,
J.E.Harlan,
E.A.Harris,
D.E.Staunton,
and
S.W.Fesik
(1998).
NMR structure and mutagenesis of the N-terminal Dbl homology domain of the nucleotide exchange factor Trio.
|
| |
Cell,
95,
269-277.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

