 |
PDBsum entry 1bhs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1bhs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.51
- 3(or 17)beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
testosterone + NADP+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 testosterone
testosterone
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
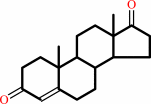 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 testosterone
testosterone
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
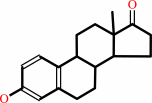 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
3:503-513
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of human estrogenic 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase at 2.20 A resolution.
|
|
D.Ghosh,
V.Z.Pletnev,
D.W.Zhu,
Z.Wawrzak,
W.L.Duax,
W.Pangborn,
F.Labrie,
S.X.Lin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: The principal human estrogen, 17 beta-estradiol, is a potent
stimulator of certain endocrine-dependent forms of breast cancer. Because human
estrogenic 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (type I 17 beta-HSD) catalyzes
the last step in the biosynthesis of 17 beta-estradiol from the less potent
estrogen, estrone, it is an attractive target for the design of inhibitors of
estrogen production and tumor growth. This human enzyme shares less than 15%
sequence identity with a bacterial 3 alpha,20 beta-HSD, for which the
three-dimensional structure is known. The amino acid sequence of 17 beta-HSD
also differs from that of bacterial 3 alpha,20 beta-HSD by two insertions (of 11
and 14 residues) and 52 additional residues at the C terminus. RESULTS: The 2.20
A resolution structure of type I 17 beta-HSD, the first mammalian steroidogenic
enzyme studied by X-ray crystallographic techniques, reveals a fold
characteristic of the short-chain dehydrogenases. The active site contains a
Tyr-X-X-X-Lys sequence (where X is any amino acid) and a serine residue,
features that are conserved in short-chain steroid dehydrogenases. The structure
also contains three alpha-helices and a helix-turn-helix motif, not observed in
short-chain dehydrogenase structures reported previously. No cofactor density
could be located. CONCLUSIONS: The helices present in 17 beta-HSD that were not
in the two previous short-chain dehydrogenase structures are located at one end
of the substrate-binding cleft away from the catalytic triad. These helices
restrict access to the active site and appear to influence substrate
specificity. Modeling the position of estradiol in the active site suggests that
a histidine side chain may play a critical role in substrate recognition. One or
more of these helices may also be involved in the reported association of the
enzyme with membranes. A model for steroid and cofactor binding as well as for
the estrone to estradiol transition state is proposed. The structure of the
active site provides a rational basis for designing more specific inhibitors of
this breast cancer associated enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. (a) Stereo ribbon diagram of a monomer of human
estrogenic 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD). The course
of the polypeptide chain is shown for residues 1–284.
α-helices are drawn as magenta coils, β-strands as blue
arrows, and turns and loops as green ropes. The side chains for
residues in the active site belonging to the catalytic triad,
Tyr155-Lys159-Ser142, are shown in white. The view is almost
parallel to the central β-sheet. (Figure prepared using the
program SETOR [43].) (b) Folding topology of strands (triangles)
and helices (circles) in 17β-HSD. Figure 1. (a) Stereo
ribbon diagram of a monomer of human estrogenic
17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD). The course of the
polypeptide chain is shown for residues 1–284. α-helices are
drawn as magenta coils, β-strands as blue arrows, and turns and
loops as green ropes. The side chains for residues in the active
site belonging to the catalytic triad, Tyr155-Lys159-Ser142, are
shown in white. The view is almost parallel to the central
β-sheet. (Figure prepared using the program SETOR [[4]43].) (b)
Folding topology of strands (triangles) and helices (circles) in
17β-HSD.
|
 |
Figure 9.
Figure 9. Helices (a) αG′ and (b) αH viewed along the
helical axis. The side chains are color coded to illustrate
their amphiphilicity, as follows: green, hydrophobic; red,
charged; and magenta, residues having a proton-donating
functional group. Figure 9. Helices (a) αG′ and (b) αH
viewed along the helical axis. The side chains are color coded
to illustrate their amphiphilicity, as follows: green,
hydrophobic; red, charged; and magenta, residues having a
proton-donating functional group. (Figure prepared using the
program SETOR [[3]43].)
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1995,
3,
503-513)
copyright 1995.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Ghosh,
J.Griswold,
M.Erman,
and
W.Pangborn
(2010).
X-ray structure of human aromatase reveals an androgen-specific active site.
|
| |
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol,
118,
197-202.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Negri,
M.Recanatini,
and
R.W.Hartmann
(2010).
Insights in 17beta-HSD1 enzyme kinetics and ligand binding by dynamic motion investigation.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e12026.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.X.Lin,
J.Chen,
M.Mazumdar,
D.Poirier,
C.Wang,
A.Azzi,
and
M.Zhou
(2010).
Molecular therapy of breast cancer: progress and future directions.
|
| |
Nat Rev Endocrinol,
6,
485-493.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Di Costanzo,
T.M.Penning,
and
D.W.Christianson
(2009).
Aldo-keto reductases in which the conserved catalytic histidine is substituted.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
178,
127-133.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Mazumdar,
D.Fournier,
D.W.Zhu,
C.Cadot,
D.Poirier,
and
S.X.Lin
(2009).
Binary and ternary crystal structure analyses of a novel inhibitor with 17beta-HSD type 1: a lead compound for breast cancer therapy.
|
| |
Biochem J,
424,
357-366.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Zhang,
Y.Xu,
Y.Sun,
W.Zhang,
and
R.Xiao
(2009).
Ser67Asp and His68Asp substitutions in candida parapsilosis carbonyl reductase alter the coenzyme specificity and enantioselectivity of ketone reduction.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
75,
2176-2183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.L.Miller
(2009).
Androgen synthesis in adrenarche.
|
| |
Rev Endocr Metab Disord,
10,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Ludwig,
P.J.Michiels,
A.Lodi,
J.Ride,
C.Bunce,
and
U.L.Günther
(2008).
Evaluation of solvent accessibility epitopes for different dehydrogenase inhibitors.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
3,
1371-1376.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Karkola,
A.Lilienkampf,
and
K.Wähälä
(2008).
A 3D QSAR model of 17beta-HSD1 inhibitors based on a thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one core applying molecular dynamics simulations and ligand-protein docking.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
3,
461-472.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.R.Chiang,
W.Ismail,
D.Heintz,
C.Schaeffer,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
and
G.Fuchs
(2008).
Study of anoxic and oxic cholesterol metabolism by Sterolibacterium denitrificans.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
905-914.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Liu,
S.Zheng,
V.Bellemare,
G.Pelletier,
F.Labrie,
and
V.Luu-The
(2007).
Expression and localization of estrogenic type 12 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the cynomolgus monkey.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
8,
2.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Paithankar,
C.Feller,
E.B.Kuettner,
A.Keim,
M.Grunow,
and
N.Sträter
(2007).
Cosubstrate-induced dynamics of D-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
5767-5779.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Vicker,
H.R.Lawrence,
G.M.Allan,
C.Bubert,
A.Smith,
H.J.Tutill,
A.Purohit,
J.M.Day,
M.F.Mahon,
M.J.Reed,
and
B.V.Potter
(2006).
Focused libraries of 16-substituted estrone derivatives and modified e-ring steroids: inhibitors of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
1,
464-481.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Price,
Y.M.Zhang,
C.O.Rock,
and
S.W.White
(2004).
Cofactor-induced conformational rearrangements establish a catalytically competent active site and a proton relay conduit in FabG.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
417-428.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Zhang,
P.Hu,
and
J.L.Napoli
(2004).
Elements in the N-terminal signaling sequence that determine cytosolic topology of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. Studies with retinol dehydrogenase type 1 and cis-retinol/androgen dehydrogenase type 1.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
51482-51489.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Shi,
and
S.X.Lin
(2004).
Cofactor hydrogen bonding onto the protein main chain is conserved in the short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family and contributes to nicotinamide orientation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
16778-16785.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Song,
W.Chen,
M.Zhang,
and
J.L.Napoli
(2003).
Identification of a mouse short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase gene, retinol dehydrogenase-similar. Function of non-catalytic amino acid residues in enzyme activity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
40079-40087.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.L.Duax,
V.Pletnev,
A.Addlagatta,
J.Bruenn,
and
C.M.Weeks
(2003).
Rational proteomics I. Fingerprint identification and cofactor specificity in the short-chain oxidoreductase (SCOR) enzyme family.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
931-943.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Zhou,
W.Qiu,
H.J.Chang,
A.Gangloff,
and
S.X.Lin
(2002).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction results of human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
1048-1050.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Ghosh,
and
P.Vihko
(2001).
Molecular mechanisms of estrogen recognition and 17-keto reduction by human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
130,
637-650.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Zhu,
L.Cantin,
V.Nahoum,
P.Rehse,
V.Luu-The,
F.Labrie,
R.Breton,
and
S.X.Lin
(2001).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the human type 3 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase at 1.8 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
589-591.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Maser,
G.Xiong,
C.Grimm,
R.Ficner,
and
K.Reuter
(2001).
3alpha-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from Comamonas testosteroni: biological significance, three-dimensional structure and gene regulation.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
130,
707-722.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Labrie,
V.Luu-The,
C.Labrie,
and
J.Simard
(2001).
DHEA and its transformation into androgens and estrogens in peripheral target tissues: intracrinology.
|
| |
Front Neuroendocrinol,
22,
185-212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Zhou,
F.Yan,
and
H.H.Tai
(2001).
C-Terminal region of human NAD+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is involved in the interaction with prostaglandin substrates.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
3368-3374.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Denessiouk,
V.V.Rantanen,
and
M.S.Johnson
(2001).
Adenine recognition: a motif present in ATP-, CoA-, NAD-, NADP-, and FAD-dependent proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
44,
282-291.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Otagiri,
G.Kurisu,
S.Swaminathan,
S.Ui,
S.Yoneda,
M.Ohkuma,
T.Kudo,
and
M.Kusunoki
(2001).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae IAM1063.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
857-859.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Terada,
Y.Sugihara,
K.Nakamura,
R.Sato,
S.Sakuma,
Y.Fujimoto,
T.Fujita,
N.Inazu,
and
M.Maeda
(2001).
Characterization of multiple Chinese hamster carbonyl reductases.
|
| |
Chem Biol Interact,
130,
847-861.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Nahoum,
A.Gangloff,
P.Legrand,
D.W.Zhu,
L.Cantin,
B.S.Zhorov,
V.Luu-The,
F.Labrie,
R.Breton,
and
S.X.Lin
(2001).
Structure of the human 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 in complex with testosterone and NADP at 1.25-A resolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
276,
42091-42098.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.S.Zhorov,
and
S.X.Lin
(2000).
Monte Carlo-minimized energy profile of estradiol in the ligand-binding tunnel of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: atomic mechanisms of steroid recognition.
|
| |
Proteins,
38,
414-427.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Loeb-Hennard,
and
J.O.McIntyre
(2000).
(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase: selective phosphatidylcholine binding by the C-terminal domain.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
11928-11938.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Chelius,
C.Loeb-Hennard,
S.Fleischer,
J.O.McIntyre,
A.R.Marks,
S.De,
S.Hahn,
M.M.Jehl,
J.Moeller,
R.Philipp,
J.G.Wise,
and
W.E.Trommer
(2000).
Phosphatidylcholine activation of human heart (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase mutants lacking active center sulfhydryls: site-directed mutagenesis of a new recombinant fusion protein.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
9687-9697.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Labrie,
V.Luu-The,
S.X.Lin,
J.Simard,
and
C.Labrie
(2000).
Role of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in sex steroid formation in peripheral intracrine tissues.
|
| |
Trends Endocrinol Metab,
11,
421-427.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Benach,
S.Atrian,
J.Fibla,
R.Gonzàlez-Duarte,
and
R.Ladenstein
(2000).
Structure-function relationships in Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase allozymes ADH(S), ADH(F) and ADH(UF), and distantly related forms.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
267,
3613-3622.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
R.L.Campbell,
A.Gangloff,
Y.W.Huang,
and
S.X.Lin
(2000).
Dehydroepiandrosterone and dihydrotestosterone recognition by human estrogenic 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. C-18/c-19 steroid discrimination and enzyme-induced strain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
1105-1111.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Terada,
Y.Sugihara,
K.Nakamura,
R.Sato,
N.Inazu,
and
M.Maeda
(2000).
Cloning and bacterial expression of monomeric short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (carbonyl reductase) from CHO-K1 cells.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
267,
6849-6857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Yamashita,
H.Kato,
S.Wakatsuki,
T.Tomizaki,
T.Nakatsu,
K.Nakajima,
T.Hashimoto,
Y.Yamada,
and
J.Oda
(1999).
Structure of tropinone reductase-II complexed with NADP+ and pseudotropine at 1.9 A resolution: implication for stereospecific substrate binding and catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
7630-7637.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.G.van Grunsven,
E.van Berkel,
P.A.Mooijer,
P.A.Watkins,
H.W.Moser,
Y.Suzuki,
L.L.Jiang,
T.Hashimoto,
G.Hoefler,
J.Adamski,
and
R.J.Wanders
(1999).
Peroxisomal bifunctional protein deficiency revisited: resolution of its true enzymatic and molecular basis.
|
| |
Am J Hum Genet,
64,
99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Tinguely,
and
B.Wermuth
(1999).
Identification of the reactive cysteine residue (Cys227) in human carbonyl reductase.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
260,
9.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.J.Shimkets
(1999).
Intercellular signaling during fruiting-body development of Myxococcus xanthus.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
53,
525-549.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Sawicki,
M.Erman,
T.Puranen,
P.Vihko,
and
D.Ghosh
(1999).
Structure of the ternary complex of human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 with 3-hydroxyestra-1,3,5,7-tetraen-17-one (equilin) and NADP+.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
840-845.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Mazza,
R.Breton,
D.Housset,
and
J.C.Fontecilla-Camps
(1998).
Unusual charge stabilization of NADP+ in 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
8145-8152.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.G.van Grunsven,
E.van Berkel,
L.Ijlst,
P.Vreken,
J.B.de Klerk,
J.Adamski,
H.Lemonde,
P.T.Clayton,
D.A.Cuebas,
and
R.J.Wanders
(1998).
Peroxisomal D-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: resolution of the enzyme defect and its molecular basis in bifunctional protein deficiency.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
2128-2133.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Möbus,
and
E.Maser
(1998).
Molecular cloning, overexpression, and characterization of steroid-inducible 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from Comamonas testosteroni. A novel member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
30888-30896.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
and
H.M.Holden
(1998).
Dramatic differences in the binding of UDP-galactose and UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
11469-11477.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Nakajima,
A.Yamashita,
H.Akama,
T.Nakatsu,
H.Kato,
T.Hashimoto,
J.Oda,
and
Y.Yamada
(1998).
Crystal structures of two tropinone reductases: different reaction stereospecificities in the same protein fold.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
4876-4881.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.McGrath,
J.T.Palmer,
D.Brömme,
and
J.R.Somoza
(1998).
Crystal structure of human cathepsin S.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
7,
1294-1302.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Rizzi,
M.Tonetti,
P.Vigevani,
L.Sturla,
A.Bisso,
A.D.Flora,
D.Bordo,
and
M.Bolognesi
(1998).
GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-D-mannose epimerase/reductase from Escherichia coli, a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of GDP-L-fucose, displays the structural characteristics of the RED protein homology superfamily.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
1453-1465.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.S.Somers,
M.L.Stahl,
and
F.X.Sullivan
(1998).
GDP-fucose synthetase from Escherichia coli: structure of a unique member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family that catalyzes two distinct reactions at the same active site.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
1601-1612.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.V.Efimov
(1997).
Structural trees for protein superfamilies.
|
| |
Proteins,
28,
241-260.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
A.D.Hegeman,
G.Wesenberg,
M.C.Chapeau,
P.A.Frey,
and
H.M.Holden
(1997).
Structural analysis of UDP-sugar binding to UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
6294-6304.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Stein,
A.Schäfer,
and
F.Giffhorn
(1997).
Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and overexpression of smoS, a component of a novel operon encoding an ABC transporter and polyol dehydrogenases of Rhodobacter sphaeroides Si4.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
179,
6335-6340.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nakanishi,
K.Matsuura,
H.Kaibe,
N.Tanaka,
T.Nonaka,
Y.Mitsui,
and
A.Hara
(1997).
Switch of coenzyme specificity of mouse lung carbonyl reductase by substitution of threonine 38 with aspartic acid.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
2218-2222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.C.Oppermann,
C.Filling,
K.D.Berndt,
B.Persson,
J.Benach,
R.Ladenstein,
and
H.Jörnvall
(1997).
Active site directed mutagenesis of 3 beta/17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase establishes differential effects on short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase reactions.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
34-40.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Liu,
J.B.Thoden,
J.Kim,
E.Berger,
A.M.Gulick,
F.J.Ruzicka,
H.M.Holden,
and
P.A.Frey
(1997).
Mechanistic roles of tyrosine 149 and serine 124 in UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
10675-10684.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Andersson,
D.Jordan,
G.Schneider,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(1996).
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene reductase from Magnaporthe grisea with NADPH and an active-site inhibitor.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
1161-1170.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Azzi,
P.H.Rehse,
D.W.Zhu,
R.L.Campbell,
F.Labrie,
and
S.X.Lin
(1996).
Crystal structure of human estrogenic 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase complexed with 17 beta-estradiol.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
3,
665-668.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Li,
and
S.X.Lin
(1996).
Fluorescence-energy transfer in human estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase-NADPH complex and studies on the coenzyme binding,.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
235,
180-186.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
P.A.Frey,
and
H.M.Holden
(1996).
High-resolution X-ray structure of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase complexed with UDP-phenol.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
2149-2161.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bennett,
B.P.Schlegel,
J.M.Jez,
T.M.Penning,
and
M.Lewis
(1996).
Structure of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase complexed with NADP+.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
10702-10711.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Matsuo,
C.M.Ensor,
and
H.H.Tai
(1996).
Cloning and expression of the cDNA for mouse NAD(+)-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1309,
21-24.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tanaka,
T.Nonaka,
M.Nakanishi,
Y.Deyashiki,
A.Hara,
and
Y.Mitsui
(1996).
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of mouse lung carbonyl reductase at 1.8 A resolution: the structural origin of coenzyme specificity in the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
33-45.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tanaka,
T.Nonaka,
T.Tanabe,
T.Yoshimoto,
D.Tsuru,
and
Y.Mitsui
(1996).
Crystal structures of the binary and ternary complexes of 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
7715-7730.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Nokelainen,
T.Puranen,
H.Peltoketo,
M.Orava,
P.Vihko,
and
R.Vihko
(1996).
Molecular cloning of mouse 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and characterization of enzyme activity.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
236,
482-490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Breton,
D.Housset,
C.Mazza,
and
J.C.Fontecilla-Camps
(1996).
The structure of a complex of human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase with estradiol and NADP+ identifies two principal targets for the design of inhibitors.
|
| |
Structure,
4,
905-915.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.C.Oppermann,
and
E.Maser
(1996).
Characterization of a 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from the gram-negative bacterium Comamonas testosteroni.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
241,
744-749.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.L.Duax,
J.F.Griffin,
and
D.Ghosh
(1996).
The fascinating complexities of steroid-binding enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
6,
813-823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Labrie,
A.Bélanger,
J.Simard,
Van Luu-The,
and
C.Labrie
(1995).
DHEA and peripheral androgen and estrogen formation: intracinology.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
774,
16-28.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Rafferty,
J.W.Simon,
C.Baldock,
P.J.Artymiuk,
P.J.Baker,
A.R.Stuitje,
A.R.Slabas,
and
D.W.Rice
(1995).
Common themes in redox chemistry emerge from the X-ray structure of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase.
|
| |
Structure,
3,
927-938.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Albalat,
M.Valls,
J.Fibla,
S.Atrian,
and
R.Gonzàlez-Duarte
(1995).
Involvement of the C-terminal tail in the activity of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase. Evaluation of truncated proteins constructed by site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
233,
498-505.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

