 |
PDBsum entry 1bd0

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.1.1.1
- alanine racemase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-alanine = D-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
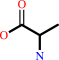 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
=
|
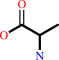 D-alanine
D-alanine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
IN5)
matches with 65.22% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
37:10438-10445
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Reaction of alanine racemase with 1-aminoethylphosphonic acid forms a stable external aldimine.
|
|
G.F.Stamper,
A.A.Morollo,
D.Ringe,
C.G.Stamper.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
(R)-1-Aminoethylphosphonic acid (L-Ala-P), a synthetic L-alanine analogue, has
antibacterial activity and is a time-dependent inactivator of all purified
Gram-positive bacterial alanine racemases that have been tested. L-Ala-P forms
an external aldimine with the bound pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) cofactor, but
is neither racemized nor efficiently hydrolyzed. To understand the structural
basis of the inactivation of the enzyme by L-Ala-P, we determined the crystal
structure of the complex between L-Ala-P and alanine racemase at 1.6 A
resolution. The cofactor derivative in the inhibited structure tilts outward
from the protein approximately 20 degrees relative to the internal aldimine. The
phosphonate oxygens are within hydrogen bonding distance of four amino acid
residues and two water molecules in the active site of the enzyme. L-Ala-P is an
effective inhibitor of alanine racemase because, upon formation of the external
aldimine, the phosphonate group interacts with putative catalytic residues,
thereby rendering them unavailable for catalysis. Furthermore, this aldimine
appears to be inappropriately aligned for efficient Calpha proton abstraction.
The combination of these effects leads to a stable aldimine derivative and
potent inactivation of alanine racemase by this compound.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.R.Scaletti,
S.R.Luckner,
and
K.L.Krause
(2012).
Structural features and kinetic characterization of alanine racemase from Staphylococcus aureus (Mu50).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
68,
82-92.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.B.Müller,
F.Wu,
B.Bergmann,
J.Knöckel,
R.D.Walter,
H.Gehring,
and
C.Wrenger
(2009).
Poisoning pyridoxal 5-phosphate-dependent enzymes: a new strategy to target the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
4,
e4406.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Spies,
J.G.Reese,
D.Dodd,
K.L.Pankow,
S.R.Blanke,
and
J.Baudry
(2009).
Determinants of catalytic power and ligand binding in glutamate racemase.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
5274-5284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.M.Couñago,
M.Davlieva,
U.Strych,
R.E.Hill,
and
K.L.Krause
(2009).
Biochemical and structural characterization of alanine racemase from Bacillus anthracis (Ames).
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
53.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Milić,
T.V.Demidkina,
N.G.Faleev,
D.Matković-Calogović,
and
A.A.Antson
(2008).
Insights into the catalytic mechanism of tyrosine phenol-lyase from X-ray structures of quinonoid intermediates.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
29206-29214.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Wu,
T.Hu,
L.Zhang,
J.Chen,
J.Du,
J.Ding,
H.Jiang,
and
X.Shen
(2008).
Residues Asp164 and Glu165 at the substrate entryway function potently in substrate orientation of alanine racemase from E. coli: Enzymatic characterization with crystal structure analysis.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
17,
1066-1076.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Barreteau,
A.Kovac,
A.Boniface,
M.Sova,
S.Gobec,
and
D.Blanot
(2008).
Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
32,
168-207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.C.Huang,
D.Jupiter,
M.Qiu,
J.M.Briggs,
and
V.Vanburen
(2008).
Cluster analysis of hydration waters around the active sites of bacterial alanine racemase using a 2-ns MD simulation.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
89,
210-219.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Au,
J.Ren,
T.S.Walter,
K.Harlos,
J.E.Nettleship,
R.J.Owens,
D.I.Stuart,
and
R.M.Esnouf
(2008).
Structures of an alanine racemase from Bacillus anthracis (BA0252) in the presence and absence of (R)-1-aminoethylphosphonic acid (L-Ala-P).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
327-333.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hu,
D.Wu,
J.Chen,
J.Ding,
H.Jiang,
and
X.Shen
(2008).
The catalytic intermediate stabilized by a "down" active site loop for diaminopimelate decarboxylase from Helicobacter pylori. Enzymatic characterization with crystal structure analysis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
21284-21293.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Eliot,
and
J.F.Kirsch
(2004).
Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
73,
383-415.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Cellini,
M.Bertoldi,
A.Paiardini,
S.D'Aguanno,
and
C.B.Voltattorni
(2004).
Site-directed mutagenesis provides insight into racemization and transamination of alanine catalyzed by Treponema denticola cystalysin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
36898-36905.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Noda,
Y.Matoba,
T.Kumagai,
and
M.Sugiyama
(2004).
Structural evidence that alanine racemase from a D-cycloserine-producing microorganism exhibits resistance to its own product.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
46153-46161.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.I.Mustata,
T.A.Soares,
and
J.M.Briggs
(2003).
Molecular dynamics studies of alanine racemase: a structural model for drug design.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
70,
186-200.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.B.Balbo,
C.N.Patel,
K.G.Sell,
R.S.Adcock,
S.Neelakantan,
P.A.Crooks,
and
M.A.Oliveira
(2003).
Spectrophotometric and steady-state kinetic analysis of the biosynthetic arginine decarboxylase of Yersinia pestis utilizing arginine analogues as inhibitors and alternative substrates.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
15189-15196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.LeMagueres,
H.Im,
A.Dvorak,
U.Strych,
M.Benedik,
and
K.L.Krause
(2003).
Crystal structure at 1.45 A resolution of alanine racemase from a pathogenic bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, contains both internal and external aldimine forms.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
14752-14761.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Watanabe,
T.Yoshimura,
B.Mikami,
H.Hayashi,
H.Kagamiyama,
and
N.Esaki
(2002).
Reaction mechanism of alanine racemase from Bacillus stearothermophilus: x-ray crystallographic studies of the enzyme bound with N-(5'-phosphopyridoxyl)alanine.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
19166-19172.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.D.Perry,
G.Riley,
F.K.Gould,
J.M.Perez,
E.Boissier,
R.T.Ouedraogo,
and
A.M.Freydière
(2002).
Alafosfalin as a selective agent for isolation of salmonella from clinical samples.
|
| |
J Clin Microbiol,
40,
3913-3916.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Cook,
I.Galve-Roperh,
A.Martínez del Pozo,
and
I.Rodríguez-Crespo
(2002).
Direct calcium binding results in activation of brain serine racemase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
27782-27792.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Uo,
T.Yoshimura,
T.Nishiyama,
and
N.Esaki
(2002).
Gene cloning, purification, and characterization of 2,3-diaminopropionate ammonia-lyase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
66,
2639-2644.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Strych,
and
M.J.Benedik
(2002).
Mutant analysis shows that alanine racemases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli are dimeric.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
4321-4325.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Saadat,
and
D.H.Harrison
(2000).
Mirroring perfection: the structure of methylglyoxal synthase complexed with the competitive inhibitor 2-phosphoglycolate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
2950-2960.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Morollo,
G.A.Petsko,
and
D.Ringe
(1999).
Structure of a Michaelis complex analogue: propionate binds in the substrate carboxylate site of alanine racemase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
3293-3301.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Kern,
M.A.Oliveira,
P.Coffino,
and
M.L.Hackert
(1999).
Structure of mammalian ornithine decarboxylase at 1.6 A resolution: stereochemical implications of PLP-dependent amino acid decarboxylases.
|
| |
Structure,
7,
567-581.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Watanabe,
Y.Kurokawa,
T.Yoshimura,
T.Kurihara,
K.Soda,
N.Esaki,
and
A.Watababe
(1999).
Role of lysine 39 of alanine racemase from Bacillus stearothermophilus that binds pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Chemical rescue studies of Lys39 --> Ala mutant.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
4189-4194.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Y.Hwang,
C.S.Cho,
S.S.Kim,
K.Baek,
S.H.Kim,
Y.G.Yu,
and
Y.Cho
(1999).
Crystallization and preliminary x-ray analysis of glutamate racemase from Aquifex pyrophilus, a hyperthermophilic bacterium.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
927-928.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.V.Grishin,
A.L.Osterman,
H.B.Brooks,
M.A.Phillips,
and
E.J.Goldsmith
(1999).
X-ray structure of ornithine decarboxylase from Trypanosoma brucei: the native structure and the structure in complex with alpha-difluoromethylornithine.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
15174-15184.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Sun,
and
M.D.Toney
(1999).
Evidence for a two-base mechanism involving tyrosine-265 from arginine-219 mutants of alanine racemase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4058-4065.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.N.Jansonius
(1998).
Structure, evolution and action of vitamin B6-dependent enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
8,
759-769.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

