 |
PDBsum entry 1bcd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase(oxo-acid)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1bcd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
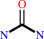 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Febs Lett
350:319-322
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of a complex between carbonic anhydrase II and a new inhibitor, trifluoromethane sulphonamide.
|
|
K.Håkansson,
A.Liljas.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
It has recently been shown that aliphatic sulphonamides are good inhibitors of
carbonic anhydrase (CA) provided that the pK of the sulphonamide is low. We have
determined the structure of the complex between CAII and CF3SO2NH2 by X-ray
crystallographic methods. The nitrogen of the sulphonamide is bound to the zinc
ion of the enzyme in the usual manner. The other parts of the inhibitor show a
different mode of binding from aromatic sulphonamides since the trifluoromethyl
group is bound at the hydrophobic part of the active site instead of pointing
out from the active site. It should be possible to design new inhibitors
specific for the different isoenzymes, starting from the present structure.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. (A) The active site of carbonic anhydrase complexed the inhibitor CF3SO2NH-. Difference electron maps were calculated after refinement
of native coordinates without waters 263,292, 318,338 and 389. Positive (continous lines) and negative (broken lines) [Fo [ - [ Fc[ contours were drawn
at +3 or. (B) The inhibitor from (A) with all atoms labelled.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. The molecular structure of carbonic anhydrase complexed with
is compared with the complex with acetazolamide (broken
The polypeptide chain f the acetazolamide complex [251 is not
since the conformatons are virtually the same in the two cases.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the Federation of European Biochemical Societies:
Febs Lett
(1994,
350,
319-322)
copyright 1994.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.M.Krishnamurthy,
G.K.Kaufman,
A.R.Urbach,
I.Gitlin,
K.L.Gudiksen,
D.B.Weibel,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(2008).
Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
108,
946.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.M.Jude,
A.L.Banerjee,
M.K.Haldar,
S.Manokaran,
B.Roy,
S.Mallik,
D.K.Srivastava,
and
D.W.Christianson
(2006).
Ultrahigh resolution crystal structures of human carbonic anhydrases I and II complexed with "two-prong" inhibitors reveal the molecular basis of high affinity.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
128,
3011-3018.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.J.Colton,
J.D.Carbeck,
J.Rao,
and
G.M.Whitesides
(1998).
Affinity capillary electrophoresis: a physical-organic tool for studying interactions in biomolecular recognition.
|
| |
Electrophoresis,
19,
367-382.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Boriack-Sjodin,
S.Zeitlin,
H.H.Chen,
L.Crenshaw,
S.Gross,
A.Dantanarayana,
P.Delgado,
J.A.May,
T.Dean,
and
D.W.Christianson
(1998).
Structural analysis of inhibitor binding to human carbonic anhydrase II.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
7,
2483-2489.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.T.Supuran,
C.W.Conroy,
and
T.H.Maren
(1997).
Is cyanate a carbonic anhydrase substrate?
|
| |
Proteins,
27,
272-278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Briganti,
S.Mangani,
P.Orioli,
A.Scozzafava,
G.Vernaglione,
and
C.T.Supuran
(1997).
Carbonic anhydrase activators: X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic investigations for the interaction of isozymes I and II with histamine.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
10384-10392.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lindskog
(1997).
Structure and mechanism of carbonic anhydrase.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
74,
1.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

