 |
PDBsum entry 1aql

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.13
- sterol esterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a sterol ester + H2O = a sterol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
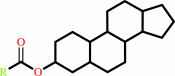 sterol ester
sterol ester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
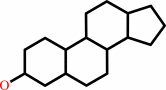 sterol
sterol
|
+
|
fatty acid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 51.43% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
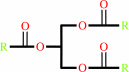 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
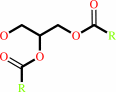 diacylglycerol
diacylglycerol
|
+
|
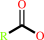 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.6
- acetylesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acetyl ester + H2O = an aliphatic alcohol + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
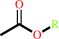 acetyl ester
acetyl ester
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
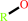 aliphatic alcohol
aliphatic alcohol
|
+
|
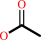 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
5:1209-1218
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of bovine bile salt activated lipase: insights into the bile salt activation mechanism.
|
|
X.Wang,
C.S.Wang,
J.Tang,
F.Dyda,
X.C.Zhang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: The intestinally located pancreatic enzyme, bile salt activated
lipase (BAL), possesses unique activities for digesting different kinds of
lipids. It also differs from other lipases in a requirement of bile salts for
activity. A structure-based explanation for these unique properties has not been
reached so far due to the absence of a three-dimensional structure. RESULTS: The
crystal structures of bovine BAL and its complex with taurocholate have been
determined at 2.8 A resolution. The overall structure of BAL belongs to the
alpha/beta hydrolase fold family. Two bile salt binding sites were found in each
BAL molecule within the BAL-taurocholate complex structure. One of these sites
is located close to a hairpin loop near the active site. Upon the binding of
taurocholate, this loop becomes less mobile and assumes a different
conformation. The other bile salt binding site is located remote from the active
site. In both structures, BAL forms similar dimers with the active sites facing
each other. CONCLUSIONS: Bile salts activate BAL by binding to a relatively
short ten-residue loop near the active site, and stabilize the loop in an open
conformation. Presumably, this conformational change leads to the formation of
the substrate-binding site, as suggested from kinetic data. The BAL dimer
observed in the crystal structure may also play a functional role under
physiological conditions.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Stereo view of the structural comparison of
apo-BAL and GCL around their active sites. The Ca trace of the
apo-BAL structure is shown in magenta; the Ca trace of GCL is
shown in blue. Selected residues from BAL are labeled in red.
Also included are the catalytic triad residues from the two
structures, which are superimposed with each other.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1997,
5,
1209-1218)
copyright 1997.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Lin,
S.J.Yeh,
I.R.Chen,
and
G.Lin
(2011).
Stereoselective inhibition of cholesterol esterase by enantiomers of exo- and endo-2-norbornyl-N-n-butylcarbamates.
|
| |
Protein J,
30,
220-227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Kurtovic,
S.N.Marshall,
X.Zhao,
and
B.K.Simpson
(2010).
Purification and properties of digestive lipases from Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and New Zealand hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae).
|
| |
Fish Physiol Biochem,
36,
1041-1060.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Maeda,
T.Mizuno,
M.Bunya,
S.Sugihara,
D.Nakayama,
S.Tsunasawa,
Y.Hirota,
and
A.Sugihara
(2008).
Characterization of novel cholesterol esterase from Trichoderma sp. AS59 with high ability to synthesize steryl esters.
|
| |
J Biosci Bioeng,
105,
341-349.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Arya,
M.Datta,
and
B.D.Malhotra
(2008).
Recent advances in cholesterol biosensor.
|
| |
Biosens Bioelectron,
23,
1083-1100.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Chiou,
M.C.Lin,
M.T.Hwang,
H.G.Chang,
and
G.Lin
(2008).
Benzene-di-N-substituted carbamates as conformationally constrained substrate analogs of cholesterol esterase.
|
| |
Protein J,
27,
276-282.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Comte,
C.Franceschi,
M.O.Sadoulet,
F.Silvy,
D.Lafitte,
L.Benkoel,
A.Nganga,
L.Daniel,
J.P.Bernard,
D.Lombardo,
and
E.Mas
(2006).
Detection of bile salt-dependent lipase, a 110 kDa pancreatic protein, in urines of healthy subjects.
|
| |
Kidney Int,
69,
1048-1055.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
S.Y.Chiou,
B.C.Hwu,
and
C.W.Hsieh
(2006).
Probing structure-function relationships of serine hydrolases and proteases with carbamate and thiocarbamate inhibitors.
|
| |
Protein J,
25,
33-43.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bencharit,
C.C.Edwards,
C.L.Morton,
E.L.Howard-Williams,
P.Kuhn,
P.M.Potter,
and
M.R.Redinbo
(2006).
Multisite promiscuity in the processing of endogenous substrates by human carboxylesterase 1.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
363,
201-214.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
W.C.Liao,
and
Z.H.Ku
(2005).
Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady state of Pseudomonas species lipase inhibitions by p-nirophenyl-N-substituted carbamates.
|
| |
Protein J,
24,
201-207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.P.McGlacken,
and
I.J.Fairlamb
(2005).
2-Pyrone natural products and mimetics: isolation, characterisation and biological activity.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
22,
369-385.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Y.Chiou,
C.Y.Lai,
L.Y.Lin,
and
G.Lin
(2005).
Probing stereoselective inhibition of the acyl binding site of cholesterol esterase with four diastereomers of 2'-N-alpha-methylbenzylcarbamyl-1, 1'-bi-2-naphthol.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
6,
17.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Aubert-Jousset,
N.Garmy,
V.Sbarra,
J.Fantini,
M.O.Sadoulet,
and
D.Lombardo
(2004).
The combinatorial extension method reveals a sphingolipid binding domain on pancreatic bile salt-dependent lipase: role in secretion.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
1437-1447.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Aubert-Jousset,
V.Sbarra,
and
D.Lombardo
(2004).
Site-directed mutagenesis of the distal basic cluster of pancreatic bile salt-dependent lipase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
39697-39704.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Bidlack,
and
P.M.Silverman
(2004).
An active type IV secretion system encoded by the F plasmid sensitizes Escherichia coli to bile salts.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
5202-5209.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.F.Mugford,
S.M.Lait,
B.A.Keay,
and
R.J.Kazlauskas
(2004).
Enantiocomplementary enzymatic resolution of the chiral auxiliary: cis,cis-6-(2,2-dimethylpropanamido)spiro[4.4]nonan-1-ol and the molecular basis for the high enantioselectivity of subtilisin Carlsberg.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
5,
980-987.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Sugihara,
Y.Shimada,
A.Nomura,
T.Terai,
M.Imayasu,
Y.Nagai,
T.Nagao,
Y.Watanabe,
and
Y.Tominaga
(2002).
Purification and characterization of a novel cholesterol esterase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with its application to cleaning lipid-stained contact lenses.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
66,
2347-2355.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Aubert,
V.Sbarra,
J.Le Petit-Thévenin,
A.Valette,
and
D.Lombardo
(2002).
Site-directed mutagenesis of the basic N-terminal cluster of pancreatic bile salt-dependent lipase. Functional significance.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
34987-34996.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Robinson,
K.J.Edwards,
P.D.Carr,
J.D.Barton,
G.D.Ewart,
and
D.L.Ollis
(2000).
Structure of the C123S mutant of dienelactone hydrolase (DLH) bound with the PMS moiety of the protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
1376-1384.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
W.C.Liao,
and
S.Y.Chiou
(2000).
Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady-state inhibition of cholesterol esterase by 4-nitrophenyl-N-substituted carbamates.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
8,
2601-2607.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Kingston,
H.M.Baker,
K.M.Loomes,
L.Bläckberg,
O.Hernell,
and
E.N.Baker
(2000).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of native and recombinant human bile-salt dependent lipase: strategies for improvement of diffraction quality.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
478-480.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Terzyan,
C.S.Wang,
D.Downs,
B.Hunter,
and
X.C.Zhang
(2000).
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human bile salt activated lipase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1783-1790.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.M.Veneziani,
F.Giallauria,
and
F.Gentile
(1999).
The disulfide bond pattern between fragments obtained by the limited proteolysis of bovine thyroglobulin.
|
| |
Biochimie,
81,
517-525.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lin,
C.T.Shieh,
Y.C.Tsai,
C.I.Hwang,
C.P.Lu,
and
G.H.Chen
(1999).
Structure-reactivity probes for active site shapes of cholesterol esterase by carbamate inhibitors.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1431,
500-511.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.van Tilbeurgh,
S.Bezzine,
C.Cambillau,
R.Verger,
and
F.Carrière
(1999).
Colipase: structure and interaction with pancreatic lipase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
173-184.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
and
C.Cambillau
(1999).
Structure-activity of cutinase, a small lipolytic enzyme.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
185-196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Chen,
L.J.Miercke,
J.Krucinski,
J.R.Starr,
G.Saenz,
X.Wang,
C.A.Spilburg,
L.G.Lange,
J.L.Ellsworth,
and
R.M.Stroud
(1998).
Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 A: novel structural features involved in lipase activation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
5107-5117.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Sbarra,
N.Bruneau,
E.Mas,
M.Hamosh,
D.Lombardo,
and
P.Hamosh
(1998).
Molecular cloning of the bile salt-dependent lipase of ferret lactating mammary gland: an overview of functional residues.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1393,
80-89.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

