 |
PDBsum entry 1z7m

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|



 311 a.a.
311 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 200 a.a.
200 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 201 a.a.
201 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Atp phosphoribosyl transferase (hiszg atp-prtase) from lactococcus lactis
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Atp phosphoribosyltransferase regulatory subunit. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes. Atp phosphoribosyltransferase. Chain: e, f, g, h. Synonym: atp-prtase, atp-prt. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Lactococcus lactis. Organism_taxid: 1358. Gene: hisz. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: hisg.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Octamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.90Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.245
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.S.Champagne,M.Sissler,Y.Larrabee,S.Doublie,C.S.Francklyn
|
Key ref:

|
 |
K.S.Champagne
et al.
(2005).
Activation of the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyl transferase through subunit interface rearrangement by a tRNA synthetase paralog.
J Biol Chem,
280,
34096-34104.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Mar-05
|
Release date:
|
09-Aug-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q02147
(HISZ_LACLA) -
ATP phosphoribosyltransferase regulatory subunit from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (strain IL1403)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
328 a.a.
311 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains E, F, G, H:
E.C.2.4.2.17
- Atp phosphoribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)-ATP + diphosphate = 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate + ATP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1-(5-phospho-beta-D-ribosyl)-ATP
|
+
|
diphosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
=
|
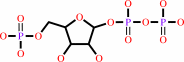 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
280:34096-34104
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Activation of the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyl transferase through subunit interface rearrangement by a tRNA synthetase paralog.
|
|
K.S.Champagne,
M.Sissler,
Y.Larrabee,
S.Doublié,
C.S.Francklyn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
ATP phosphoribosyl transferase (ATP-PRT) joins ATP and
5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) in a highly regulated reaction that
initiates histidine biosynthesis. The unusual hetero-octameric version of
ATP-PRT includes four HisG(S) catalytic subunits based on the periplasmic
binding protein fold and four HisZ regulatory subunits that resemble
histidyl-tRNA synthetases. Here, we present the first structure of a PRPP-bound
ATP-PRT at 2.9 A and provide a structural model for allosteric activation based
on comparisons with other inhibited and activated ATP-PRTs from both the
hetero-octameric and hexameric families. The activated state of the octameric
enzyme is characterized by an interstitial phosphate ion in the HisZ-HisG
interface and new contacts between the HisZ motif 2 loop and the HisG(S) dimer
interface. These contacts restructure the interface to recruit conserved
residues to the active site, where they activate pyrophosphate to promote
catalysis. Additionally, mutational analysis identifies the histidine binding
sites within a region highly conserved between HisZ and the functional HisRS.
Through the oligomerization and functional re-assignment of protein domains
associated with aminoacylation and phosphate binding, the HisZ-HisG octameric
ATP-PRT acquired the ability to initiate the synthesis of a key metabolic
intermediate in an allosterically regulated fashion.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
The reaction catalyzed by ATP-phosphoribosyl transferase in
L. lactis. The 5′-phosphoribosyl group of PRPP is transferred
to ATP yielding PR-ATP and inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). This
reaction is dependant on magnesium and is inhibited by
histidine, the end product of the pathway, and the cellular
effectors AMP and ADP.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Inter-subunit communications involved in
activation/regulation of the HisZG ATP-PRTase. a, location of
the interstitial phosphate ion in the interface between HisG
(green) and HisZ (blue). The residues that coordinate the ion
are close to a HisZ active site loop (magenta) that comprises
part of the predicted histidine binding pocket. The interstitial
phosphate is observed in only two of the four HisZ-HisG
interfaces, namely those featuring an ordered motif 2 loop. b,
interactions between the ordered HisZ motif 2 loop (blue) and
the HisG dimer interface (green and gold). Motif 2 loop residues
pack against strand β8 leading to the active site, whereas
Arg-120 hydrogen bonds to Glu-59′ at the C-terminal end of
helices α2 and α3.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2005,
280,
34096-34104)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Richards,
C.E.Short,
W.R.Driedzic,
and
K.V.Ewart
(2010).
Seasonal changes in hepatic gene expression reveal modulation of multiple processes in rainbow smelt (Osmerus mordax).
|
| |
Mar Biotechnol (NY),
12,
650-663.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Sippel,
A.H.Robbins,
R.Reutzel,
S.K.Boehlein,
K.Namiki,
S.Goodison,
M.Agbandje-McKenna,
C.J.Rosser,
and
R.McKenna
(2009).
Structural insights into the extracytoplasmic thiamine-binding lipoprotein p37 of Mycoplasma hyorhinis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
191,
2585-2592.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Coseno,
G.Martin,
C.Berger,
G.Gilmartin,
W.Keller,
and
S.Doublié
(2008).
Crystal structure of the 25 kDa subunit of human cleavage factor Im.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
3474-3483.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Cho,
T.R.Ioerger,
and
J.C.Sacchettini
(2008).
Discovery of novel nitrobenzothiazole inhibitors for Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP phosphoribosyl transferase (HisG) through virtual screening.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
51,
5984-5992.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Champagne,
E.Piscitelli,
and
C.S.Francklyn
(2006).
Substrate recognition by the hetero-octameric ATP phosphoribosyltransferase from Lactococcus lactis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
14933-14943.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
| |

