 |
PDBsum entry 1x8t

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.19
- 3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Shikimate and Chorismate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phosphoshikimate + phosphoenolpyruvate = 5-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-3- phosphoshikimate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phosphoshikimate
|
+
|
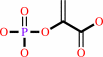 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
=
|
5-O-(1-carboxyvinyl)-3- phosphoshikimate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 84.00% similarity
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
44:3241-3248
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Interaction of phosphonate analogues of the tetrahedral reaction intermediate with 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase in atomic detail.
|
|
M.A.Priestman,
M.L.Healy,
A.Becker,
D.G.Alberg,
P.A.Bartlett,
G.H.Lushington,
E.Schönbrunn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) catalyzes the
penultimate step of the shikimate pathway and is the target of the
broad-spectrum herbicide glyphosate. Since the functionality of the shikimate
pathway is vital not only for plants but also for microorganisms, EPSPS is
considered a prospective target for the development of novel antibiotics. We
have kinetically analyzed and determined the crystal structures of Escherichia
coli EPSPS inhibited by (R)- and (S)-configured phosphonate analogues of the
tetrahedral reaction intermediate. Both diastereomers are competitive inhibitors
with respect to the substrates of the EPSPS reaction, shikimate-3-phosphate
(S3P) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Remarkably, the (S)-phosphonate (K(iS3P) =
750 nM), whose configuration corresponds to that of the genuine tetrahedral
intermediate, is a much weaker inhibitor than the (R)-phosphonate analogue
(K(iS3P) = 16 nM). The crystal structures of EPSPS liganded with the (S)- and
(R)-phosphonates, at 1.5 and 1.9 A resolution, respectively, revealed that
binding of the (R)-phosphonate induces conformational changes of the strictly
conserved residues Arg124 and Glu341 within the active site. This appears to
give rise to substantial structural alterations in the amino-terminal globular
domain of the enzyme. By contrast, binding of the (S)-phosphonate renders the
enzyme structure unchanged. Thus, EPSPS may facilitate the tight binding of
structurally diverse ligands through conformational flexibility. Molecular
docking calculations did not explain why the (R)-phosphonate is the better
inhibitor. Therefore, we propose that the structural events during the
open-closed transition of EPSPS are altered as a result of inhibitor action.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
T.Funke,
Y.Yang,
H.Han,
M.Healy-Fried,
S.Olesen,
A.Becker,
and
E.Schönbrunn
(2009).
Structural basis of glyphosate resistance resulting from the double mutation Thr97 -> Ile and Pro101 -> Ser in 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
9854-9860.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Funke,
H.Han,
M.L.Healy-Fried,
M.Fischer,
and
E.Schönbrunn
(2006).
Molecular basis for the herbicide resistance of Roundup Ready crops.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
13010-13015.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

