 |
PDBsum entry 1x8f

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of apo-kdo8p synthase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase. Chain: a. Synonym: phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyoctonate aldolase, 3-deoxy-d-manno- octulosonic acid 8-phosphate synthetase, kdo-8-phosphate synthetase, kdo 8-p synthase, kdops. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: kdsa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.239
|
R-free:
|
0.255
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Vainer,V.Belakhov,E.Rabkin,T.Baasov,N.Adir
|
Key ref:

|
 |
R.Vainer
et al.
(2005).
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli KDO8P synthase complexes reveal the source of catalytic irreversibility.
J Mol Biol,
351,
641-652.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
18-Aug-04
|
Release date:
|
26-Jul-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A715
(KDSA_ECOLI) -
2-dehydro-3-deoxyphosphooctonate aldolase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
284 a.a.
272 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.55
- 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-arabinose 5-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
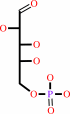 D-arabinose 5-phosphate
D-arabinose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
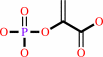 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
3-deoxy-alpha-D- manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
351:641-652
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of Escherichia coli KDO8P synthase complexes reveal the source of catalytic irreversibility.
|
|
R.Vainer,
V.Belakhov,
E.Rabkin,
T.Baasov,
N.Adir.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate synthase (KDO8PS)
catalyses the condensation of arabinose 5-phosphate (A5P) and phosphoenol
pyruvate (PEP) to obtain 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonate-8-phosphate (KDO8P). We
have elucidated initial modes of ligand binding in KDO8PS binary complexes by
X-ray crystallography. Structures of the apo-enzyme and of binary complexes with
the substrate PEP, the product KDO8P and the catalytically inactive 1-deoxy
analog of arabinose 5-phosphate (1dA5P) were obtained. The KDO8PS active site
resembles an irregular funnel with positive electrostatic potential situated at
the bottom of the PEP-binding sub-site, which is the primary attractive force
towards negatively charged phosphate moieties of all ligands. The structures of
the ligand-free apo-KDO8PS and the binary complex with the product KDO8P
visualize for the first time the role of His202 as an active-site gate.
Examination of the crystal structures of KDO8PS with the KDO8P or 1dA5P shows
these ligands bound to the enzyme in the PEP-binding sub-site, and not as
expected to the A5P sub-site. Taken together, the structures presented here
strengthen earlier evidence that this enzyme functions predominantly through
positional catalysis, map out the roles of active-site residues and provide
evidence that explains the total lack of catalytic reversibility.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Electron density maps contoured over ligands
bound within the KDO8PS active site. (a) The 2F[o] -F[c]
electron density map overlaid onto the apo-KDO8PS His202
residue, contoured at 1.5s (orange) and at 0.9s (blue) showing
the major and minor side-chain orientations. (b) The 2F[o] -F[c]
electron density map overlaid onto the bound PEP contoured at 2s
(orange) and at 1s (blue) is overlaid onto the PEP substrate.
(c) The F[o] -F[c] omit electron density map overlaid onto the
KDO8P product contoured at 2s (orange) and at 1s (blue). Note
that the electron density allows the absolute assignment as the
a-pyranoside anomer. (d) The F[o] -F[c] omit electron density
map overlaid onto the 1dA5P analog contoured at 2s (orange) and
at 1s (blue). In all Figures, atoms are colored according to:
red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen; green, carbon; and magenta,
phosphorus.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Superposition of the KDO8PS binary structures
with KDO8P (carbon atoms orange), 1dA5P (carbon atoms gray) and
the mechanism-based inhibitor (Inh) as visualized in the 1G7V
structure (carbon atoms magenta). The light cyan cartoon shows
the position of the protein secondary structure surrounding the
active site. Important residues have been placed to denote the
direction of the active site. His202 (shown in ball-and-stick
representation) is shown in its two alternative positions, with
the closed conformation found in the KDO8PS·KDO8P
structure denoted with an asterisk (*). The closed conformation
is identical with the minor His202 orientation in the apo-KDO8PS
structure as seen in Figure 1.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2005,
351,
641-652)
copyright 2005.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
L.Cipolla,
L.Gabrielli,
D.Bini,
L.Russo,
and
N.Shaikh
(2010).
Kdo: a critical monosaccharide for bacteria viability.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
27,
1618-1629.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

