 |
PDBsum entry 1w5r

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.5
- arylamine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an arylamine + acetyl-CoA = an N-acetylarylamine + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
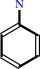 arylamine
arylamine
|
+
|
 acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
|
=
|
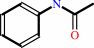 N-acetylarylamine
N-acetylarylamine
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochem J
390:115-123
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Investigation of the catalytic triad of arylamine N-acetyltransferases: essential residues required for acetyl transfer to arylamines.
|
|
J.Sandy,
A.Mushtaq,
S.J.Holton,
P.Schartau,
M.E.Noble,
E.Sim.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The NATs (arylamine N-acetyltransferases) are a well documented family of
enzymes found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. NATs are responsible for the
acetylation of a range of arylamine, arylhydrazine and hydrazine compounds. We
present here an investigation into the catalytic triad of residues (Cys-His-Asp)
and other structural features of NATs using a variety of methods, including
site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography and bioinformatics analysis, in
order to investigate whether each of the residues of the catalytic triad is
essential for catalytic activity. The catalytic triad of residues, Cys-His-Asp,
is a well defined motif present in several families of enzymes. We mutated each
of the catalytic residues in turn to investigate the role they play in
catalysis. We also mutated a key residue, Gly126, implicated in acetyl-CoA
binding, to examine the effects on acetylation activity. In addition, we have
solved the structure of a C70Q mutant of Mycobacterium smegmatis NAT to a
resolution of 1.45 A (where 1 A=0.1 nm). This structure confirms that the
mutated protein is correctly folded, and provides a structural model for an
acetylated NAT intermediate. Our bioinformatics investigation analysed the
extent of sequence conservation between all eukaryotic and prokaryotic NAT
enzymes for which sequence data are available. This revealed several new
sequences, not yet reported, of NAT paralogues. Together, these studies have
provided insight into the fundamental core of NAT enzymes, and the regions where
sequence differences account for the functional diversity of this family. We
have confirmed that each of the three residues of the triad is essential for
acetylation activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Hein
(2009).
N-acetyltransferase SNPs: emerging concepts serve as a paradigm for understanding complexities of personalized medicine.
|
| |
Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol,
5,
353-366.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Zhou,
N.Zhang,
L.Liu,
K.J.Walters,
P.E.Hanna,
and
C.R.Wagner
(2009).
Probing the catalytic potential of the hamster arylamine N-acetyltransferase 2 catalytic triad by site-directed mutagenesis of the proximal conserved residue, Tyr190.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
6928-6941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.L.Sikora,
B.A.Frankel,
and
J.S.Blanchard
(2008).
Kinetic and chemical mechanism of arylamine N-acetyltransferase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
10781-10789.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Sim,
J.Sandy,
D.Evangelopoulos,
E.Fullam,
S.Bhakta,
I.Westwood,
A.Krylova,
N.Lack,
and
M.Noble
(2008).
Arylamine N-acetyltransferases in mycobacteria.
|
| |
Curr Drug Metab,
9,
510-519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Walraven,
Y.Zang,
J.O.Trent,
and
D.W.Hein
(2008).
Structure/function evaluations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in human N-acetyltransferase 2.
|
| |
Curr Drug Metab,
9,
471-486.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Westwood,
and
E.Sim
(2007).
Kinetic characterisation of arylamine N-acetyltransferase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
|
| |
BMC Biochem,
8,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zang,
M.A.Doll,
S.Zhao,
J.C.States,
and
D.W.Hein
(2007).
Functional characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes of human N-acetyltransferase 2.
|
| |
Carcinogenesis,
28,
1665-1671.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zang,
S.Zhao,
M.A.Doll,
J.Christopher States,
and
D.W.Hein
(2007).
Functional characterization of the A411T (L137F) and G364A (D122N) genetic polymorphisms in human N-acetyltransferase 2.
|
| |
Pharmacogenet Genomics,
17,
37-45.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

