 |
PDBsum entry 1tcd

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Trypanosoma cruzi triosephosphate isomerase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Triosephosphate isomerase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: tim. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Trypanosoma cruzi. Organism_taxid: 5693. Strain: mexican ninoa. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Homo-Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.83Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.258
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Maldonado,M.Soriano-Garcia,N.Cabrera,G.Garza-Ramos,M.Tuena De Gomez-Puyou,A.Gomez-Puyou,R.Perez-Montfort
|
Key ref:

|
 |
E.Maldonado
et al.
(1998).
Differences in the intersubunit contacts in triosephosphate isomerase from two closely related pathogenic trypanosomes.
J Mol Biol,
283,
193-203.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Jan-98
|
Release date:
|
13-Jan-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P52270
(TPIS_TRYCR) -
Triosephosphate isomerase, glycosomal from Trypanosoma cruzi
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
251 a.a.
248 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.1
- triose-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
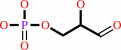 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
=
|
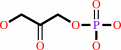 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
283:193-203
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Differences in the intersubunit contacts in triosephosphate isomerase from two closely related pathogenic trypanosomes.
|
|
E.Maldonado,
M.Soriano-García,
A.Moreno,
N.Cabrera,
G.Garza-Ramos,
M.de Gómez-Puyou,
A.Gómez-Puyou,
R.Perez-Montfort.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The aligned amino acid sequences of TIM from Trypanosoma cruzi (TcTIM) and
Trypanosoma brucei (TbTIM) have a positional identity of 68%. The two enzymes
have markedly similar catalytic properties. Agents that interact with their
interface Cys inhibit TcTIM and TbTIM; and those TIMs that lack this Cys (such
as human TIM) are largely or completely insensitive to these agents. The
susceptibility of TcTIM to the agents is approximately 100 times higher than
that of TbTIM. To ascertain the cause of this large difference, the crystal
structure of TcTIM was solved at 1.83 A resolution. The two enzymes are very
similar homodimers. In TcTIM and TbTIM their respective Cys, 15 or 14, forms
part of the dimer interface. In both, the contacts of the Cys with residues of
the other subunit are almost identical. Nevertheless, there are noteworthy
differences between the two; the existence of glutamine 18 in TbTIM instead of
glutamic acid in TcTIM at the beginning of helix 1 decreases the contacts
between this portion of the protein and helix 3 of the other subunit. In
addition, TcTIM has proline at position 24 in the first helix of the TIM barrel;
this is absent in the other TIM. Pro24 disrupts the regular helix arrangement,
making the pitch of this helix 1.2 A longer than in TbTIM. When Pro24 of TcTIM
was substituted for Glu, the sensitivity of TcTIM to sulfhydryl reagents
increased about fivefold, possibly as a consequence of an increase in the space
between the first portion of helix 1 and helix 3 of the other subunit.
Therefore, it may be concluded that the geometry of the latter region is central
in the accessibility to agents that perturb the interface Cys. In human TIM this
region is more compact.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. (a) Stereoview of the 3 F[o] -2 F[c]electron
density map contoured at 1s of Cys15 of TcTIM and its
surrounding loop 3 residues. (b) Stereoview of the interface Cys
of TcTIM (orange) and TbTIM (green) and surrounding residues.
The oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur atoms are represented in red,
blue and yellow, respectively.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Stereoview of the region between the end of loop
1 in monomer B and a portion of helix 3 of the adjoining
subunit. TcTIM and TbTIM are depicted in orange and green,
respectively. The color-code for the atoms is as in Figure 2(b).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(1998,
283,
193-203)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Moraes,
R.Arreola,
N.Cabrera,
L.Saramago,
D.Freitas,
A.Masuda,
I.da Silva Vaz,
M.Tuena de Gomez-Puyou,
R.Perez-Montfort,
A.Gomez-Puyou,
and
C.Logullo
(2011).
Structural and biochemical characterization of a recombinant triosephosphate isomerase from Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus.
|
| |
Insect Biochem Mol Biol,
41,
400-409.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chávez-Calvillo,
M.Costas,
and
J.Hernández-Trujillo
(2010).
Theoretical analysis of intermolecular interactions of selected residues of triosephosphate isomerase from Trypanosoma cruzi with its inhibitor 3-(2-benzothiazolylthio)-1-propanesulfonic acid.
|
| |
Phys Chem Chem Phys,
12,
2067-2074.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Thakur,
P.D.Deepalakshmi,
P.Gayathri,
M.Banerjee,
M.R.Murthy,
and
P.Balaram
(2009).
Detection of the protein dimers, multiple monomeric states and hydrated forms of Plasmodium falciparum triosephosphate isomerase in the gas phase.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
22,
289-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Olivares-Illana,
A.Rodríguez-Romero,
I.Becker,
M.Berzunza,
J.García,
R.Pérez-Montfort,
N.Cabrera,
F.López-Calahorra,
M.T.de Gómez-Puyou,
and
A.Gómez-Puyou
(2007).
Perturbation of the Dimer Interface of Triosephosphate Isomerase and its Effect on Trypanosoma cruzi.
|
| |
PLoS Negl Trop Dis,
1,
e1.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Zomosa-Signoret,
B.Aguirre-López,
G.Hernández-Alcántara,
R.Pérez-Montfort,
M.T.de Gómez-Puyou,
and
A.Gómez-Puyou
(2007).
Crosstalk between the subunits of the homodimeric enzyme triosephosphate isomerase.
|
| |
Proteins,
67,
75-83.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Reyes-Vivas,
E.Martínez-Martínez,
G.Mendoza-Hernández,
G.López-Velázquez,
R.Pérez-Montfort,
M.Tuena de Gómez-Puyou,
and
A.Gómez-Puyou
(2002).
Susceptibility to proteolysis of triosephosphate isomerase from two pathogenic parasites: characterization of an enzyme with an intact and a nicked monomer.
|
| |
Proteins,
48,
580-590.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Maithal,
G.Ravindra,
H.Balaram,
and
P.Balaram
(2002).
Inhibition of plasmodium falciparum triose-phosphate isomerase by chemical modification of an interface cysteine. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis of differential cysteine reactivities.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
25106-25114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Verlinde,
V.Hannaert,
C.Blonski,
M.Willson,
J.J.Périé,
L.A.Fothergill-Gilmore,
F.R.Opperdoes,
M.H.Gelb,
W.G.Hol,
and
P.A.Michels
(2001).
Glycolysis as a target for the design of new anti-trypanosome drugs.
|
| |
Drug Resist Updat,
4,
50-65.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Reyes-Vivas,
G.Hernández-Alcantara,
G.López-Velazquez,
N.Cabrera,
R.Pérez-Montfort,
M.T.de Gómez-Puyou,
and
A.Gómez-Puyou
(2001).
Factors that control the reactivity of the interface cysteine of triosephosphate isomerase from Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3134-3140.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Maes,
J.P.Zeelen,
N.Thanki,
N.Beaucamp,
M.Alvarez,
M.H.Thi,
J.Backmann,
J.A.Martial,
L.Wyns,
R.Jaenicke,
and
R.K.Wierenga
(1999).
The crystal structure of triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) from Thermotoga maritima: a comparative thermostability structural analysis of ten different TIM structures.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
441-453.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Alvarez,
J.Wouters,
D.Maes,
V.Mainfroid,
F.Rentier-Delrue,
L.Wyns,
E.Depiereux,
and
J.A.Martial
(1999).
Lys13 plays a crucial role in the functional adaptation of the thermophilic triose-phosphate isomerase from Bacillus stearothermophilus to high temperatures.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
19181-19187.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.G.Gao,
E.Maldonado,
R.Pérez-Montfort,
G.Garza-Ramos,
M.T.de Gómez-Puyou,
A.Gómez-Puyou,
and
A.Rodríguez-Romero
(1999).
Crystal structure of triosephosphate isomerase from Trypanosoma cruzi in hexane.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
96,
10062-10067.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

