 |
PDBsum entry 1spi

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase (phosphoric monoester)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1spi
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase (phosphoric monoester)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.8 angstroms resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Spinacia oleracea. Spinach. Organism_taxid: 3562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
V.Villeret,S.Huang,Y.Zhang,Y.Xue,W.N.Lipscomb
|
Key ref:

|
 |
V.Villeret
et al.
(1995).
Crystal structure of spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.8 A resolution.
Biochemistry,
34,
4299-4306.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Dec-94
|
Release date:
|
27-Feb-95
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P22418
(F16P1_SPIOL) -
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, chloroplastic from Spinacia oleracea
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
415 a.a.
333 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.11
- fructose-bisphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (later stages)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate + H2O = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
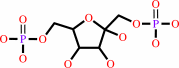 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
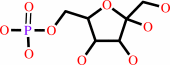 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
34:4299-4306
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.8 A resolution.
|
|
V.Villeret,
S.Huang,
Y.Zhang,
Y.Xue,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional structure of the spinach chloroplast
fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fru-1,6-Pase) has been solved by the molecular
replacement method at 2.8 A resolution and refined to a crystallographic R
factor of 0.203. The enzyme is composed of four monomers and displays pseudo D2
symmetry. Comparison with the allosteric Fru-1,6-Pase from pig kidney shows
orientationally displaced dimers within the quaternary structure of the
chloroplast enzyme. When the C1C2 dimers of the two enzymes are superimposed,
the C3C4 dimer of the chloroplast enzyme is rotated 20 degrees and 5 degrees
relative to the C3C4 dimer of the R and T forms of the pig kidney enzyme,
respectively. This new quaternary structure, designated as S, may be described
as a super-T form and is outside of the pathway of the allosteric transition
which occurs in the pig kidney enzyme, which shows a 15 degrees rotation between
T and R forms. Chloroplast Fru-1,6-Pase, unlike the pig kidney enzyme, is
insensitive to allosteric transformation by AMP. Structural changes in the AMP
binding site involving mainly helices H1, H2, and H3 and the loop between H1 and
H2 at the dimer interface interfere with binding of the phosphate of AMP.
Finally, the location of cysteines residues provides a basis for a preliminary
discussion of the activation of the enzyme by reduction of cysteines via the
ferredoxin-thioredoxin f system; this process is complementary to activation by
pH changes, Mg2+ or Ca2+, Fru-1,6-P2, and possibly Fru-2,6-P2.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Chibani,
J.Couturier,
B.Selles,
J.P.Jacquot,
and
N.Rouhier
(2010).
The chloroplastic thiol reducing systems: dual functions in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism and regeneration of antioxidant enzymes, emphasis on the poplar redoxin equipment.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
104,
75-99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Serrato,
J.de Dios Barajas-López,
A.Chueca,
and
M.Sahrawy
(2009).
Changing sugar partitioning in FBPase-manipulated plants.
|
| |
J Exp Bot,
60,
2923-2931.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Brown,
A.Singer,
V.V.Lunin,
M.Proudfoot,
T.Skarina,
R.Flick,
S.Kochinyan,
R.Sanishvili,
A.Joachimiak,
A.M.Edwards,
A.Savchenko,
and
A.F.Yakunin
(2009).
Structural and biochemical characterization of the type II fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase GlpX from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
3784-3792.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Schürmann,
and
B.B.Buchanan
(2008).
The ferredoxin/thioredoxin system of oxygenic photosynthesis.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
10,
1235-1274.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
M.F.Roberts,
W.Li,
and
B.Stec
(2007).
Crystal structure of the tetrameric inositol 1-phosphate phosphatase (TM1415) from the hyperthermophile, Thermotoga maritima.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
2461-2469.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Lemaire,
L.Michelet,
M.Zaffagnini,
V.Massot,
and
E.Issakidis-Bourguet
(2007).
Thioredoxins in chloroplasts.
|
| |
Curr Genet,
51,
343-365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Gopalan,
Z.He,
K.P.Battaile,
S.Luan,
and
K.Swaminathan
(2006).
Structural comparison of oxidized and reduced FKBP13 from Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Proteins,
65,
789-795.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Hines,
H.J.Fromm,
and
R.B.Honzatko
(2006).
Novel allosteric activation site in Escherichia coli fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
18386-18393.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.B.Buchanan,
and
Y.Balmer
(2005).
Redox regulation: a broadening horizon.
|
| |
Annu Rev Plant Biol,
56,
187-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Cazalis,
A.Chueca,
M.Sahrawy,
and
J.López-Gorgé
(2004).
Construction of chimeric cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatases by insertion of a chloroplastic redox regulatory cluster.
|
| |
J Physiol Biochem,
60,
7.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Brodegger,
A.Stockmann,
J.Oberstrass,
W.Nellen,
and
H.Follmann
(2004).
Novel thioredoxin targets in Dictyostelium discoideum identified by two-hybrid analysis: interactions of thioredoxin with elongation factor 1alpha and yeast alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
1185-1192.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Stieglitz,
B.A.Seaton,
J.F.Head,
B.Stec,
and
M.F.Roberts
(2003).
Unexpected similarity in regulation between an archaeal inositol monophosphatase/fructose bisphosphatase and chloroplast fructose bisphosphatase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
760-767.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Schürmann
(2003).
Redox signaling in the chloroplast: the ferredoxin/thioredoxin system.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
5,
69-78.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Verhees,
J.Akerboom,
E.Schiltz,
W.M.de Vos,
and
J.van der Oost
(2002).
Molecular and biochemical characterization of a distinct type of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Pyrococcus furiosus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
184,
3401-3405.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Jacquot,
N.Rouhier,
and
E.Gelhaye
(2002).
Redox control by dithiol-disulfide exchange in plants: I. The chloroplastic systems.
|
| |
Ann N Y Acad Sci,
973,
508-519.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Nakamura,
T.Tada,
K.Wada,
T.Kinoshita,
M.Tamoi,
S.Shigeoka,
and
K.Nishimura
(2001).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of the fructose-1,6-/sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase of Synechococcus PCC 7942.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
454-456.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.W.Zhang,
F.K.Zhao,
and
G.J.Xu
(2000).
Molecular cloning, expression and purification of muscle fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Zaocys dhumnades: the role of the N-terminal sequence in AMP activation at alkaline pH.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
381,
561-566.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Nocek,
K.Huang,
and
B.M.Hoffman
(2000).
Extension of transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy techniques to allosteric proteins: CO- and paramagnetic fluoromet-hemoglobin [beta (15N-valine)].
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
97,
2538-2543.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Schurmann,
and
J.P.Jacquot
(2000).
PLANT THIOREDOXIN SYSTEMS REVISITED.
|
| |
Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol,
51,
371-400.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Weeks,
A.W.Roszak,
M.Erman,
R.Kaiser,
H.Jörnvall,
and
D.Ghosh
(1999).
Structure of rabbit liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase at 2.3 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
93.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Ruelland,
and
M.Miginiac-Maslow
(1999).
Regulation of chloroplast enzyme activities by thioredoxins: activation or relief from inhibition?
|
| |
Trends Plant Sci,
4,
136-141.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Chiadmi,
A.Navaza,
M.Miginiac-Maslow,
J.P.Jacquot,
and
J.Cherfils
(1999).
Redox signalling in the chloroplast: structure of oxidized pea fructose-1,6-bisphosphate phosphatase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
18,
6809-6815.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Mora-García,
R.Rodríguez-Suárez,
and
R.A.Wolosiuk
(1998).
Role of electrostatic interactions on the affinity of thioredoxin for target proteins. Recognition of chloroplast fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase by mutant Escherichia coli thioredoxins.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
16273-16280.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Chen,
J.W.Wu,
G.J.Xu,
C.L.Tsou,
and
Z.X.Wang
(1997).
Inactivation kinetics of the reduced spinach chloroplast fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by subtilisin.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
248,
925-929.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Mattevi,
M.Rizzi,
and
M.Bolognesi
(1996).
New structures of allosteric proteins revealing remarkable conformational changes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
6,
824-829.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Stec,
R.Abraham,
E.Giroux,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1996).
Crystal structures of the active site mutant (Arg-243-->Ala) in the T and R allosteric states of pig kidney fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase expressed in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
1541-1553.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.von Itzstein,
and
P.Colman
(1996).
Design and synthesis of carbohydrate-based inhibitors of protein-carbohydrate interactions.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
6,
703-709.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

