
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of ctp-ligated t state aspartate transcarbamoylase at 2.5 angstroms resolution: implications for atcase mutants and the mechanism of negative cooperativity
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalytic chain. Chain: a, c. Synonym: aspartate transcarbamylase, atcase. Engineered: yes. Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory chain. Chain: b, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 83333. Strain: k12. Gene: pyrb, b4245, jw4204. Gene: pyri, b4244, jw4203
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from
)
Dodecamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.P.Kosman,J.E.Gouaux,W.N.Lipscomb
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.P.Kosman
et al.
(1993).
Crystal structure of CTP-ligated T state aspartate transcarbamoylase at 2.5 A resolution: implications for ATCase mutants and the mechanism of negative cooperativity.
Proteins,
15,
147-176.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Aug-92
|
Release date:
|
31-Jan-94
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, C:
E.C.2.1.3.2
- aspartate carbamoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
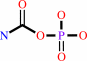 carbamoyl phosphate
carbamoyl phosphate
|
+
|
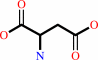 L-aspartate
L-aspartate
|
=
|
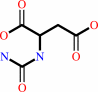 N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains B, D:
E.C.?
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Proteins
15:147-176
(1993)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of CTP-ligated T state aspartate transcarbamoylase at 2.5 A resolution: implications for ATCase mutants and the mechanism of negative cooperativity.
|
|
R.P.Kosman,
J.E.Gouaux,
W.N.Lipscomb.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The X-ray crystal structure of CTP-ligated T state aspartate transcarbamoylase
has been refined to an R factor of 0.182 at 2.5 A resolution using the computer
program X-PLOR. The structure contains 81 sites for solvent and has rms
deviations from ideality in bond lengths and bond angles of 0.018 A and 3.722
degrees, respectively. The cytosine base of CTP interacts with the main chain
carbonyl oxygens of rTyr-89 and rIle-12, the main chain NH of rIle-12, and the
amino group of rLys-60. The ribose hydroxyls form polar contacts with the amino
group of rLys-60, a carboxylate oxygen of rAsp-19, and the main chain carbonyl
oxygen of rVal-9. The phosphate oxygens of CTP interact with the amino group of
rLys-94, the hydroxyl of rThr-82, and an imidazole nitrogen of rHis-20. Recent
mutagenesis experiments evaluated in parallel with the structure reported here
indicate that alterations in the hydrogen bonding environment of the side chain
of rAsn-111 may be responsible for the homotropic behavior of the pAR5 mutant of
ATCase. The location of the first seven residues of the regulatory chain has
been identified for the first time in a refined ATCase crystal structure, and
the proximity of this portion of the regulatory chain to the allosteric site
suggests a potential role for these residues in nucleotide binding to the
enzyme. Finally, a series of amino acid side chain rearrangements leading from
the R1 CTP allosteric to the R6 CTP allosteric site has been identified which
may constitute the molecular mechanism of distinct CTP binding sites on ATCase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Stec,
M.K.Williams,
K.A.Stieglitz,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2007).
Comparison of two T-state structures of regulatory-chain mutants of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase suggests that His20 and Asp19 modulate the response to heterotropic effectors.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1243-1253.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wang,
K.A.Stieglitz,
J.P.Cardia,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2005).
Structural basis for ordered substrate binding and cooperativity in aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
8881-8886.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Alam,
K.A.Stieglitz,
M.D.Caban,
S.Gourinath,
H.Tsuruta,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2004).
240s loop interactions stabilize the T state of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
23302-23310.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Sakash,
A.Tsen,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(2000).
The use of nucleotide analogs to evaluate the mechanism of the heterotropic response of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
53-63.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Thomas,
K.Hinsen,
M.J.Field,
and
D.Perahia
(1999).
Tertiary and quaternary conformational changes in aspartate transcarbamylase: a normal mode study.
|
| |
Proteins,
34,
96.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Thoden,
F.M.Raushel,
G.Wesenberg,
and
H.M.Holden
(1999).
The binding of inosine monophosphate to Escherichia coli carbamoyl phosphate synthetase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
22502-22507.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Jin,
B.Stec,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1999).
Insights into the mechanisms of catalysis and heterotropic regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase based upon a structure of the enzyme complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate at 2.1 A.
|
| |
Proteins,
37,
729-742.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Durbecq,
T.L.Thia-Toong,
D.Charlier,
V.Villeret,
M.Roovers,
R.Wattiez,
C.Legrain,
and
N.Glansdorff
(1999).
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase from the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Cloning, sequence analysis, enzyme purification and characterization.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
264,
233-241.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Shi,
H.Morizono,
Y.Ha,
M.Aoyagi,
M.Tuchman,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1998).
1.85-A resolution crystal structure of human ornithine transcarbamoylase complexed with N-phosphonacetyl-L-ornithine. Catalytic mechanism and correlation with inherited deficiency.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
34247-34254.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Williams,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1998).
Threonine 82 in the regulatory chain is important for nucleotide affinity and for the allosteric stabilization of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1429,
249-258.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Purcarea,
G.Hervé,
M.M.Ladjimi,
and
R.Cunin
(1997).
Aspartate transcarbamylase from the deep-sea hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus abyssi: genetic organization, structure, and expression in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
179,
4143-4157.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Matsuda,
and
S.Tanase
(1997).
The ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) gene: mutations in 50 Japanese families with OTC deficiency.
|
| |
Am J Med Genet,
71,
378-383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Eriksson,
U.Uhlin,
S.Ramaswamy,
M.Ekberg,
K.Regnström,
B.M.Sjöberg,
and
H.Eklund
(1997).
Binding of allosteric effectors to ribonucleotide reductase protein R1: reduction of active-site cysteines promotes substrate binding.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
1077-1092.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Schuller,
G.A.Grant,
and
L.J.Banaszak
(1995).
The allosteric ligand site in the Vmax-type cooperative enzyme phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
2,
69-76.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Baker,
L.Fetler,
R.T.Keiser,
P.Vachette,
and
E.R.Kantrowitz
(1995).
Weakening of the interface between adjacent catalytic chains promotes domain closure in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
258-267.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Tuchman,
H.Morizono,
O.Reish,
X.Yuan,
and
N.M.Allewell
(1995).
The molecular basis of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: modelling the human enzyme and the effects of mutations.
|
| |
J Med Genet,
32,
680-688.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Madej,
J.F.Gibrat,
and
S.H.Bryant
(1995).
Threading a database of protein cores.
|
| |
Proteins,
23,
356-369.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

