 |
PDBsum entry 1qdb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1qdb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.7.2.2
- nitrite reductase (cytochrome; ammonia-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
6 Fe(III)-[cytochrome c] + NH4+ + 2 H2O = 6 Fe(II)-[cytochrome c] + nitrite + 8 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
6
×
Fe(III)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
+
|
2
×
H2O
|
=
|
6
×
Fe(II)-[cytochrome c]
|
+
|
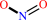 nitrite
nitrite
|
+
|
8
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+); Heme
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Ca(2+)
|
Heme
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
HEC)
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nature
400:476-480
(1999)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of cytochrome c nitrite reductase.
|
|
O.Einsle,
A.Messerschmidt,
P.Stach,
G.P.Bourenkov,
H.D.Bartunik,
R.Huber,
P.M.Kroneck.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme cytochrome c nitrite reductase catalyses the six-electron reduction
of nitrite to ammonia as one of the key steps in the biological nitrogen cycle,
where it participates in the anaerobic energy metabolism of dissimilatory
nitrate ammonification. Here we report on the crystal structure of this enzyme
from the microorganism Sulfurospirillum deleyianum, which we solved by
multiwavelength anomalous dispersion methods. We propose a reaction scheme for
the transformation of nitrite based on structural and spectroscopic information.
Cytochrome c nitrite reductase is a functional dimer, with 10 close-packed haem
groups of type c and an unusual lysine-coordinated high-spin haem at the active
site. By comparing the haem arrangement of this nitrite reductase with that of
other multihaem cytochromes, we have been able to identify a family of proteins
in which the orientation of haem groups is conserved whereas structure and
function are not.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1: The nitrite reductase dimer. A front view with the
dimer axis orientated vertically, the five haems in each monomer
(white), the Ca^2+ ions (grey) and Lys 133 which coordinates the
active-site iron atom (yellow). In the right monomer, the
protein chain is coloured blue from the amino-terminal end to
red at the carboxy-terminal end, in the left monomer according
to secondary structure. The dimer interface is dominated by
three long  -helices
per monomer. All haems in the dimer are covalently attached to
the protein and their iron atoms are arranged almost in a plane
parallel to the plane of the paper. -helices
per monomer. All haems in the dimer are covalently attached to
the protein and their iron atoms are arranged almost in a plane
parallel to the plane of the paper.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2: Haem arrangement. The overall orientation
corresponds to Fig. 1, with the active site located at haem 1
and the line indicating the dimer interface. Haems in the left
monomer are numbered according to their attachment to the
protein chain. In the right monomer, the Fe–Fe distances
(å) between the haems are given. Haems 5 interact across
the dimer interface with a distance closer than haems 2 and 3
within each monomer.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nature
(1999,
400,
476-480)
copyright 1999.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Lockwood,
J.N.Butt,
T.A.Clarke,
and
D.J.Richardson
(2011).
Molecular interactions between multihaem cytochromes: probing the protein-protein interactions between pentahaem cytochromes of a nitrite reductase complex.
|
| |
Biochem Soc Trans,
39,
263-268.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Bykov,
and
F.Neese
(2011).
Substrate binding and activation in the active site of cytochrome c nitrite reductase: a density functional study.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
16,
417-430.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Bertini,
G.Cavallaro,
and
A.Rosato
(2011).
Principles and patterns in the interaction between mono-heme cytochrome c and its partners in electron transfer processes.
|
| |
Metallomics,
3,
354-362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Trofimov,
K.M.Polyakov,
K.M.Boyko,
T.V.Tikhonova,
T.N.Safonova,
A.V.Tikhonov,
A.N.Popov,
and
V.O.Popov
(2010).
Structures of complexes of octahaem cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Thioalkalivibrio nitratireducens with sulfite and cyanide.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
1043-1047.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Silveira,
S.Besson,
I.Moura,
J.J.Moura,
and
M.G.Almeida
(2010).
Measuring the cytochrome C nitrite reductase activity-practical considerations on the enzyme assays.
|
| |
Bioinorg Chem Appl,
(),
0.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.L.Kemp,
T.A.Clarke,
S.J.Marritt,
C.Lockwood,
S.R.Poock,
A.M.Hemmings,
D.J.Richardson,
M.R.Cheesman,
and
J.N.Butt
(2010).
Kinetic and thermodynamic resolution of the interactions between sulfite and the pentahaem cytochrome NrfA from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochem J,
431,
73-80.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Grigg,
J.Cheung,
D.E.Heinrichs,
and
M.E.Murphy
(2010).
Specificity of Staphyloferrin B recognition by the SirA receptor from Staphylococcus aureus.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
34579-34588.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Sharma,
G.Cavallaro,
and
A.Rosato
(2010).
A systematic investigation of multiheme c-type cytochromes in prokaryotes.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
15,
559-571.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Han,
K.Kim,
J.Oh,
J.Park,
and
Y.Kim
(2008).
TPR domain of NrfG mediates complex formation between heme lyase and formate-dependent nitrite reductase in Escherichia coli O157:H7.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
900-914.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Heitmann,
and
O.Einsle
(2008).
Pseudo-merohedral twinning in crystals of the dihaem c-type cytochrome DHC2 from Geobacter sulfurreducens.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
993-999.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Kim,
A.Zatsman,
A.K.Upadhyay,
M.Whittaker,
D.Bergmann,
M.P.Hendrich,
and
A.B.Hooper
(2008).
Membrane tetraheme cytochrome c(m552) of the ammonia-oxidizing nitrosomonas europaea: a ubiquinone reductase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
6539-6551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Moura,
S.R.Pauleta,
and
J.J.Moura
(2008).
Enzymatic activity mastered by altering metal coordination spheres.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
13,
1185-1195.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kostera,
M.D.Youngblut,
J.M.Slosarczyk,
and
A.A.Pacheco
(2008).
Kinetic and product distribution analysis of NO* reductase activity in Nitrosomonas europaea hydroxylamine oxidoreductase.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
13,
1073-1083.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Bowman,
and
K.L.Bren
(2008).
The chemistry and biochemistry of heme c: functional bases for covalent attachment.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
25,
1118-1130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.V.Tikhonova,
E.S.Slutskaya,
A.A.Filimonenkov,
K.M.Boyko,
S.Y.Kleimenov,
P.V.Konarev,
K.M.Polyakov,
D.I.Svergun,
A.A.Trofimov,
V.G.Khomenkov,
R.A.Zvyagilskaya,
and
V.O.Popov
(2008).
Isolation and oligomeric composition of cytochrome c nitrite reductase from the haloalkaliphilic bacterium Thioalkalivibrio nitratireducens.
|
| |
Biochemistry (Mosc),
73,
164-170.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kartal,
M.M.Kuypers,
G.Lavik,
J.Schalk,
H.J.Op den Camp,
M.S.Jetten,
and
M.Strous
(2007).
Anammox bacteria disguised as denitrifiers: nitrate reduction to dinitrogen gas via nitrite and ammonium.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
9,
635-642.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Hartshorne,
M.Kern,
B.Meyer,
T.A.Clarke,
M.Karas,
D.J.Richardson,
and
J.Simon
(2007).
A dedicated haem lyase is required for the maturation of a novel bacterial cytochrome c with unconventional covalent haem binding.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
64,
1049-1060.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Upadhyay,
A.B.Hooper,
and
M.P.Hendrich
(2006).
NO reductase activity of the tetraheme cytochrome C554 of Nitrosomonas europaea.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
128,
4330-4337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Marboutin,
A.Boussac,
and
C.Berthomieu
(2006).
Redox infrared markers of the heme and axial ligands in microperoxidase: Bases for the analysis of c-type cytochromes.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
11,
811-823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Rodrigues,
T.F.Oliveira,
I.A.Pereira,
and
M.Archer
(2006).
X-ray structure of the membrane-bound cytochrome c quinol dehydrogenase NrfH reveals novel haem coordination.
|
| |
EMBO J,
25,
5951-5960.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Rodrigues,
T.Oliveira,
P.M.Matias,
I.C.Martins,
F.M.Valente,
I.A.Pereira,
and
M.Archer
(2006).
Crystallization and preliminary structure determination of the membrane-bound complex cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
62,
565-568.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Teschner,
L.Yatsunyk,
V.Schünemann,
H.Paulsen,
H.Winkler,
C.Hu,
W.R.Scheidt,
F.A.Walker,
and
A.X.Trautwein
(2006).
Models of the membrane-bound cytochromes: mössbauer spectra of crystalline low-spin ferriheme complexes having axial ligand plane dihedral angles ranging from 0 degree to 90 degrees.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
128,
1379-1389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.G.Mowat,
and
S.K.Chapman
(2005).
Multi-heme cytochromes--new structures, new chemistry.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
3381-3389.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Bergmann,
A.B.Hooper,
and
M.G.Klotz
(2005).
Structure and sequence conservation of hao cluster genes of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: evidence for their evolutionary history.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
71,
5371-5382.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kura,
S.Kuwata,
and
T.Ikariya
(2005).
N-Methylhydroxylamido(1-)- and nitrosomethaneruthenium complexes derived from nitrosyl complexes: reversible N-protonation of an N-coordinated nitrosoalkane.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
44,
6406-6409.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Crow,
R.M.Acheson,
N.E.Le Brun,
and
A.Oubrie
(2004).
Structural basis of Redox-coupled protein substrate selection by the cytochrome c biosynthesis protein ResA.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
23654-23660.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Einsle,
and
P.M.Kroneck
(2004).
Structural basis of denitrification.
|
| |
Biol Chem,
385,
875-883.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Cabello,
C.Pino,
M.F.Olmo-Mira,
F.Castillo,
M.D.Roldán,
and
C.Moreno-Vivián
(2004).
Hydroxylamine assimilation by Rhodobacter capsulatus E1F1. requirement of the hcp gene (hybrid cluster protein) located in the nitrate assimilation nas gene region for hydroxylamine reduction.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
45485-45494.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Clarke,
V.Dennison,
H.E.Seward,
B.Burlat,
J.A.Cole,
A.M.Hemmings,
and
D.J.Richardson
(2004).
Purification and spectropotentiometric characterization of Escherichia coli NrfB, a decaheme homodimer that transfers electrons to the decaheme periplasmic nitrite reductase complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
41333-41339.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Cunha,
S.Macieira,
J.M.Dias,
G.Almeida,
L.L.Goncalves,
C.Costa,
J.Lampreia,
R.Huber,
J.J.Moura,
I.Moura,
and
M.J.Romão
(2003).
Cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ATCC 27774. The relevance of the two calcium sites in the structure of the catalytic subunit (NrfA).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
17455-17465.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Aragão,
C.Frazão,
L.Sieker,
G.M.Sheldrick,
J.LeGall,
and
M.A.Carrondo
(2003).
Structure of dimeric cytochrome c3 from Desulfovibrio gigas at 1.2 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
644-653.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Bergmann,
and
A.B.Hooper
(2003).
Cytochrome P460 of Nitrosomonas europaea. Formation of the heme-lysine cross-link in a heterologous host and mutagenic conversion to a non-cross-linked cytochrome c'.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
1935-1941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Greene,
C.Hubert,
M.Nemati,
G.E.Jenneman,
and
G.Voordouw
(2003).
Nitrite reductase activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria prevents their inhibition by nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria.
|
| |
Environ Microbiol,
5,
607-617.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Allen,
O.Daltrop,
J.M.Stevens,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(2003).
C-type cytochromes: diverse structures and biogenesis systems pose evolutionary problems.
|
| |
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci,
358,
255-266.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Almeida,
S.Macieira,
L.L.Gonçalves,
R.Huber,
C.A.Cunha,
M.J.Romão,
C.Costa,
J.Lampreia,
J.J.Moura,
and
I.Moura
(2003).
The isolation and characterization of cytochrome c nitrite reductase subunits (NrfA and NrfH) from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans ATCC 27774. Re-evaluation of the spectroscopic data and redox properties.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
270,
3904-3915.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Brigé,
D.Leys,
T.E.Meyer,
M.A.Cusanovich,
and
J.J.Van Beeumen
(2002).
The 1.25 A resolution structure of the diheme NapB subunit of soluble nitrate reductase reveals a novel cytochrome c fold with a stacked heme arrangement.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
4827-4836.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Leys,
T.E.Meyer,
A.S.Tsapin,
K.H.Nealson,
M.A.Cusanovich,
and
J.J.Van Beeumen
(2002).
Crystal structures at atomic resolution reveal the novel concept of "electron-harvesting" as a role for the small tetraheme cytochrome c.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
35703-35711.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.C.Angove,
J.A.Cole,
D.J.Richardson,
and
J.N.Butt
(2002).
Protein film voltammetry reveals distinctive fingerprints of nitrite and hydroxylamine reduction by a cytochrome C nitrite reductase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
23374-23381.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Simon
(2002).
Enzymology and bioenergetics of respiratory nitrite ammonification.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
26,
285-309.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Allen,
E.J.Tomlinson,
L.Hong,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(2002).
The Escherichia coli cytochrome c maturation (Ccm) system does not detectably attach heme to single cysteine variants of an apocytochrome c.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
33559-33563.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Daltrop,
J.W.Allen,
A.C.Willis,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(2002).
In vitro formation of a c-type cytochrome.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
7872-7876.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Einsle,
P.Stach,
A.Messerschmidt,
O.Klimmek,
J.Simon,
A.Kröger,
and
P.M.Kroneck
(2002).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the membrane-bound cytochrome c nitrite reductase complex (NrfHA) from Wolinella succinogenes.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
341-342.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Pisa,
T.Stein,
R.Eichler,
R.Gross,
and
J.Simon
(2002).
The nrfI gene is essential for the attachment of the active site haem group of Wolinella succinogenes cytochrome c nitrite reductase.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
43,
763-770.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Poock,
E.R.Leach,
J.W.Moir,
J.A.Cole,
and
D.J.Richardson
(2002).
Respiratory detoxification of nitric oxide by the cytochrome c nitrite reductase of Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
23664-23669.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.A.Bamford,
H.C.Angove,
H.E.Seward,
A.J.Thomson,
J.A.Cole,
J.N.Butt,
A.M.Hemmings,
and
D.J.Richardson
(2002).
Structure and spectroscopy of the periplasmic cytochrome c nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
2921-2931.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Moura,
and
J.J.Moura
(2001).
Structural aspects of denitrifying enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
5,
168-175.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Einsle,
S.Foerster,
K.Mann,
G.Fritz,
A.Messerschmidt,
and
P.M.Kroneck
(2001).
Spectroscopic investigation and determination of reactivity and structure of the tetraheme cytochrome c3 from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans Essex 6.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
3028-3035.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.W.Munro,
P.Taylor,
and
M.D.Walkinshaw
(2000).
Structures of redox enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Biotechnol,
11,
369-376.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Bothe,
G.Jost,
M.Schloter,
B.B.Ward,
and
K.Witzel
(2000).
Molecular analysis of ammonia oxidation and denitrification in natural environments.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
24,
673-690.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Simon,
R.Gross,
O.Einsle,
P.M.Kroneck,
A.Kröger,
and
O.Klimmek
(2000).
A NapC/NirT-type cytochrome c (NrfH) is the mediator between the quinone pool and the cytochrome c nitrite reductase of Wolinella succinogenes.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
35,
686-696.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Barker,
and
S.J.Ferguson
(1999).
Still a puzzle: why is haem covalently attached in c-type cytochromes?
|
| |
Structure,
7,
R281-R290.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

