 |
PDBsum entry 1pmt

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
RX
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
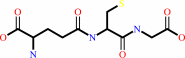 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
6:721-734
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A mixed disulfide bond in bacterial glutathione transferase: functional and evolutionary implications.
|
|
J.Rossjohn,
G.Polekhina,
S.C.Feil,
N.Allocati,
M.Masulli,
C.De Illio,
M.W.Parker.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are a multifunctional group of
enzymes, widely distributed in aerobic organisms, that have a critical role in
the cellular detoxification process. Unlike their mammalian counterparts,
bacterial GSTs often catalyze quite specific reactions, suggesting that their
roles in bacteria might be different. The GST from Proteus mirabilis (PmGST
B1-1) is known to bind certain antibiotics tightly and reduce the antimicrobial
activity of beta-lactam drugs. Hence, bacterial GSTs may play a part in
bacterial resistance towards antibiotics and are the subject of intense
interest. RESULTS: Here we present the structure of a bacterial GST, PmGST B1-1,
which has been determined from two different crystal forms. The enzyme adopts
the canonical GST fold although it shares less than 20% sequence identity with
GSTs from higher organisms. The most surprising aspect of the structure is the
observation that the substrate, glutathione, is covalently bound to Cys 10 of
the enzyme. In addition, the highly structurally conserved N-terminal domain is
found to have an additional beta strand. CONCLUSIONS: The crystal structure of
PmGST B1-1 has highlighted the importance of a cysteine residue in the catalytic
cycle. Sequence analyses suggest that a number of other GSTs share this
property, leading us to propose a new class of GSTs - the beta class. The data
suggest that the in vivo role of the beta class GSTs could be as metabolic or
redox enzymes rather than conjugating enzymes. Compelling evidence is presented
that the theta class of GSTs evolved from an ancestral member of the thioredoxin
superfamily.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Evolution of GSH thiol interactions within the
active sites of different GSTs. The active sites of GSTs from
three classes are shown: (a) bacterial theta class GST (b)
insect theta class GST [13]; and (c) human pi class GST [31].
GSH and residues involved in the interactions are shown in
ball-and-stick form. (The figure was produced using MOLSCRIPT
[56] and is adapted from Figure 5 of [12] © 1997 American
Chemical Society with kind permission of Richard Armstrong.)
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(1998,
6,
721-734)
copyright 1998.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Oakley
(2011).
Glutathione transferases: a structural perspective.
|
| |
Drug Metab Rev,
43,
138-151.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Belchik,
and
L.Xun
(2011).
S-glutathionyl-(chloro)hydroquinone reductases: a new class of glutathione transferases functioning as oxidoreductases.
|
| |
Drug Metab Rev,
43,
307-316.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Allocati,
L.Federici,
M.Masulli,
and
C.Di Ilio
(2009).
Glutathione transferases in bacteria.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
58-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Littler,
S.J.Harrop,
L.J.Brown,
G.J.Pankhurst,
A.V.Mynott,
P.Luciani,
R.A.Mandyam,
M.Mazzanti,
S.Tanda,
M.A.Berryman,
S.N.Breit,
and
P.M.Curmi
(2008).
Comparison of vertebrate and invertebrate CLIC proteins: the crystal structures of Caenorhabditis elegans EXC-4 and Drosophila melanogaster DmCLIC.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
364-378.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Allocati,
L.Federici,
M.Masulli,
B.Favaloro,
and
C.Di Ilio
(2008).
Cysteine 10 is critical for the activity of Ochrobactrum anthropi glutathione transferase and its mutation to alanine causes the preferential binding of glutathione to the H-site.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
16-23.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Garcia,
R.F.Travensolo,
N.C.Rodrigues,
J.R.Muniz,
C.S.Caruso,
E.G.Lemos,
A.P.Araujo,
and
E.Carrilho
(2008).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a glutathione S-transferase from Xylella fastidiosa.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
85-87.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.I.Tocheva,
P.D.Fortin,
L.D.Eltis,
and
M.E.Murphy
(2006).
Structures of ternary complexes of BphK, a bacterial glutathione S-transferase that reductively dechlorinates polychlorinated biphenyl metabolites.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
30933-30940.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Hearne,
and
R.F.Colman
(2006).
Contribution of the mu loop to the structure and function of rat glutathione transferase M1-1.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
1277-1289.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bresell,
R.Weinander,
G.Lundqvist,
H.Raza,
M.Shimoji,
T.H.Sun,
L.Balk,
R.Wiklund,
J.Eriksson,
C.Jansson,
B.Persson,
P.J.Jakobsson,
and
R.Morgenstern
(2005).
Bioinformatic and enzymatic characterization of the MAPEG superfamily.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
1688-1703.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Hansen,
Y.Gu,
M.Li,
M.Andrykovitch,
D.S.Waugh,
D.J.Jin,
and
X.Ji
(2005).
Structural basis for the function of stringent starvation protein a as a transcription factor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
17380-17391.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Schuller,
Q.Liu,
I.A.Kriksunov,
A.M.Campbell,
J.Barrett,
P.M.Brophy,
and
Q.Hao
(2005).
Crystal structure of a new class of glutathione transferase from the model human hookworm nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus.
|
| |
Proteins,
61,
1024-1031.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Hearne,
and
R.F.Colman
(2005).
Delineation of xenobiotic substrate sites in rat glutathione S-transferase M1-1.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
2526-2536.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Ricci,
P.Turella,
F.De Maria,
G.Antonini,
L.Nardocci,
P.G.Board,
M.W.Parker,
M.G.Carbonelli,
G.Federici,
and
A.M.Caccuri
(2004).
Binding and kinetic mechanisms of the Zeta class glutathione transferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
33336-33342.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.M.Hegazy,
B.Mannervik,
and
G.Stenberg
(2004).
Functional role of the lock and key motif at the subunit interface of glutathione transferase p1-1.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
9586-9596.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Pennelli,
P.Sacchetta,
C.Catitti,
F.Amicarelli,
and
C.Di Ilio
(2003).
Effects of glutathione on kinetics and structural properties of amphibian BbGSTP1-1.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
35,
415-421.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.G.Jeppesen,
P.Ortiz,
W.Shepard,
T.G.Kinzy,
J.Nyborg,
and
G.R.Andersen
(2003).
The crystal structure of the glutathione S-transferase-like domain of elongation factor 1Bgamma from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
47190-47198.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Todd,
C.A.Orengo,
and
J.M.Thornton
(2002).
Plasticity of enzyme active sites.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
27,
419-426.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.M.Caccuri,
G.Antonini,
N.Allocati,
C.Di Ilio,
F.De Maria,
F.Innocenti,
M.W.Parker,
M.Masulli,
M.Lo Bello,
P.Turella,
G.Federici,
and
G.Ricci
(2002).
GSTB1-1 from Proteus mirabilis: a snapshot of an enzyme in the evolutionary pathway from a redox enzyme to a conjugating enzyme.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
18777-18784.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Dainelli,
D.Paludi,
B.Dragani,
R.Cocco,
D.R.Principe,
M.Petrucci,
F.Mucilli,
A.Faraone,
and
A.Aceto
(2002).
A novel glutathione transferase from Haemophilus influenzae which has high affinity towards antibiotics.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
34,
916-920.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Dixon,
A.Lapthorn,
and
R.Edwards
(2002).
Plant glutathione transferases.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
3,
REVIEWS3004.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Dixon,
B.G.Davis,
and
R.Edwards
(2002).
Functional divergence in the glutathione transferase superfamily in plants. Identification of two classes with putative functions in redox homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
30859-30869.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Luo,
J.A.Hornby,
L.A.Wallace,
J.Chen,
R.N.Armstrong,
and
H.W.Dirr
(2002).
Impact of domain interchange on conformational stability and equilibrium folding of chimeric class micro glutathione transferases.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
2208-2217.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Oakley,
K.Jirajaroenrat,
T.Harnnoi,
A.J.Ketterman,
and
M.C.Wilce
(2001).
Crystallization of two glutathione S-transferases from an unusual gene family.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
870-872.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Oakley,
T.Harnnoi,
R.Udomsinprasert,
K.Jirajaroenrat,
A.J.Ketterman,
and
M.C.Wilce
(2001).
The crystal structures of glutathione S-transferases isozymes 1-3 and 1-4 from Anopheles dirus species B.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
2176-2185.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Polekhina,
P.G.Board,
A.C.Blackburn,
and
M.W.Parker
(2001).
Crystal structure of maleylacetoacetate isomerase/glutathione transferase zeta reveals the molecular basis for its remarkable catalytic promiscuity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1567-1576.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Bousset,
H.Belrhali,
J.Janin,
R.Melki,
and
S.Morera
(2001).
Structure of the globular region of the prion protein Ure2 from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Structure,
9,
39-46.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.E.Labrou,
L.V.Mello,
and
Y.D.Clonis
(2001).
The conserved Asn49 of maize glutathione S-transferase I modulates substrate binding, catalysis and intersubunit communication.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
3950-3957.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Micaloni,
A.P.Mazzetti,
M.Nuccetelli,
J.Rossjohn,
W.J.McKinstry,
G.Antonini,
A.M.Caccuri,
A.J.Oakley,
G.Federici,
G.Ricci,
M.W.Parker,
and
M.Lo Bello
(2000).
Valine 10 may act as a driver for product release from the active site of human glutathione transferase P1-1.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
15961-15970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Dowd,
and
D.Sheehan
(1999).
Variable expression of glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes in the fungus, Mucor circinelloides.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
170,
13-17.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.U.Flanagan,
J.Rossjohn,
M.W.Parker,
P.G.Board,
and
G.Chelvanayagam
(1999).
Mutagenic analysis of conserved arginine residues in and around the novel sulfate binding pocket of the human Theta class glutathione transferase T2-2.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
2205-2212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.N.Armstrong
(1998).
Mechanistic imperatives for the evolution of glutathione transferases.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
2,
618-623.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

