 |
PDBsum entry 1pm2

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1pm2
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of manganese substituted r2-d84e (d84e mutant of the r2 subunit of e. Coli ribonucleotide reductase)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase 1 beta chain. Chain: a, b. Synonym: ribonucleotide reductase 1, b2 protein, r2 protein. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: rir2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.185
|
R-free:
|
0.215
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
W.C.Voegtli,M.Sommerhalter,J.Baldwin,L.Saleh,J.M.Bollinger Jr., A.C.Rosenzweig
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
W.C.Voegtli
et al.
(2003).
Variable coordination geometries at the diiron(II) active site of ribonucleotide reductase R2.
J Am Chem Soc,
125,
15822-15830.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Jun-03
|
Release date:
|
13-Jan-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P69924
(RIR2_ECOLI) -
Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase 1 subunit beta from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
376 a.a.
339 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.17.4.1
- ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
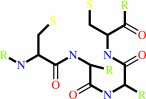
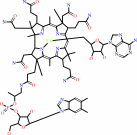
a 2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-disulfide + H2O = a ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphate + [thioredoxin]-dithiol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
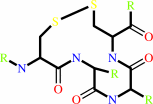 thioredoxin disulfide
thioredoxin disulfide
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
 ribonucleoside diphosphate
ribonucleoside diphosphate
|
+
|
 thioredoxin
thioredoxin
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
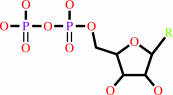
Fe(3+) or adenosylcob(III)alamin or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(3+)
|
or
|
 adenosylcob(III)alamin
adenosylcob(III)alamin
|
or
|
Mn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
125:15822-15830
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Variable coordination geometries at the diiron(II) active site of ribonucleotide reductase R2.
|
|
W.C.Voegtli,
M.Sommerhalter,
L.Saleh,
J.Baldwin,
J.M.Bollinger,
A.C.Rosenzweig.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The R2 subunit of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase contains a dinuclear
iron center that generates a catalytically essential stable tyrosyl radical by
one electron oxidation of a nearby tyrosine residue. After acquisition of Fe(II)
ions by the apo protein, the resulting diiron(II) center reacts with O(2) to
initiate formation of the radical. Knowledge of the structure of the reactant
diiron(II) form of R2 is a prerequisite for a detailed understanding of the O(2)
activation mechanism. Whereas kinetic and spectroscopic studies of the reaction
have generally been conducted at pH 7.6 with reactant produced by the addition
of Fe(II) ions to the apo protein, the available crystal structures of diferrous
R2 have been obtained by chemical or photoreduction of the oxidized diiron(III)
protein at pH 5-6. To address this discrepancy, we have generated the diiron(II)
states of wildtype R2 (R2-wt), R2-D84E, and R2-D84E/W48F by infusion of Fe(II)
ions into crystals of the apo proteins at neutral pH. The structures of
diferrous R2-wt and R2-D48E determined from these crystals reveal diiron(II)
centers with active site geometries that differ significantly from those
observed in either chemically or photoreduced crystals. Structures of R2-wt and
R2-D48E/W48F determined at both neutral and low pH are very similar, suggesting
that the differences are not due solely to pH effects. The structures of these
"ferrous soaked" forms are more consistent with circular dichroism (CD) and
magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectroscopic data and provide alternate
starting points for consideration of possible O(2) activation mechanisms.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Boal,
J.A.Cotruvo,
J.Stubbe,
and
A.C.Rosenzweig
(2010).
Structural basis for activation of class Ib ribonucleotide reductase.
|
| |
Science,
329,
1526-1530.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Bollinger,
Y.Diao,
M.L.Matthews,
G.Xing,
and
C.Krebs
(2009).
myo-Inositol oxygenase: a radical new pathway for O(2) and C-H activation at a nonheme diiron cluster.
|
| |
Dalton Trans,
(),
905-914.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Roca,
E.Torrents,
M.Sahlin,
I.Gibert,
and
B.M.Sjöberg
(2008).
NrdI essentiality for class Ib ribonucleotide reduction in Streptococcus pyogenes.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
4849-4858.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Carrondo,
I.Bento,
P.M.Matias,
and
P.F.Lindley
(2007).
Crystallographic evidence for dioxygen interactions with iron proteins.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
12,
429-442.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Wade,
S.E.Stayrook,
and
W.F.Degrado
(2006).
The structure of a designed diiron(III) protein: implications for cofactor stabilization and catalysis.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
45,
4951-4954.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sommerhalter,
L.Saleh,
J.M.Bollinger,
and
A.C.Rosenzweig
(2005).
Structure of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase R2 in space group P6122.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1649-1654.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.R.Strand,
S.Karlsen,
M.Kolberg,
A.K.Røhr,
C.H.Görbitz,
and
K.K.Andersson
(2004).
Crystal structural studies of changes in the native dinuclear iron center of ribonucleotide reductase protein R2 from mouse.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
46794-46801.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lu,
E.Libby,
L.Saleh,
G.Xing,
J.M.Bollinger,
and
P.Moënne-Loccoz
(2004).
Characterization of NO adducts of the diiron center in protein R2 of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase and site-directed variants; implications for the O2 activation mechanism.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
9,
818-827.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

