 |
PDBsum entry 1ofq

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the tyrosine-regulated 3-deoxy-d-arabino- heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from saccharomyces cerevisiae in complex with manganese(ii)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: phospho-2-keto-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase dahp synthetase, 3- deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase, phospho-2- dehydro- 3-deoxyheptonate aldolase. Engineered: yes. Other_details: metal ion\: manganese(ii)
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Baker's yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Strain: rh1326. Expressed in: saccharomyces cerevisiae. Expression_system_taxid: 4932
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.221
|
R-free:
|
0.245
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
V.Koenig,A.Pfeil,G.Heinrich,G.H.Braus,T.R.Schneider
|
Key ref:

|
 |
V.König
et al.
(2004).
Substrate and metal complexes of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae provide new insights into the catalytic mechanism.
J Mol Biol,
337,
675-690.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Apr-03
|
Release date:
|
15-Apr-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P32449
(AROG_YEAST) -
Phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase, tyrosine-inhibited from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
370 a.a.
343 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.54
- 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Shikimate and Chorismate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-erythrose 4-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
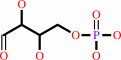 D-erythrose 4-phosphate
D-erythrose 4-phosphate
|
+
|
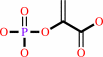 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
337:675-690
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate and metal complexes of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae provide new insights into the catalytic mechanism.
|
|
V.König,
A.Pfeil,
G.H.Braus,
T.R.Schneider.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthases are metal-dependent
enzymes that catalyse the first committed step in the biosynthesis of aromatic
amino acids in microorganisms and plants, the condensation of
2-phophoenolpyruvate (PEP) and d-erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P) to DAHP. The DAHP
synthases are possible targets for fungicides and represent a model system for
feedback regulation in metabolic pathways. To gain further insight into the role
of the metal ion and the catalytic mechanism in general, the crystal structures
of several complexes between the tyrosine-regulated form of DAHP synthase from
Saccharomyces cerevisiae and different metal ions and ligands have been
determined. The crystal structures provide evidence that the simultaneous
presence of a metal ion and PEP result in an ordering of the protein into a
conformation that is prepared for binding the second substrate E4P. The site and
binding mode of E4P was derived from the 1.5A resolution crystal structure of
DAHP synthase in complex with PEP, Co2+, and the E4P analogue glyceraldehyde
3-phosphate. Our data suggest that the oxygen atom of the reactive carbonyl
group of E4P replaces a water molecule coordinated to the metal ion, strongly
favouring a reaction mechanism where the initial step is a nucleophilic attack
of the double bond of PEP on the metal-activated carbonyl group of E4P.
Mutagenesis experiments substituting specific amino acids coordinating PEP, the
divalent metal ion or the second substrate E4P, result in stable but inactive
Aro4p-derivatives and show the importance of these residues for the catalytic
mechanism.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. (a) Topology plot of DAHPS. The b-strands and
a-helices belonging to the canonical ba-barrel are shown in
light blue and dark blue, respectively; non-canonical modules
are shown in cyan. Regions of the structure that were found to
be flexible or disordered in any of the crystal forms are marked
by a grey background. The location of residues interacting with
PEP, G3P, and the metal is indicated using different flags (red
for PEP, yellow for G3P, grey for metal). (b) Schematic view of
the crystal structure of DAHPS in complex with PEP (red), G3P
(yellow), and Co2+ (grey) with phosphorus atoms shown in
magenta. (c) The same as (b) but the view is towards the
C-terminal face of the barrel.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Figure 8. Stereoview of the active site in the
DAHPS·Co2+·PEP·G3P-complex showing the
water molecules on the re-side of PEP in green. In this view,
the si-side of PEP is on top of PEP, the re-side on the bottom.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2004,
337,
675-690)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Webby,
J.S.Lott,
H.M.Baker,
E.N.Baker,
and
E.J.Parker
(2005).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
403-406.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gunawan,
D.Simard,
M.Gilbert,
A.L.Lovering,
W.W.Wakarchuk,
M.E.Tanner,
and
N.C.Strynadka
(2005).
Structural and mechanistic analysis of sialic acid synthase NeuB from Neisseria meningitidis in complex with Mn2+, phosphoenolpyruvate, and N-acetylmannosaminitol.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
3555-3563.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Ahn,
A.L.Pietersma,
L.R.Schofield,
and
E.J.Parker
(2005).
Mechanistic divergence of two closely related aldol-like enzyme-catalysed reactions.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
3,
4046-4049.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

