
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain B:
E.C.3.1.1.3
- triacylglycerol lipase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a triacylglycerol + H2O = a diacylglycerol + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
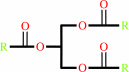 triacylglycerol
triacylglycerol
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
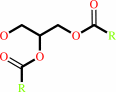 diacylglycerol
diacylglycerol
|
+
|
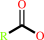 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
34:2751-2762
(1995)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The 2.46 A resolution structure of the pancreatic lipase-colipase complex inhibited by a C11 alkyl phosphonate.
|
|
M.P.Egloff,
F.Marguet,
G.Buono,
R.Verger,
C.Cambillau,
H.van Tilbeurgh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Pancreatic lipase belongs to the serine esterase family and can therefore be
inhibited by classical serine reagents such as diisopropyl fluoride or E600. In
an attempt to further characterize the active site and catalytic mechanism, we
synthesized a C11 alkyl phosphonate compound. This compound is an effective
inhibitor of pancreatic lipase. The crystal structure of the pancreatic
lipase-colipase complex inhibited by this compound was determined at a
resolution of 2.46 A and refined to a final R-factor of 18.3%. As was observed
in the case of the structure of the ternary pancreatic
lipase-colipase-phospholipid complex, the binding of the ligand induces
rearrangements of two surface loops in comparison with the closed structure of
the enzyme (van Tilbeurgh et al., 1993b). The inhibitor, which could be clearly
observed in the active site, was covalently bound to the active site serine
Ser152. A racemic mixture of the inhibitor was used in the crystallization, and
there exists evidence that both enantiomers are bound at the active site. The
C11 alkyl chain of the first enantiomer fits into a hydrophobic groove and is
though to thus mimic the interaction between the leaving fatty acid of a
triglyceride substrate and the protein. The alkyl chain of the second enantiomer
also has an elongated conformation and interacts with hydrophobic patches on the
surface of the open amphipathic lid. This may indicate the location of a second
alkyl chain of a triglyceride substrate. Some of the detergent molecules, needed
for the crystallization, were also observed in the crystal. Some of them were
located at the entrance of the active site, bound to the hydrophobic part of the
lid. On the basis of this crystallographic study, a hypothesis about the binding
mode of real substrates and the organization of the active site is proposed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
V.Belle,
A.Fournel,
B.Guigliarelli,
and
F.Carrière
(2011).
Probing structural transitions in both structured and disordered proteins using site-directed spin-labeling EPR spectroscopy.
|
| |
J Pept Sci,
17,
315-328.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Y.Colin,
P.Deprez-Beauclair,
N.Silva,
L.Infantes,
and
B.Kerfelec
(2010).
Modification of pancreatic lipase properties by directed molecular evolution.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
365-373.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Labar,
C.Bauvois,
F.Borel,
J.L.Ferrer,
J.Wouters,
and
D.M.Lambert
(2010).
Crystal structure of the human monoacylglycerol lipase, a key actor in endocannabinoid signaling.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
218-227.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Kozarich
(2010).
S28 peptidases: lessons from a seemingly 'dysfunctional' family of two.
|
| |
BMC Biol,
8,
87.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Soisson,
S.B.Patel,
P.D.Abeywickrema,
N.J.Byrne,
R.E.Diehl,
D.L.Hall,
R.E.Ford,
J.C.Reid,
K.W.Rickert,
J.M.Shipman,
S.Sharma,
and
K.J.Lumb
(2010).
Structural definition and substrate specificity of the S28 protease family: the crystal structure of human prolylcarboxypeptidase.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
10,
16.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Kerfelec,
M.Allouche,
D.Colin,
M.H.Van Eyck,
R.Brasseur,
and
A.Thomas
(2008).
Computational study of colipase interaction with lipid droplets and bile salt micelles.
|
| |
Proteins,
73,
828-838.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Diaz,
J.Cordova,
J.Baratti,
F.Carriere,
and
A.Abousalham
(2007).
Effect of nonionic surfactants on Rhizopus homothallicus lipase activity: a comparative kinetic study.
|
| |
Mol Biotechnol,
35,
205-214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Quevillon-Cheruel,
N.Leulliot,
M.Graille,
N.Hervouet,
F.Coste,
H.Bénédetti,
C.Zelwer,
J.Janin,
and
H.Van Tilbeurgh
(2005).
Crystal structure of yeast YHR049W/FSH1, a member of the serine hydrolase family.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1350-1356.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Shmulevitz,
R.F.Epand,
R.M.Epand,
and
R.Duncan
(2004).
Structural and functional properties of an unusual internal fusion peptide in a nonenveloped virus membrane fusion protein.
|
| |
J Virol,
78,
2808-2818.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Birner-Grünberger,
H.Scholze,
K.Faber,
and
A.Hermetter
(2004).
Identification of various lipolytic enzymes in crude porcine pancreatic lipase preparations using covalent fluorescent inhibitors.
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
85,
147-154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kokotos,
S.Kotsovolou,
and
R.Verger
(2003).
Novel trifluoromethyl ketones as potent gastric lipase inhibitors.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
4,
90-95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Miled,
A.Roussel,
C.Bussetta,
L.Berti-Dupuis,
M.Rivière,
G.Buono,
R.Verger,
C.Cambillau,
and
S.Canaan
(2003).
Inhibition of dog and human gastric lipases by enantiomeric phosphonate inhibitors: a structure-activity study.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
11587-11593.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.A.Larsen,
J.M.Turner,
J.Stevens,
S.J.Rosser,
A.Basran,
R.A.Lerner,
N.C.Bruce,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2002).
Crystal structure of a bacterial cocaine esterase.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
9,
17-21.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Chiou,
R.Verger,
and
G.Kokotos
(2001).
Synthetic routes and lipase-inhibiting activity of long-chain alpha-keto amides.
|
| |
Lipids,
36,
535-542.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Peters,
and
R.P.Bywater
(2001).
Influence of a lipid interface on protein dynamics in a fungal lipase.
|
| |
Biophys J,
81,
3052-3065.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.González-Navarro,
M.C.Bañó,
and
C.Abad
(2001).
The closed/open model for lipase activation. Addressing intermediate active forms of fungal enzymes by trapping of conformers in water-restricted environments.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
3174-3183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.P.Sugar,
N.K.Mizuno,
M.M.Momsen,
and
H.L.Brockman
(2001).
Lipid lateral organization in fluid interfaces controls the rate of colipase association.
|
| |
Biophys J,
81,
3387-3397.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Svendsen
(2000).
Lipase protein engineering.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1543,
223-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.P.Klaholz,
and
D.Moras
(2000).
Structural role of a detergent molecule in retinoic acid nuclear receptor crystals.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
933-935.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Kokotos,
R.Verger,
and
A.Chiou
(2000).
Synthesis of 2-Oxo amide triacylglycerol analogues and study of their inhibition effect on pancreatic and gastric lipases.
|
| |
Chemistry,
6,
4211-4217.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Roussel,
S.Canaan,
M.P.Egloff,
M.Rivière,
L.Dupuis,
R.Verger,
and
C.Cambillau
(1999).
Crystal structure of human gastric lipase and model of lysosomal acid lipase, two lipolytic enzymes of medical interest.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
16995-17002.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Zandonella,
P.Stadler,
L.Haalck,
F.Spener,
F.Paltauf,
and
A.Hermetter
(1999).
Interactions of fluorescent triacylglycerol analogs covalently bound to the active site of a lipase from Rhizopus oryzae.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
262,
63-69.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.van Tilbeurgh,
S.Bezzine,
C.Cambillau,
R.Verger,
and
F.Carrière
(1999).
Colipase: structure and interaction with pancreatic lipase.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
173-184.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Cavalier,
S.Ransac,
R.Verger,
and
G.Buono
(1999).
Inhibition of human gastric and pancreatic lipases by chiral alkylphosphonates. A kinetic study with 1,2-didecanoyl-sn-glycerol monolayer.
|
| |
Chem Phys Lipids,
100,
3.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Simons,
M.D.van Kampen,
I.Ubarretxena-Belandia,
R.C.Cox,
C.M.Alves dos Santos,
M.R.Egmond,
and
H.M.Verheij
(1999).
Identification of a calcium binding site in Staphylococcus hyicus lipase: generation of calcium-independent variants.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
2.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Simons,
R.C.Cox,
M.R.Egmond,
and
H.M.Verheij
(1999).
Rational design of alpha-keto triglyceride analogues as inhibitors for Staphylococcus hyicus lipase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
6346-6351.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.E.Jaeger,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
M.T.Reetz
(1999).
Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
53,
315-351.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nardini,
I.S.Ridder,
H.J.Rozeboom,
K.H.Kalk,
R.Rink,
D.B.Janssen,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1999).
The x-ray structure of epoxide hydrolase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1. An enzyme to detoxify harmful epoxides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
14579-14586.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.K.Yue,
I.J.Kass,
N.S.Sampson,
and
A.Vrielink
(1999).
Crystal structure determination of cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces and structural characterization of key active site mutants.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4277-4286.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bezzine,
F.Ferrato,
M.G.Ivanova,
V.Lopez,
R.Verger,
and
F.Carrière
(1999).
Human pancreatic lipase: colipase dependence and interfacial binding of lid domain mutants.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5499-5510.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Canaan,
A.Roussel,
R.Verger,
and
C.Cambillau
(1999).
Gastric lipase: crystal structure and activity.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
197-204.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
and
C.Cambillau
(1999).
Structure-activity of cutinase, a small lipolytic enzyme.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
185-196.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Peelman,
N.Vinaimont,
A.Verhee,
B.Vanloo,
J.L.Verschelde,
C.Labeur,
S.Seguret-Mace,
N.Duverger,
G.Hutchinson,
J.Vandekerckhove,
J.Tavernier,
and
M.Rosseneu
(1998).
A proposed architecture for lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT): identification of the catalytic triad and molecular modeling.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
7,
587-599.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Gonzalez-Navarro,
and
L.Braco
(1998).
Lipase-enhanced activity in flavour ester reactions by trapping enzyme conformers in the presence of interfaces
|
| |
Biotechnol Bioeng,
59,
122-127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Pleiss,
M.Fischer,
and
R.D.Schmid
(1998).
Anatomy of lipase binding sites: the scissile fatty acid binding site.
|
| |
Chem Phys Lipids,
93,
67-80.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.van Kampen,
N.Dekker,
M.R.Egmond,
and
H.M.Verheij
(1998).
Substrate specificity of Staphylococcus hyicus lipase and Staphylococcus aureus lipase as studied by in vivo chimeragenesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
3459-3466.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.S.Sampson,
I.J.Kass,
and
K.B.Ghoshroy
(1998).
Assessment of the role of an omega loop of cholesterol oxidase: a truncated loop mutant has altered substrate specificity.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
5770-5778.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bezzine,
A.Roussel,
J.de Caro,
L.Gastinel,
A.de Caro,
F.Carrière,
S.Leydier,
R.Verger,
and
C.Cambillau
(1998).
An inactive pancreatic lipase-related protein is activated into a triglyceride-lipase by mutagenesis based on the 3-D structure.
|
| |
Chem Phys Lipids,
93,
103-114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bezzine,
F.Carrière,
J.De Caro,
R.Verger,
and
A.De Caro
(1998).
Human pancreatic lipase: an exposed hydrophobic loop from the C-terminal domain may contribute to interfacial binding.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
11846-11855.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Carrière,
K.Thirstrup,
S.Hjorth,
F.Ferrato,
P.F.Nielsen,
C.Withers-Martinez,
C.Cambillau,
E.Boel,
L.Thim,
and
R.Verger
(1997).
Pancreatic lipase structure-function relationships by domain exchange.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
239-248.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Labourdenne,
O.Brass,
M.Ivanova,
A.Cagna,
and
R.Verger
(1997).
Effects of colipase and bile salts on the catalytic activity of human pancreatic lipase. A study using the oil drop tensiometer.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
3423-3429.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Longhi,
M.Mannesse,
H.M.Verheij,
G.H.De Haas,
M.Egmond,
E.Knoops-Mouthuy,
and
C.Cambillau
(1997).
Crystal structure of cutinase covalently inhibited by a triglyceride analogue.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
6,
275-286.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Nicolas,
M.Egmond,
C.T.Verrips,
J.de Vlieg,
S.Longhi,
C.Cambillau,
and
C.Martinez
(1996).
Contribution of cutinase serine 42 side chain to the stabilization of the oxyanion transition state.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
398-410.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Mingarro,
H.González-Navarro,
and
L.Braco
(1996).
Trapping of different lipase conformers in water-restricted environments.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
9935-9944.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Hermoso,
D.Pignol,
B.Kerfelec,
I.Crenon,
C.Chapus,
and
J.C.Fontecilla-Camps
(1996).
Lipase activation by nonionic detergents. The crystal structure of the porcine lipase-colipase-tetraethylene glycol monooctyl ether complex.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
18007-18016.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Verger,
M.Aoubalå,
F.Carrière,
S.Ransac,
L.Dupuis,
J.De Caro,
F.Ferrato,
I.Douchet,
R.Laugier,
and
A.De Caro
(1996).
Regulation of lumen fat digestion: enzymic aspects.
|
| |
Proc Nutr Soc,
55,
5.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

