 |
PDBsum entry 1l2u

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.23
- orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
orotidine 5'-phosphate + H+ = UMP + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 orotidine 5'-phosphate
orotidine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
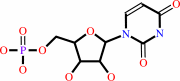 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
318:1019-1029
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate binding induces domain movements in orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
P.Harris,
J.C.Poulsen,
K.F.Jensen,
S.Larsen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (ODCase) catalyses the decarboxylation
of orotidine 5'-monophosphate to uridine 5'-monophosphate (UMP). We have earlier
determined the structure of ODCase from Escherichia coli complexed with the
inhibitor 1-(5'-phospho-beta-d-ribofuranosyl)barbituric acid (BMP); here we
present the 2.5 A structure of the uncomplexed apo enzyme, determined from
twinned crystals. A structural analysis and comparison of the two structures of
the E. coli enzyme show that binding of the inhibitor is accompanied by
significant domain movements of approximately 12 degrees around a hinge that
crosses the active site. Hence, the ODCase dimer, which contains two active
sites, may be divided in three domains: a central domain that is fixed, and two
lids which independently move 12 degrees upon binding. Corresponding analyses,
presented herein, of the two Saccharomyces cerevisiae ODCase structures (with
and without BMP) and the Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum ODCase structures
(with and without 6-aza UMP) show very similar, but somewhat smaller domain
movements. The domain movements seem to be initiated by the phosphoryl binding
to the enzyme and can explain why the binding of the phosphoryl group is
essential for the catalytic function.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Molscript figure of the domain movements in
ODCase from E. coli caused by binding of the inhibitor BMP
(shown in yellow). The complexed enzyme is shown in dark red,
and domain I of the apo enzyme is shown in blue. Domain IIA of
the apo enzyme is shown in green and domain IIB of the apo
enzyme is shown in cyan. The rotation angles around the hinges
(shown as arrows) are 12°.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. The active site. The complexed structure is shown
in red with the loop residues in bright red and the inhibitor
BMP is shown in yellow. The apo structure is shown in blue.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
318,
1019-1029)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Toth,
T.L.Amyes,
B.M.Wood,
K.K.Chan,
J.A.Gerlt,
and
J.P.Richard
(2009).
An examination of the relationship between active site loop size and thermodynamic activation parameters for orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from mesophilic and thermophilic organisms.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8006-8013.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Toth,
T.L.Amyes,
B.M.Wood,
K.Chan,
J.A.Gerlt,
and
J.P.Richard
(2007).
Product deuterium isotope effect for orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: evidence for the existence of a short-lived carbanion intermediate.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
12946-12947.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Hillig,
and
L.Renault
(2006).
Detecting and overcoming hemihedral twinning during the MIR structure determination of Rna1p.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
750-765.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Houborg,
P.Harris,
J.C.Poulsen,
P.Schneider,
A.Svendsen,
and
S.Larsen
(2003).
The structure of a mutant enzyme of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase provides an understanding of its increased thermostability.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
997.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Houborg,
P.Harris,
J.Petersen,
P.Rowland,
J.C.Poulsen,
P.Schneider,
J.Vind,
and
S.Larsen
(2003).
Impact of the physical and chemical environment on the molecular structure of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
989-996.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

