
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.1.1.1.34
- hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Mevalonate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(R)-mevalonate + 2 NADP+ + CoA = (3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + 2 NADPH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
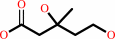 (R)-mevalonate
(R)-mevalonate
|
+
|
2
×
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 56.25% similarity
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
=
|
(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA
|
+
|
 2
×
NADPH
2
×
NADPH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Science
292:1160-1164
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase.
|
|
E.S.Istvan,
J.Deisenhofer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
HMG-CoA (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A) reductase (HMGR) catalyzes the
committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis. Statins are HMGR inhibitors with
inhibition constant values in the nanomolar range that effectively lower serum
cholesterol levels and are widely prescribed in the treatment of
hypercholesterolemia. We have determined structures of the catalytic portion of
human HMGR complexed with six different statins. The statins occupy a portion of
the binding site of HMG-CoA, thus blocking access of this substrate to the
active site. Near the carboxyl terminus of HMGR, several catalytically relevant
residues are disordered in the enzyme-statin complexes. If these residues were
not flexible, they would sterically hinder statin binding.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Statins exploit the conformational flexibility of HMGR
to create a hydrophobic binding pocket near the active site. (A)
Active site of human HMGR in complex with HMG, CoA, and NADP.
The active site is located at a monomer-monomer interface. One
monomer is colored yellow, the other monomer is in blue.
Selected side chains of residues that contact the substrates or
the statin are shown in a ball-and-stick representation (20).
Secondary structure elements are marked by black labels. HMG and
CoA are colored in magenta; NADP is colored in green. To
illustrate the molecular volume occupied by the substrates,
transparent spheres with a radius of 1.6 Å are laid over
the ball-and-stick representation of the substrates or the
statin. (B) Binding of rosuvastatin to HMGR. Rosuvastatin is
colored in purple; other colors and labels are as in (A). This
figure and Figs. 3 and 4 were prepared with Bobscript (22), GLR
(23), and POV-Ray (24).
|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Mode of binding of compactin (A), simvastatin (B),
fluvastatin (C), cerivastatin (D), atorvastatin (E), and
rosuvastatin (F) to human HMGR. Interactions between the HMG
moieties of the statins and the protein are mostly ionic or
polar. They are similar for all inhibitors and are indicated by
the dotted lines. Numbers next to the lines indicate distances
in Å (13). The rigid hydrophobic groups of the statins are
situated in a shallow groove between helices L  1 and L 1 and L
 10.
Additional interactions between Arg590 and the fluorophenyl
group are present in the type 2 statins (C, D, E, F).
Atorvastatin and rosuvastatin form a hydrogen bond between
Ser565 and a carbonyl oxygen atom (atorvastatin) (E) or a
sulfone oxygen atom (rosuvastatin) (F). 10.
Additional interactions between Arg590 and the fluorophenyl
group are present in the type 2 statins (C, D, E, F).
Atorvastatin and rosuvastatin form a hydrogen bond between
Ser565 and a carbonyl oxygen atom (atorvastatin) (E) or a
sulfone oxygen atom (rosuvastatin) (F).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the AAAs:
Science
(2001,
292,
1160-1164)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Chidley,
H.Haruki,
M.G.Pedersen,
E.Muller,
and
K.Johnsson
(2011).
A yeast-based screen reveals that sulfasalazine inhibits tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
7,
375-383.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Vaklavas,
Y.S.Chatzizisis,
and
A.M.Tsimberidou
(2011).
Common cardiovascular medications in cancer therapeutics.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
130,
177-190.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Puttananjaiah,
M.A.Dhale,
V.Gaonkar,
and
S.Keni
(2011).
Statins: 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) Reductase Inhibitors Demonstrate Anti-Atherosclerotic Character due to Their Antioxidant Capacity.
|
| |
Appl Biochem Biotechnol,
163,
215-222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Saito,
K.Miyamoto,
and
M.Ochiai
(2011).
Hypervalent phenyl-λ(3)-iodane-mediated para-selective aromatic fluorination of 3-phenylpropyl ethers.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
47,
3410-3412.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Konrad,
J.S.Troutt,
and
G.Cao
(2011).
Effects of currently prescribed LDL-C-lowering drugs on PCSK9 and implications for the next generation of LDL-C-lowering agents.
|
| |
Lipids Health Dis,
10,
38.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Miller,
F.Yang,
C.E.Wise,
F.Meng,
S.Priester,
M.K.Munshi,
M.Guerrier,
D.E.Dostal,
and
S.S.Glaser
(2011).
Simvastatin stimulates apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma by inhibition of Rac1 activity.
|
| |
Dig Liver Dis,
43,
395-403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Ali,
I.Nouvel,
K.F.Leung,
A.N.Hume,
and
M.C.Seabra
(2010).
A novel statin-mediated "prenylation block-and-release" assay provides insight into the membrane targeting mechanisms of small GTPases.
|
| |
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,
397,
34-41.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.H.Park,
J.Y.Kim,
J.I.Jung,
and
J.Y.Han
(2010).
Lovastatin overcomes gefitinib resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells with K-Ras mutations.
|
| |
Invest New Drugs,
28,
791-799.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Klawitter,
T.Shokati,
V.Moll,
U.Christians,
and
J.Klawitter
(2010).
Effects of lovastatin on breast cancer cells: a proteo-metabonomic study.
|
| |
Breast Cancer Res,
12,
R16.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Fogerty,
D.Efron,
A.Morandi,
J.S.Guy,
N.N.Abumrad,
and
A.Barbul
(2010).
Effect of preinjury statin use on mortality and septic shock in elderly burn patients.
|
| |
J Trauma,
69,
99.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.S.Tiseni,
and
R.Peters
(2010).
Catalytic asymmetric formation of delta-lactones from unsaturated acyl halides.
|
| |
Chemistry,
16,
2503-2517.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zhou,
and
J.K.Liao
(2010).
Pleiotropic effects of statins. - Basic research and clinical perspectives -.
|
| |
Circ J,
74,
818-826.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Li,
J.A.Friesen,
K.C.Holford,
and
D.W.Borst
(2010).
Methyl farnesoate synthesis in the lobster mandibular organ: the roles of HMG-CoA reductase and farnesoic acid O-methyltransferase.
|
| |
Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol,
155,
49-55.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Phillips,
and
S.Schaefer
(2010).
LDL = 5: Virtues and dangers of multidrug therapy of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
|
| |
Prev Cardiol,
13,
69-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Z.Ran,
X.Ran,
Z.W.Zong,
D.Q.Liu,
G.M.Xiang,
Y.P.Su,
and
H.E.Zheng
(2010).
Protective effect of atorvastatin on radiation-induced vascular endothelial cell injury in vitro.
|
| |
J Radiat Res (Tokyo),
51,
527-533.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.S.Chatzizisis,
K.C.Koskinas,
G.Misirli,
C.Vaklavas,
A.Hatzitolios,
and
G.D.Giannoglou
(2010).
Risk factors and drug interactions predisposing to statin-induced myopathy: implications for risk assessment, prevention and treatment.
|
| |
Drug Saf,
33,
171-187.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Süle,
L.Szente,
and
F.Csempesz
(2009).
Enhancement of drug solubility in supramolecular and colloidal systems.
|
| |
J Pharm Sci,
98,
484-494.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Sassano,
M.Lo Iacono,
G.Antico,
A.Jordan,
S.Uddin,
R.A.Calogero,
and
L.C.Platanias
(2009).
Regulation of leukemic cell differentiation and retinoid-induced gene expression by statins.
|
| |
Mol Cancer Ther,
8,
615-625.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Lowe,
J.B.Maller,
I.Pe'er,
B.M.Neale,
J.Salit,
E.E.Kenny,
J.L.Shea,
R.Burkhardt,
J.G.Smith,
W.Ji,
M.Noel,
J.N.Foo,
M.L.Blundell,
V.Skilling,
L.Garcia,
M.L.Sullivan,
H.E.Lee,
A.Labek,
H.Ferdowsian,
S.B.Auerbach,
R.P.Lifton,
C.Newton-Cheh,
J.L.Breslow,
M.Stoffel,
M.J.Daly,
D.M.Altshuler,
and
J.M.Friedman
(2009).
Genome-wide association studies in an isolated founder population from the Pacific Island of Kosrae.
|
| |
PLoS Genet,
5,
e1000365.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Perchellet,
E.M.Perchellet,
K.R.Crow,
K.R.Buszek,
N.Brown,
S.Ellappan,
G.Gao,
D.Luo,
M.Minatoya,
and
G.H.Lushington
(2009).
Novel synthetic inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase activity that inhibit tumor cell proliferation and are structurally unrelated to existing statins.
|
| |
Int J Mol Med,
24,
633-643.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Medina,
and
R.M.Krauss
(2009).
The role of HMGCR alternative splicing in statin efficacy.
|
| |
Trends Cardiovasc Med,
19,
173-177.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.O.Nassar,
C.A.Nassar,
M.R.Guimarães,
S.G.Aquino,
D.C.Andia,
M.N.Muscara,
D.M.Spolidorio,
C.Rossa,
and
L.C.Spolidorio
(2009).
Simvastatin therapy in cyclosporine A-induced alveolar bone loss in rats.
|
| |
J Periodontal Res,
44,
479-488.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zhou,
and
J.K.Liao
(2009).
Statins and cardiovascular diseases: from cholesterol lowering to pleiotropy.
|
| |
Curr Pharm Des,
15,
467-478.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Zhou,
and
J.K.Liao
(2009).
Rho kinase: an important mediator of atherosclerosis and vascular disease.
|
| |
Curr Pharm Des,
15,
3108-3115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Barrios,
and
C.Escobar
(2009).
Rosuvastatin along the cardiovascular continuum: from JUPITER to AURORA.
|
| |
Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther,
7,
1317-1327.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Gao,
X.Xie,
I.Pashkov,
M.R.Sawaya,
J.Laidman,
W.Zhang,
R.Cacho,
T.O.Yeates,
and
Y.Tang
(2009).
Directed evolution and structural characterization of a simvastatin synthase.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
16,
1064-1074.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Cleves,
and
A.N.Jain
(2008).
Effects of inductive bias on computational evaluations of ligand-based modeling and on drug discovery.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
22,
147-159.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Zhuge,
H.Y.Fang,
H.Yu,
Z.M.Rao,
W.Shen,
J.Song,
and
J.Zhuge
(2008).
Bioconversion of lovastatin to a novel statin by Amycolatopsis sp.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
79,
209-216.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Bate,
M.Tayebi,
L.Diomede,
M.Salmona,
and
A.Williams
(2008).
Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids increase prion formation in neuronal cells.
|
| |
BMC Biol,
6,
39.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.P.Chen,
L.Yao,
X.Lu,
L.Li,
and
S.J.Hu
(2008).
Tissue-specific effects of atorvastatin on 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarylcoenzyme A reductase expression and activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
29,
1181-1186.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Soran,
and
P.Durrington
(2008).
Rosuvastatin: efficacy, safety and clinical effectiveness.
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
9,
2145-2160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Crouse
(2008).
An evaluation of rosuvastatin: pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and tolerability.
|
| |
Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol,
4,
287-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.McDonald,
and
A.G.Jardine
(2008).
The use of fluvastatin in cardiovascular risk management.
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
9,
1407-1414.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.R.Solomon,
and
M.R.Freeman
(2008).
Do the cholesterol-lowering properties of statins affect cancer risk?
|
| |
Trends Endocrinol Metab,
19,
113-121.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Meloni,
M.R.Manca,
I.Loddo,
G.Cioglia,
P.Cocco,
A.Schwartz,
S.Muntoni,
and
S.Muntoni
(2008).
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency protects against coronary heart disease.
|
| |
J Inherit Metab Dis,
31,
412-417.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Medina,
F.Gao,
W.Ruan,
J.I.Rotter,
and
R.M.Krauss
(2008).
Alternative splicing of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase is associated with plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol response to simvastatin.
|
| |
Circulation,
118,
355-362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.K.Kapur,
and
K.Musunuru
(2008).
Clinical efficacy and safety of statins in managing cardiovascular risk.
|
| |
Vasc Health Risk Manag,
4,
341-353.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Adam,
and
U.Laufs
(2008).
Antioxidative effects of statins.
|
| |
Arch Toxicol,
82,
885-892.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Bhindi,
O.Ormerod,
J.Newton,
A.P.Banning,
and
L.Testa
(2008).
Interaction between statins and clopidogrel: is there anything clinically relevant?
|
| |
QJM,
101,
915-925.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Yandell,
W.C.Harvey,
N.J.Fernandes,
P.W.Barr,
and
M.Feldman
(2008).
Radioiodine studies, low serum thyrotropin, and the influence of statin drugs.
|
| |
Thyroid,
18,
1039-1042.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.V.Pak,
M.Koo,
M.J.Kim,
H.J.Yang,
L.Yun,
and
D.Y.Kwon
(2008).
Modeling an active conformation for linear peptides and design of a competitive inhibitor for HMG-CoA reductase.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
21,
224-232.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.B.Reiss,
and
E.Wirkowski
(2007).
Role of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in neurological disorders : progress to date.
|
| |
Drugs,
67,
2111-2120.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Cheng,
R.G.Coleman,
K.T.Smyth,
Q.Cao,
P.Soulard,
D.R.Caffrey,
A.C.Salzberg,
and
E.S.Huang
(2007).
Structure-based maximal affinity model predicts small-molecule druggability.
|
| |
Nat Biotechnol,
25,
71-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Hughes,
M.J.Rogers,
A.I.Idris,
and
J.C.Crockett
(2007).
A comparison between the effects of hydrophobic and hydrophilic statins on osteoclast function in vitro and ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo.
|
| |
Calcif Tissue Int,
81,
403-413.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Roelofs,
C.M.Edwards,
R.G.Russell,
F.H.Ebetino,
M.J.Rogers,
and
P.A.Hulley
(2007).
Apomine enhances the antitumor effects of lovastatin on myeloma cells by down-regulating 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase.
|
| |
J Pharmacol Exp Ther,
322,
228-235.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Goldfarb-Rumyantzev,
A.N.Habib,
B.C.Baird,
L.L.Barenbaum,
and
A.K.Cheung
(2007).
The association of lipid-modifying medications with mortality in patients on long-term peritoneal dialysis.
|
| |
Am J Kidney Dis,
50,
791-802.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Shachaf,
O.D.Perez,
S.Youssef,
A.C.Fan,
S.Elchuri,
M.J.Goldstein,
A.E.Shirer,
O.Sharpe,
J.Chen,
D.J.Mitchell,
M.Chang,
G.P.Nolan,
L.Steinman,
and
D.W.Felsher
(2007).
Inhibition of HMGcoA reductase by atorvastatin prevents and reverses MYC-induced lymphomagenesis.
|
| |
Blood,
110,
2674-2684.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.P.Martin,
R.L.Talbert,
D.S.Burgess,
and
J.I.Peters
(2007).
Effectiveness of statins in reducing the rate of severe sepsis: a retrospective evaluation.
|
| |
Pharmacotherapy,
27,
20-26.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Zhao
(2007).
Scaffold selection and scaffold hopping in lead generation: a medicinal chemistry perspective.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
12,
149-155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Jeon,
M.V.Thomas,
and
D.A.Puleo
(2007).
Bioerodible devices for intermittent release of simvastatin acid.
|
| |
Int J Pharm,
340,
6.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Dhale,
S.Divakar,
S.Umesh-Kumar,
and
G.Vijayalakshmi
(2007).
Characterization of dehydromonacolin-MV2 from Monascus purpureus mutant.
|
| |
J Appl Microbiol,
103,
2168-2173.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Kim,
L.F.Peng,
W.Lin,
W.H.Choe,
N.Sakamoto,
N.Kato,
M.Ikeda,
S.L.Schreiber,
and
R.T.Chung
(2007).
A cell-based, high-throughput screen for small molecule regulators of hepatitis C virus replication.
|
| |
Gastroenterology,
132,
311-320.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hayashi,
K.Yokote,
Y.Saito,
and
A.Iguchi
(2007).
Pitavastatin: efficacy and safety in intensive lipid lowering.
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
8,
2315-2327.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.B.Wali,
and
P.W.Sylvester
(2007).
Synergistic antiproliferative effects of gamma-tocotrienol and statin treatment on mammary tumor cells.
|
| |
Lipids,
42,
1113-1123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.G.Xu,
S.H.Zhou,
Y.G.Li,
C.H.Zheng,
X.P.Li,
Q.M.Liu,
D.M.Xu,
and
S.Chen
(2007).
The mechanism underlying vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis induced by atorvastatin may be mainly associated with down-regulation of survivin expression.
|
| |
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther,
21,
145-153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Mix,
S.M.Ibrahim,
J.Pahnke,
A.Glass,
I.Mazón-Peláez,
S.Lemcke,
D.Koczan,
U.Gimsa,
S.Bansemer,
T.Scheel,
T.Karopka,
T.Böttcher,
J.Müller,
E.Dazert,
V.Antipova,
R.Hoffrogge,
A.Wree,
M.Zschiesche,
U.Strauss,
G.Kundt,
R.Warzok,
L.Gierl,
and
A.Rolfs
(2006).
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor Atorvastatin mediated effects depend on the activation status of target cells in PLP-EAE.
|
| |
J Autoimmun,
27,
251-265.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Liu,
K.Kalantarinia,
and
M.H.Rosner
(2006).
Management of lipid abnormalities associated with end-stage renal disease.
|
| |
Semin Dial,
19,
391-401.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Horiuchi,
and
T.Maeda
(2006).
Statins and bone metabolism.
|
| |
Oral Dis,
12,
85.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Wiviott,
and
C.P.Cannon
(2006).
Update on lipid-lowering therapy and LDL-cholesterol targets.
|
| |
Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med,
3,
424-436.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Steffens,
and
F.Mach
(2006).
Drug insight: Immunomodulatory effects of statins--potential benefits for renal patients?
|
| |
Nat Clin Pract Nephrol,
2,
378-387.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Grabarkiewicz,
P.Grobelny,
M.Hoffmann,
and
J.Mielcarek
(2006).
DFT study on hydroxy acid-lactone interconversion of statins: The case of fluvastatin.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
4,
4299-4306.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Pucadyil,
and
A.Chattopadhyay
(2006).
Role of cholesterol in the function and organization of G-protein coupled receptors.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
45,
295-333.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.Laufs,
F.Custodis,
and
M.Böhm
(2006).
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in chronic heart failure: potential mechanisms of benefit and risk.
|
| |
Drugs,
66,
145-154.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.V.Pak,
S.H.Kim,
M.Koo,
N.Lee,
K.M.Shakhidoyatov,
and
D.Y.Kwon
(2006).
Peptide design of a competitive inhibitor for HMG-CoA reductase based on statin structure.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
84,
586-594.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Shitara,
and
Y.Sugiyama
(2006).
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors: drug-drug interactions and interindividual differences in transporter and metabolic enzyme functions.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
112,
71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Bednarski,
S.C.Elgin,
and
H.B.Pakrasi
(2005).
An inquiry into protein structure and genetic disease: introducing undergraduates to bioinformatics in a large introductory course.
|
| |
Cell Biol Educ,
4,
207-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Mason
(2005).
The statins--therapeutic diversity in renal disease?
|
| |
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens,
14,
17-24.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Liao,
and
U.Laufs
(2005).
Pleiotropic effects of statins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol,
45,
89.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.C.Ferdinand
(2005).
Rosuvastatin: a risk-benefit assessment for intensive lipid lowering.
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
6,
1897-1910.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Endres
(2005).
Statins and stroke.
|
| |
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,
25,
1093-1110.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Jain,
and
P.M.Ridker
(2005).
Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: clinical evidence and basic mechanisms.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
4,
977-987.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Schachter
(2005).
Chemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of statins: an update.
|
| |
Fundam Clin Pharmacol,
19,
117-125.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Y.Mukhtar,
J.Reid,
and
J.P.Reckless
(2005).
Pitavastatin.
|
| |
Int J Clin Pract,
59,
239-252.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Du,
D.Zhao,
and
K.Ding
(2004).
Enantioselective catalysis of the hetero-Diels-Alder reaction between Brassard's diene and aldehydes by hydrogen-bonding activation: a one-step synthesis of (S)-(+)-dihydrokawain.
|
| |
Chemistry,
10,
5964-5970.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Schuster,
and
J.C.Fox
(2004).
Investigating cardiovascular risk reduction--the Rosuvastatin GALAXY Programme.
|
| |
Expert Opin Pharmacother,
5,
1187-1200.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Friesen,
and
V.W.Rodwell
(2004).
The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductases.
|
| |
Genome Biol,
5,
248.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Smit,
and
M.Diamant
(2004).
Genetically defined hyperlipidemia.
|
| |
Pharmacogenomics,
5,
295-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hedl,
and
V.W.Rodwell
(2004).
Inhibition of the class II HMG-CoA reductase of Pseudomonas mevalonii.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
1693-1697.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Calabro,
and
E.T.Yeh
(2004).
Multitasking of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitor: beyond cardiovascular diseases.
|
| |
Curr Atheroscler Rep,
6,
36-41.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Wierzbicki,
R.Poston,
and
A.Ferro
(2003).
The lipid and non-lipid effects of statins.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
99,
95.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Blouin,
Y.Boucher,
and
A.J.Roger
(2003).
Inferring functional constraints and divergence in protein families using 3D mapping of phylogenetic information.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
31,
790-797.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.von Stechow,
S.Fish,
D.Yahalom,
I.Bab,
M.Chorev,
R.Müller,
and
J.M.Alexander
(2003).
Does simvastatin stimulate bone formation in vivo?
|
| |
BMC Musculoskelet Disord,
4,
8.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.J.Gober,
M.Kistowska,
L.Angman,
P.Jenö,
L.Mori,
and
G.De Libero
(2003).
Human T cell receptor gammadelta cells recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells.
|
| |
J Exp Med,
197,
163-168.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chen,
Z.G.Zhang,
Y.Li,
Y.Wang,
L.Wang,
H.Jiang,
C.Zhang,
M.Lu,
M.Katakowski,
C.S.Feldkamp,
and
M.Chopp
(2003).
Statins induce angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis after stroke.
|
| |
Ann Neurol,
53,
743-751.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Machius
(2003).
Structural biology: a high-tech tool for biomedical research.
|
| |
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens,
12,
431-438.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Inoue,
M.Tanabe,
K.Kono,
K.Maruyama,
T.Ikemoto,
and
M.Endo
(2003).
Ca2+-releasing effect of cerivastatin on the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mouse and rat skeletal muscle fibers.
|
| |
J Pharmacol Sci,
93,
279-288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.S.Rosenson
(2003).
Rosuvastatin: a new inhibitor of HMG-coA reductase for the treatment of dyslipidemia.
|
| |
Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther,
1,
495-505.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Teague
(2003).
Implications of protein flexibility for drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
527-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Weitz-Schmidt
(2002).
Statins as anti-inflammatory agents.
|
| |
Trends Pharmacol Sci,
23,
482-486.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.K.Liao
(2002).
Isoprenoids as mediators of the biological effects of statins.
|
| |
J Clin Invest,
110,
285-288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Zapata,
D.Martín,
M.D.Piulachs,
and
X.Bellés
(2002).
Effects of hypocholesterolaemic agents on the expression and activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase in the fat body of the German cockroach.
|
| |
Arch Insect Biochem Physiol,
49,
177-186.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Altieri
(2001).
Statins' benefits begin to sprout.
|
| |
J Clin Invest,
108,
365-366.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

