 |
PDBsum entry 1dqr

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase, a glycolytic enzyme that moonlights as neuroleukin, autocrine motility factor, and differentiation mediator
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phosphoglucose isomerase. Chain: a, b. Ec: 5.3.1.9
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Oryctolagus cuniculus. Rabbit. Organism_taxid: 9986. Tissue: muscle
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.212
|
R-free:
|
0.265
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.J.Bahnson,C.J.Jeffery,D.Ringe,G.A.Petsko
|
Key ref:

|
 |
C.J.Jeffery
et al.
(2000).
Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase, a glycolytic enzyme that moonlights as neuroleukin, autocrine motility factor, and differentiation mediator.
Biochemistry,
39,
955-964.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Jan-00
|
Release date:
|
09-Feb-00
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9N1E2
(G6PI_RABIT) -
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase from Oryctolagus cuniculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
558 a.a.
555 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.9
- glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 94.12% similarity
|
=
|
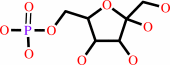 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
39:955-964
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase, a glycolytic enzyme that moonlights as neuroleukin, autocrine motility factor, and differentiation mediator.
|
|
C.J.Jeffery,
B.J.Bahnson,
W.Chien,
D.Ringe,
G.A.Petsko.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The multifunctional protein phosphoglucose isomerase, also known as neuroleukin,
autocrine motility factor, and differentiation and maturation mediator, has
different roles inside and outside the cell. In the cytoplasm, it catalyzes the
second step in glycolysis. Outside the cell, it serves as a nerve growth factor
and cytokine. We have determined the three-dimensional structure of rabbit
muscle phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with the competitive inhibitor
D-gluconate 6-phosphate by X-ray crystallography at 2.5 A resolution. The
structure shows that the enzyme is a dimer with two alpha/beta-sandwich domains
in each subunit. The location of the bound D-gluconate 6-phosphate inhibitor
leads to the identification of residues involved in substrate specificity
(Ser209, Ser159, Thr214, Thr217, and Thr211). The results of previously
published kinetic studies suggest that a lysine and a histidine are involved in
the catalytic mechanism. The crystal structure suggests active site residues
Lys518 and His388 might be these residues. In addition, the positions of amino
acid residues that are substituted in the genetic disease nonspherocytic
hemolytic anemia suggest how these substitutions can result in altered catalysis
or protein stability.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Troncoso-Ponce,
J.Rivoal,
F.J.Cejudo,
S.Dorion,
R.Garcés,
and
E.Martínez-Force
(2010).
Cloning, biochemical characterisation, tissue localisation and possible post-translational regulatory mechanism of the cytosolic phosphoglucose isomerase from developing sunflower seeds.
|
| |
Planta,
232,
845-859.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Wang,
W.B.Watt,
C.Aakre,
and
N.Hawthorne
(2009).
Emergence of complex haplotypes from microevolutionary variation in sequence and structure of Colias phosphoglucose isomerase.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
68,
433-447.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Funasaka,
V.Hogan,
and
A.Raz
(2009).
Phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor mediates epithelial and mesenchymal phenotype conversions in breast cancer.
|
| |
Cancer Res,
69,
5349-5356.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.L.Lee,
and
T.T.Li
(2008).
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic study of the phosphoglucose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
1181-1183.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Funasaka,
and
A.Raz
(2007).
The role of autocrine motility factor in tumor and tumor microenvironment.
|
| |
Cancer Metastasis Rev,
26,
725-735.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Steinke,
S.Hoegg,
H.Brinkmann,
and
A.Meyer
(2006).
Three rounds (1R/2R/3R) of genome duplications and the evolution of the glycolytic pathway in vertebrates.
|
| |
BMC Biol,
4,
16.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Haga
(2005).
[Possibility that AMF will serve as a target molecule for the diagnosis and treatment of a metastatic neoplasm]
|
| |
Yakugaku Zasshi,
125,
169-175.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Lee,
and
C.J.Jeffery
(2005).
The crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with D-sorbitol-6-phosphate, an analog of the open chain form of D-glucose-6-phosphate.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
727-734.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
B.Schlichting,
M.Felgendreher,
and
P.Schönheit
(2005).
Cupin-type phosphoglucose isomerases (Cupin-PGIs) constitute a novel metal-dependent PGI family representing a convergent line of PGI evolution.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
1621-1631.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Yanagawa,
T.Funasaka,
S.Tsutsumi,
T.Raz,
N.Tanaka,
and
A.Raz
(2005).
Differential regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor activities by protein kinase CK2 phosphorylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
10419-10426.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Cordeiro,
P.A.Michels,
L.F.Delboni,
and
O.H.Thiemann
(2004).
The crystal structure of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase from Leishmania mexicana reveals novel active site features.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
2765-2772.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Cordeiro,
R.Hardré,
P.A.Michels,
L.Salmon,
L.F.Delboni,
and
O.H.Thiemann
(2004).
Leishmania mexicana mexicana glucose-6-phosphate isomerase: crystallization, molecular-replacement solution and inhibition.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
915-919.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.W.Hardy,
and
N.P.Peet
(2004).
The multiple orthogonal tools approach to define molecular causation in the validation of druggable targets.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
9,
117-126.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.K.Swan,
T.Hansen,
P.Schönheit,
and
C.Davies
(2004).
A novel phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI)/phosphomannose isomerase from the crenarchaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum is a member of the PGI superfamily: structural evidence at 1.16-A resolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
39838-39845.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Naba,
N.Tanaka,
K.Shiraiwa,
Y.Kusakabe,
T.Funasaka,
A.Haga,
H.Nagase,
A.Raz,
and
K.T.Nakamura
(2004).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of mouse autocrine motility factor.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
2084-2086.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
D.Wendorff,
and
P.Schönheit
(2004).
Bifunctional phosphoglucose/phosphomannose isomerases from the Archaea Aeropyrum pernix and Thermoplasma acidophilum constitute a novel enzyme family within the phosphoglucose isomerase superfamily.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
2262-2272.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Davies,
and
H.Muirhead
(2003).
Structure of native phosphoglucose isomerase from rabbit: conformational changes associated with catalytic function.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
453-465.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Davies,
H.Muirhead,
and
J.Chirgwin
(2003).
The structure of human phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with a transition-state analogue.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1111-1113.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Amraei,
Z.Jia,
P.Reboul,
and
I.R.Nabi
(2003).
Acid-induced conformational changes in phosphoglucose isomerase result in its increased cell surface association and deposition on fibronectin fibrils.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
38935-38941.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Engel,
A.Chaboud,
C.Dumas,
and
S.McCormick
(2003).
Sperm cells of Zea mays have a complex complement of mRNAs.
|
| |
Plant J,
34,
697-707.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Chakrabarti,
S.Bhattacharya,
and
S.K.Bhattacharya
(2003).
Biochemical engineering: cues from cells.
|
| |
Trends Biotechnol,
21,
204-209.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Arsenieva,
R.Hardre,
L.Salmon,
and
C.J.Jeffery
(2002).
The crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with 5-phospho-D-arabinonohydroxamic acid.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
5872-5877.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.S.Rangarajan,
J.Sivaraman,
A.Matte,
and
M.Cygler
(2002).
Crystal structure of D-ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RpiA) from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Proteins,
48,
737-740.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.S.Ford,
and
L.D.Gottlieb
(2002).
Single mutations silence PGiC2 genes in two very recent allotetraploid species of Clarkia.
|
| |
Evolution Int J Org Evolution,
56,
699-707.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.T.Cordeiro,
P.H.Godoi,
L.F.Delboni,
G.Oliva,
and
O.H.Thiemann
(2001).
Human phosphoglucose isomerase: expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
592-595.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Jeffery,
R.Hardré,
and
L.Salmon
(2001).
Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with 5-phospho-D-arabinonate identifies the role of Glu357 in catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
1560-1566.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Verlinde,
V.Hannaert,
C.Blonski,
M.Willson,
J.J.Périé,
L.A.Fothergill-Gilmore,
F.R.Opperdoes,
M.H.Gelb,
W.G.Hol,
and
P.A.Michels
(2001).
Glycolysis as a target for the design of new anti-trypanosome drugs.
|
| |
Drug Resist Updat,
4,
50-65.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Chen,
Z.Zhao,
T.M.Hallis,
Z.Guo,
and
Liu Hw
(2001).
Insights into the Branched-Chain Formation of Mycarose: Methylation Catalyzed by an (S)-Adenosylmethionine-Dependent Methyltransferase We are grateful to Dr. Eugene Seno and the Lilly Research Laboratories for their generous gift of the plasmid pHJL311 and to the National Institutes of Health for grants (GM 35 906 and 54 346). H.-w.L. also thanks the National Institute of General Medical Sciences for a MERIT Award. T.M.H. was a trainee of the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (Biotechnology Training Grant: 2 T32 GM08347).
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
40,
607-610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Lee,
K.Z.Chang,
V.Patel,
and
C.J.Jeffery
(2001).
Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
7799-7805.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
M.Oehlmann,
and
P.Schönheit
(2001).
Novel type of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
183,
3428-3435.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Erlandsen,
E.E.Abola,
and
R.C.Stevens
(2000).
Combining structural genomics and enzymology: completing the picture in metabolic pathways and enzyme active sites.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
10,
719-730.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

