 |
PDBsum entry 1ddt
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.36
- NAD(+)--diphthamide ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2] + NAD+ = N-(ADP-D- ribosyl)diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2] + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2]
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
N-(ADP-D- ribosyl)diphthamide-[translation elongation factor 2]
|
+
|
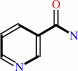 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
3:1444-1463
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Refined structure of dimeric diphtheria toxin at 2.0 A resolution.
|
|
M.J.Bennett,
S.Choe,
D.Eisenberg.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The refined structure of dimeric diphtheria toxin (DT) at 2.0 A resolution,
based on 37,727 unique reflections (F > 1 sigma (F)), yields a final R factor
of 19.5% with a model obeying standard geometry. The refined model consists of
523 amino acid residues, 1 molecule of the bound dinucleotide inhibitor adenylyl
3'-5' uridine 3' monophosphate (ApUp), and 405 well-ordered water molecules. The
2.0-A refined model reveals that the binding motif for ApUp includes residues in
the catalytic and receptor-binding domains and is different from the Rossmann
dinucleotide-binding fold. ApUp is bound in part by a long loop (residues 34-52)
that crosses the active site. Several residues in the active site were
previously identified as NAD-binding residues. Glu 148, previously identified as
playing a catalytic role in ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by DT, is
about 5 A from uracil in ApUp. The trigger for insertion of the transmembrane
domain of DT into the endosomal membrane at low pH may involve 3 intradomain and
4 interdomain salt bridges that will be weakened at low pH by protonation of
their acidic residues. The refined model also reveals that each molecule in
dimeric DT has an "open" structure unlike most globular proteins, which we call
an open monomer. Two open monomers interact by "domain swapping" to form a
compact, globular dimeric DT structure. The possibility that the open monomer
resembles a membrane insertion intermediate is discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.H.Chu,
W.C.Lo,
H.W.Wang,
Y.C.Hsu,
J.K.Hwang,
P.C.Lyu,
T.W.Pai,
and
C.Y.Tang
(2010).
Detection and alignment of 3D domain swapping proteins using angle-distance image-based secondary structural matching techniques.
|
| |
PLoS One,
5,
e13361.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Collet,
and
J.Messens
(2010).
Structure, function, and mechanism of thioredoxin proteins.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
13,
1205-1216.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Shameer,
G.Pugalenthi,
K.K.Kandaswamy,
P.N.Suganthan,
G.Archunan,
and
R.Sowdhamini
(2010).
Insights into Protein Sequence and Structure-Derived Features Mediating 3D Domain Swapping Mechanism using Support Vector Machine Based Approach.
|
| |
Bioinform Biol Insights,
4,
33-42.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Wouters,
S.W.Fan,
and
N.L.Haworth
(2010).
Disulfides as redox switches: from molecular mechanisms to functional significance.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
12,
53-91.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Man,
C.Montagner,
H.Vitrac,
D.Kavan,
S.Pichard,
D.Gillet,
E.Forest,
and
V.Forge
(2010).
Accessibility changes within diphtheria toxin T domain when in the functional molten globule state, as determined using hydrogen/deuterium exchange measurements.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
653-662.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Nagarkar,
R.A.Hule,
D.J.Pochan,
and
J.P.Schneider
(2010).
Domain swapping in materials design.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
94,
141-155.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Ercole,
R.A.Colamarino,
E.Pizzo,
F.Fogolari,
R.Spadaccini,
and
D.Picone
(2009).
Comparison of the structural and functional properties of RNase A and BS-RNase: A stepwise mutagenesis approach.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
91,
1009-1017.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Dvir,
M.E.Lundberg,
S.K.Maji,
R.Riek,
and
S.Choe
(2009).
Mistic: cellular localization, solution behavior, polymerization, and fibril formation.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
1564-1570.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Kent,
H.Yim,
J.K.Murton,
S.Satija,
J.Majewski,
and
I.Kuzmenko
(2008).
Oligomerization of membrane-bound diphtheria toxin (CRM197) facilitates a transition to the open form and deep insertion.
|
| |
Biophys J,
94,
2115-2127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Rodnin,
Y.O.Posokhov,
C.Contino-Pépin,
J.Brettmann,
A.Kyrychenko,
S.S.Palchevskyy,
B.Pucci,
and
A.S.Ladokhin
(2008).
Interactions of fluorinated surfactants with diphtheria toxin T-domain: testing new media for studies of membrane proteins.
|
| |
Biophys J,
94,
4348-4357.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Potala,
S.K.Sahoo,
and
R.S.Verma
(2008).
Targeted therapy of cancer using diphtheria toxin-derived immunotoxins.
|
| |
Drug Discov Today,
13,
807-815.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Benfield,
B.B.Whiddon,
J.H.Clements,
and
S.F.Martin
(2007).
Structural and energetic aspects of Grb2-SH2 domain-swapping.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
462,
47-53.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Vernier,
A.Chenal,
H.Vitrac,
R.Barumandzadhe,
C.Montagner,
and
V.Forge
(2007).
Interactions of apomyoglobin with membranes: mechanisms and effects on heme uptake.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
391-400.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Chavas,
S.Torii,
H.Kamikubo,
M.Kawasaki,
K.Ihara,
R.Kato,
M.Kataoka,
T.Izumi,
and
S.Wakatsuki
(2007).
Structure of the small GTPase Rab27b shows an unexpected swapped dimer.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
769-779.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Song,
and
R.L.Jernigan
(2006).
An enhanced elastic network model to represent the motions of domain-swapped proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
63,
197-209.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Tilley,
and
H.R.Saibil
(2006).
The mechanism of pore formation by bacterial toxins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
16,
230-236.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Merlino,
M.A.Ceruso,
L.Vitagliano,
and
L.Mazzarella
(2005).
Open interface and large quaternary structure movements in 3D domain swapped proteins: insights from molecular dynamics simulations of the C-terminal swapped dimer of ribonuclease A.
|
| |
Biophys J,
88,
2003-2012.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.U.Singer,
D.Desveaux,
L.Betts,
J.H.Chang,
Z.Nimchuk,
S.R.Grant,
J.L.Dangl,
and
J.Sondek
(2004).
Crystal structures of the type III effector protein AvrPphF and its chaperone reveal residues required for plant pathogenesis.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
1669-1681.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Wouters,
K.K.Lau,
and
P.J.Hogg
(2004).
Cross-strand disulphides in cell entry proteins: poised to act.
|
| |
Bioessays,
26,
73-79.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Stehr,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(2004).
NrdH-redoxin of Corynebacterium ammoniagenes forms a domain-swapped dimer.
|
| |
Proteins,
55,
613-619.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kundu,
and
R.L.Jernigan
(2004).
Molecular mechanism of domain swapping in proteins: an analysis of slower motions.
|
| |
Biophys J,
86,
3846-3854.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.S.Stavridi,
Y.Huyen,
I.R.Loreto,
D.M.Scolnick,
T.D.Halazonetis,
N.P.Pavletich,
and
P.D.Jeffrey
(2002).
Crystal structure of the FHA domain of the Chfr mitotic checkpoint protein and its complex with tungstate.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
891-899.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.H.Gan,
R.A.Perlow,
S.Roy,
J.Ko,
M.Wu,
J.Huang,
S.Yan,
A.Nicoletta,
J.Vafai,
D.Sun,
L.Wang,
J.E.Noah,
S.Pasquali,
and
T.Schlick
(2002).
Analysis of protein sequence/structure similarity relationships.
|
| |
Biophys J,
83,
2781-2791.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Liu,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2002).
3D domain swapping: as domains continue to swap.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1285-1299.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Rousseau,
J.W.Schymkowitz,
H.R.Wilkinson,
and
L.S.Itzhaki
(2001).
Three-dimensional domain swapping in p13suc1 occurs in the unfolded state and is controlled by conserved proline residues.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
5596-5601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.O'Neill,
D.E.Kim,
K.Johnsen,
D.Baker,
and
K.Y.Zhang
(2001).
Single-site mutations induce 3D domain swapping in the B1 domain of protein L from Peptostreptococcus magnus.
|
| |
Structure,
9,
1017-1027.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.W.Schymkowitz,
F.Rousseau,
H.R.Wilkinson,
A.Friedler,
and
L.S.Itzhaki
(2001).
Observation of signal transduction in three-dimensional domain swapping.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
8,
888-892.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Steere,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2000).
Characterization of high-order diphtheria toxin oligomers.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
15901-15909.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.K.Holmes
(2000).
Biology and molecular epidemiology of diphtheria toxin and the tox gene.
|
| |
J Infect Dis,
181,
S156-S167.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Fromen-Romano,
P.Drevet,
A.Robert,
A.Ménez,
and
M.Léonetti
(1999).
Recombinant Staphylococcus strains as live vectors for the induction of neutralizing anti-diphtheria toxin antisera.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
67,
5007-5011.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.R.Westhead,
T.W.Slidel,
T.P.Flores,
and
J.M.Thornton
(1999).
Protein structural topology: Automated analysis and diagrammatic representation.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
897-904.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Ren,
J.C.Sharpe,
R.J.Collier,
and
E.London
(1999).
Membrane translocation of charged residues at the tips of hydrophobic helices in the T domain of diphtheria toxin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
976-984.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Saint-Jean,
K.R.Phillips,
D.J.Creighton,
and
M.J.Stone
(1998).
Active monomeric and dimeric forms of Pseudomonas putida glyoxalase I: evidence for 3D domain swapping.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
10345-10353.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ruf,
G.de Murcia,
and
G.E.Schulz
(1998).
Inhibitor and NAD+ binding to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as derived from crystal structures and homology modeling.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
3893-3900.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Del Giudice,
M.Pizza,
and
R.Rappuoli
(1998).
Molecular basis of vaccination.
|
| |
Mol Aspects Med,
19,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Lobeck,
P.Drevet,
M.Léonetti,
C.Fromen-Romano,
F.Ducancel,
E.Lajeunesse,
C.Lemaire,
and
A.Ménez
(1998).
Towards a recombinant vaccine against diphtheria toxin.
|
| |
Infect Immun,
66,
418-423.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Landgraf,
M.Pegram,
D.J.Slamon,
and
D.Eisenberg
(1998).
Cytotoxicity and specificity of directed toxins composed of diphtheria toxin and the EGF-like domain of heregulin beta1.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
3220-3228.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Zakharov,
M.Lindeberg,
Y.Griko,
Z.Salamon,
G.Tollin,
F.G.Prendergast,
and
W.A.Cramer
(1998).
Membrane-bound state of the colicin E1 channel domain as an extended two-dimensional helical array.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
4282-4287.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.E.Malenbaum,
R.J.Collier,
and
E.London
(1998).
Membrane topography of the T domain of diphtheria toxin probed with single tryptophan mutants.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
17915-17922.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Bell,
and
D.Eisenberg
(1997).
Crystal structure of nucleotide-free diphtheria toxin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
481-488.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.V.Louie,
W.Yang,
M.E.Bowman,
and
S.Choe
(1997).
Crystal structure of the complex of diphtheria toxin with an extracellular fragment of its receptor.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
1,
67-78.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Bergdoll,
M.H.Remy,
C.Cagnon,
J.M.Masson,
and
P.Dumas
(1997).
Proline-dependent oligomerization with arm exchange.
|
| |
Structure,
5,
391-401.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.D.Huynh,
C.Cui,
H.Zhan,
K.J.Oh,
R.J.Collier,
and
A.Finkelstein
(1997).
Probing the structure of the diphtheria toxin channel. Reactivity in planar lipid bilayer membranes of cysteine-substituted mutant channels with methanethiosulfonate derivatives.
|
| |
J Gen Physiol,
110,
229-242.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ruf,
J.Mennissier de Murcia,
G.de Murcia,
and
G.E.Schulz
(1996).
Structure of the catalytic fragment of poly(AD-ribose) polymerase from chicken.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
93,
7481-7485.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.K.Beattie,
G.A.Prentice,
and
A.R.Merrill
(1996).
Investigation into the catalytic role for the tryptophan residues within domain III of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
15134-15142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Bell,
and
D.Eisenberg
(1996).
Crystal structure of diphtheria toxin bound to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
1137-1149.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.A.Merritt,
and
W.G.Hol
(1995).
AB5 toxins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
5,
165-171.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bennett,
M.P.Schlunegger,
and
D.Eisenberg
(1995).
3D domain swapping: a mechanism for oligomer assembly.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
4,
2455-2468.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Raju,
D.Navaneetham,
D.Okita,
B.Diethelm-Okita,
D.McCormick,
and
B.M.Conti-Fine
(1995).
Epitopes for human CD4+ cells on diphtheria toxin: structural features of sequence segments forming epitopes recognized by most subjects.
|
| |
Eur J Immunol,
25,
3207-3214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.J.Bennett,
and
D.Eisenberg
(1994).
Refined structure of monomeric diphtheria toxin at 2.3 A resolution.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
3,
1464-1475.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

