 |
PDBsum entry 1awr

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Complex (isomerase/peptide)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1awr
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Complex (isomerase/peptide)
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Cypa complexed with hagpia
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cyclophilin a. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Engineered: yes. Peptide from the HIV-1 capsid protein. Chain: g, h, i, j, k, l. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Cellular_location: cytoplasm. Gene: cyclophilin. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.58Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.394
|
R-free:
|
0.461
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.F.Vajdos
|
Key ref:

|
 |
F.F.Vajdos
et al.
(1997).
Crystal structure of cyclophilin A complexed with a binding site peptide from the HIV-1 capsid protein.
Protein Sci,
6,
2297-2307.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Oct-97
|
Release date:
|
18-Mar-98
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P62937
(PPIA_HUMAN) -
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
165 a.a.
164 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.2.1.8
- peptidylprolyl isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[protein]-peptidylproline (omega=180) = [protein]-peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
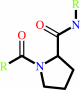 Peptidylproline (omega=180)
Peptidylproline (omega=180)
|
=
|
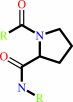 peptidylproline (omega=0)
peptidylproline (omega=0)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
6:2297-2307
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of cyclophilin A complexed with a binding site peptide from the HIV-1 capsid protein.
|
|
F.F.Vajdos,
S.Yoo,
M.Houseweart,
W.I.Sundquist,
C.P.Hill.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The cellular protein, cyclophilin A (CypA), is incorporated into the virion of
the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) via a direct interaction with
the capsid domain of the viral Gag polyprotein. We demonstrate that the capsid
sequence 87His-Ala-Gly-Pro-Ile-Ala92 (87HAGPIA92) encompasses the primary
cyclophilin A binding site and present an X-ray crystal structure of the
CypA/HAGPIA complex. In contrast to the cis prolines observed in all previously
reported structures of CypA complexed with model peptides, the proline in this
peptide, Pro 90, binds the cyclophilin A active site in a trans conformation. We
also report the crystal structure of a complex between CypA and the hexapeptide
HVGPIA, which also maintains the trans conformation. Comparison with the
recently determined structures of CypA in complexes with larger fragments of the
HIV-1 capsid protein demonstrates that CypA recognition of these hexapeptides
involves contacts with peptide residues Ala(Val) 88, Gly 89, and Pro 90, and is
independent of the context of longer sequences.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Fig. 6. A: HAGPIA and CypA are shown in CPK and ribbon representa-
tions, respectively. B: Orthogonal view. C: The molecular surface of CypA
is colored gray and green according to curvature. CypA residues that in-
teract with HAGPIA are shown, and residues that hydrogen bond (magen-
ta) HAGPIA re in yellow. H drogen bonds are defined as acceptor
to donor distances of less than 3.3
x.
The HAGPIA N-terminal histidine
and C-terminal alanine are labeled in For clarity, the side chains f the
histidine and isoleucine have been omitted. Two ordered water
that form bridging hydrogen bonds between peptide main chain
and CypA active site residues are shown as blue spheres.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Fig. 7. Superposition of HAGPIA and peptides refined in the
pseudo (P4~)-cell. CypA CA atoms (residues 2-165) were overlapped by
least squares (Kabsch, 976). CypA residues that hydrogen bond pep-
tide ligands are HAGPIA (magenta), (cyan). Ala/Val 88
and the peptide proline residues are labeled.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(1997,
6,
2297-2307)
copyright 1997.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Caines,
K.Bichel,
A.J.Price,
W.A.McEwan,
G.J.Towers,
B.J.Willett,
S.M.Freund,
and
L.C.James
(2012).
Diverse HIV viruses are targeted by a conformationally dynamic antiviral.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
19,
411-416.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Galat,
and
J.Bua
(2010).
Molecular aspects of cyclophilins mediating therapeutic actions of their ligands.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
67,
3467-3488.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.H.Robbins,
J.F.Domsic,
M.Agbandje-McKenna,
and
R.McKenna
(2010).
Structure of a monoclinic polymorph of human carbonic anhydrase II with a doubled a axis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
628-634.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Davis,
J.R.Walker,
V.Campagna-Slater,
P.J.Finerty,
R.Paramanathan,
G.Bernstein,
F.MacKenzie,
W.Tempel,
H.Ouyang,
W.H.Lee,
E.Z.Eisenmesser,
and
S.Dhe-Paganon
(2010).
Structural and biochemical characterization of the human cyclophilin family of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases.
|
| |
PLoS Biol,
8,
e1000439.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.P.Mascarenhas,
and
K.Musier-Forsyth
(2009).
The capsid protein of human immunodeficiency virus: interactions of HIV-1 capsid with host protein factors.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
6118-6127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ramanathan,
and
P.K.Agarwal
(2009).
Computational identification of slow conformational fluctuations in proteins.
|
| |
J Phys Chem B,
113,
16669-16680.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Hamelberg,
and
J.A.McCammon
(2009).
Mechanistic insight into the role of transition-state stabilization in cyclophilin A.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
147-152.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Guelker,
L.Stagg,
P.Wittung-Stafshede,
and
Y.Shamoo
(2009).
Pseudosymmetry, high copy number and twinning complicate the structure determination of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans (ATCC 29577) flavodoxin.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
523-534.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Yang,
J.M.Robotham,
H.B.Nelson,
A.Irsigler,
R.Kenworthy,
and
H.Tang
(2008).
Cyclophilin A is an essential cofactor for hepatitis C virus infection and the principal mediator of cyclosporine resistance in vitro.
|
| |
J Virol,
82,
5269-5278.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.O.Peters,
M.G.Mendoza,
R.E.Capina,
M.Luo,
X.Mao,
M.Gubbins,
N.J.Nagelkerke,
I.Macarthur,
B.B.Sheardown,
J.Kimani,
C.Wachihi,
S.Thavaneswaran,
and
F.A.Plummer
(2008).
An integrative bioinformatic approach for studying escape mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag in the Pumwani Sex Worker Cohort.
|
| |
J Virol,
82,
1980-1992.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Song,
and
C.Aiken
(2007).
Analysis of human cell heterokaryons demonstrates that target cell restriction of cyclosporine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants is genetically dominant.
|
| |
J Virol,
81,
11946-11956.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.F.Koslover,
and
D.J.Wales
(2007).
Geometry optimization for peptides and proteins: Comparison of Cartesian and internal coordinates.
|
| |
J Chem Phys,
127,
234105.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Rits,
K.A.van Dort,
C.Münk,
A.B.Meijer,
and
N.A.Kootstra
(2007).
Efficient transduction of simian cells by HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors that contain mutations in the capsid protein.
|
| |
Mol Ther,
15,
930-937.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Abdurahman,
S.Höglund,
A.Höglund,
and
A.Vahlne
(2007).
Mutation in the loop C-terminal to the cyclophilin A binding site of HIV-1 capsid protein disrupts proper virus assembly and infectivity.
|
| |
Retrovirology,
4,
19.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Oldfield
(2007).
CAALIGN: a program for pairwise and multiple protein-structure alignment.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
514-525.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Venugopal,
B.Sen,
A.K.Datta,
and
R.Banerjee
(2007).
Structure of cyclophilin from Leishmania donovani at 1.97 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
60-64.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Trzesniak,
and
W.F.van Gunsteren
(2006).
Catalytic mechanism of cyclophilin as observed in molecular dynamics simulations: pathway prediction and reconciliation of X-ray crystallographic and NMR solution data.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
2544-2551.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Oksanen,
V.P.Jaakola,
T.Tolonen,
K.Valkonen,
B.Akerström,
N.Kalkkinen,
V.Virtanen,
and
A.Goldman
(2006).
Reindeer beta-lactoglobulin crystal structure with pseudo-body-centred noncrystallographic symmetry.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
1369-1374.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Agarwal
(2006).
Enzymes: An integrated view of structure, dynamics and function.
|
| |
Microb Cell Fact,
5,
2.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.C.Mische,
H.Javanbakht,
B.Song,
F.Diaz-Griffero,
M.Stremlau,
B.Strack,
Z.Si,
and
J.Sodroski
(2005).
Retroviral restriction factor TRIM5alpha is a trimer.
|
| |
J Virol,
79,
14446-14450.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.X.Guo,
F.Wang,
K.Q.Yu,
J.Chen,
D.L.Bai,
K.X.Chen,
X.Shen,
and
H.L.Jiang
(2005).
Novel cyclophilin D inhibitors derived from quinoxaline exhibit highly inhibitory activity against rat mitochondrial swelling and Ca2+ uptake/ release.
|
| |
Acta Pharmacol Sin,
26,
1201-1211.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Korostelev,
M.O.Fenley,
and
M.S.Chapman
(2004).
Impact of a Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatic restraint on protein structures refined at medium resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1786-1794.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Sokolskaja,
D.M.Sayah,
and
J.Luban
(2004).
Target cell cyclophilin A modulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity.
|
| |
J Virol,
78,
12800-12808.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Henriksson,
P.Johansson,
T.Unge,
and
S.L.Mowbray
(2004).
X-ray structure of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
4107-4113.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Agarwal
(2004).
Cis/trans isomerization in HIV-1 capsid protein catalyzed by cyclophilin A: insights from computational and theoretical studies.
|
| |
Proteins,
56,
449-463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Goff
(2004).
Genetic control of retrovirus susceptibility in mammalian cells.
|
| |
Annu Rev Genet,
38,
61-85.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.R.Howard,
F.F.Vajdos,
S.Li,
W.I.Sundquist,
and
C.P.Hill
(2003).
Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of cyclophilin A.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
10,
475-481.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Padilla,
and
T.O.Yeates
(2003).
A statistic for local intensity differences: robustness to anisotropy and pseudo-centering and utility for detecting twinning.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1124-1130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.R.Barends,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2003).
Acetobacter turbidans alpha-amino acid ester hydrolase: merohedral twinning in P21 obscured by pseudo-translational NCS.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
2237-2241.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Saphire,
M.D.Bobardt,
and
P.A.Gallay
(2002).
trans-Complementation rescue of cyclophilin A-deficient viruses reveals that the requirement for cyclophilin A in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication is independent of its isomerase activity.
|
| |
J Virol,
76,
2255-2262.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Fabiola,
R.Bertram,
A.Korostelev,
and
M.S.Chapman
(2002).
An improved hydrogen bond potential: impact on medium resolution protein structures.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
1415-1423.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Höglund,
J.Su,
S.S.Reneby,
A.Végvári,
S.Hjertén,
I.M.Sintorn,
H.Foster,
Y.P.Wu,
I.Nyström,
and
A.Vahlne
(2002).
Tripeptide interference with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 morphogenesis.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
46,
3597-3605.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Poy,
M.Lepourcelet,
R.A.Shivdasani,
and
M.J.Eck
(2001).
Structure of a human Tcf4-beta-catenin complex.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
8,
1053-1057.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Dietrich,
L.S.Ehrlich,
T.J.LaGrassa,
D.Ebbets-Reed,
and
C.Carter
(2001).
Structural consequences of cyclophilin A binding on maturational refolding in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid protein.
|
| |
J Virol,
75,
4721-4733.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

