- For example hundreds of 3 letter codes (like D1P in entries 1g5d, 1g5e) are useless duplicates of existing ones like ORP and in cases like these the 3 letter code D1P has become obsolete and replaced by ORP
- In thousands other cases the atom names in PDB ATOM lines, do not match with other entries, for the same 3 letter code.
- Secondary structure
- Quaternary structure of the biological entity
- Active sites
- Classification cross-references
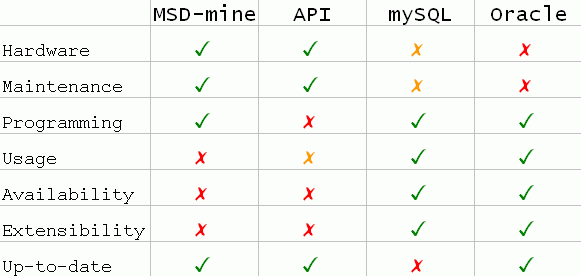
How to access and use MSDSD
We expect that the majority of the users will use MSDSD indirectly by accessing some of our online search services available from our website. All these services depend and use the production MSDSD database that we maintain and update on a regular (weekly) basis. Most of these services also depend on several other internal optimisation structures and components that are not part of the MSDSD core. For this, we do not always intend to offer them as a package that one would be able to download and run locally.For more demanding users of the MSDSD database we have several options for using directly relational operations on MSDSD. The idea is that these users may take advantage of the power and flexibility of database technology in order to utilise the MSDSD in novel ways, and also built on it or extend it independently. The choice of which option to use will depend on the needs and resources such as:
-
Available hardware:
Could you invest on hardware resources that may required (i.e. disk space - server hosts for replication)
-
Maintenance:
Could you invest on skilled people at your site that have the capability and the time to maintain MSDSD locally (i.e. Oracle DBA)?
-
Programming:
Do you have the programming skills that may be required (i.e. in order to use an available API)?
-
Heavy usage:
Do you intend to make heavy usage of MSDSD, that our online search services do not allow?
-
Availability:
Would you prefer not to be bound to availability of MSDSD over the web?
-
Extensibility:
Do you plan to extend MSDSD with new tables relevant to your goals and projects?
-
Up-to-date:
Do you need to be up-to-date (as much as possible) with the master MSDSD and the PDB?
MSD-API and MSD-mine
These are online services that offer direct SQL execution over the web. Both these services will impose limitations on what an individual user may do and the resources (database CPU time, temporary disk space etc) he may use. This is done in order to avoid over-demanding requests that would degrade the availability and performance of our local databases. Users that are not satisfied by what these services offer will have to replicate a local copy of MSDSD using one of the other options described below.In brief MSD-mine is a web application for interactive exploration of MSDSD. It allows users to interactively build arbitrary queries over MSDSD that can then be also used for interactive data-analysis and data mining. Its main aim is to familiarise users with the MSDSD data.
The MSD-API web service enables developers to query the MSDSD directly from their own application programs in their favourite environment - such as Java, C/C++, Perl using technologies like SOAP and WSDL and is based on Distributed Computing and Grid concepts. The MSD-API offers the full power and flexibility of ad-hoc SQL but needs programming and SQL skills and is available for registered users.
For more information and details follow the corresponding links given above.
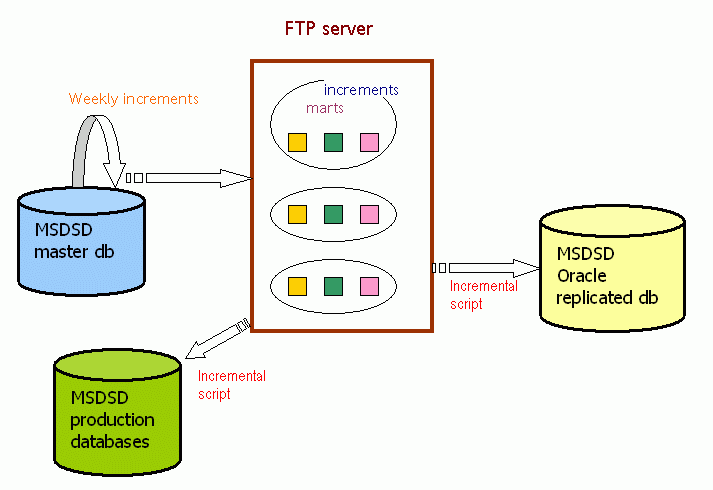
Replication on Oracle
MSDSD is free for academic research and can be downloaded from our ftp site.To obtain a license, please fill an application form and post three copies to:
Dr Melford John Database administrator Macromolecular Database Structure European Bioinformatics Institute Welcome Trust Genome Campus Hinxton, Cambridge, CB10 1SD United Kingdom
This is the most advanced remote replication option that we offer. It is available for registered users that fill in and post a free of charge MSDSD license document.
It uses one of the most advanced and powerful commercial relational database servers and is the option that we recommend for the more
serious users of MSDSD and our collaborators. Additionally since we also use it at MSD, we are able to offer more support and advice.
For the Oracle replication option we also offer frequent (weekly) increments for users that wish to follow closely the evolution of our local master MSDSD and of the PDB.
The disadvantages of this option are that users will need to have an oracle server license, some database administration support and adequate hardware infrastructure.
Typically a user of this replication will download and install the latest full release (full transformation) of MSDSD using the full installation instructions. Such full releases take place on a sparse (yearly) basis, and this is the time of MSDSD reconciliation, since all PDB entries are refreshed and creeping inconsistencies are resolved.
In the meantime between releases (full transformations) the user may run the automatic synchronisation script (typically set in a crontab) that will allow the download and inclusion of increments for the new PDB entries that are released every week.
Any corrections in reference data will not propagate back to the affected old entries in order to keep the increments manageable, so the only time that the full set of MSDSD relational constraints is guaranteed, is only immediately after a full release.
The MSDSD and the incremental updates are organised in sections ("marts") so users are free to install and increment, just the marts that they are interested in. There is also the option to specify which tables of a mart a user wishes to have installed, so users may in general replicate just a few individual tables.
For more information you may contact the PDBe group
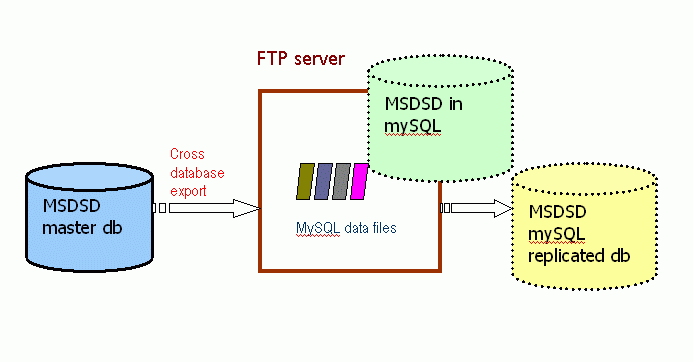
Replication on mySQL
This is the alternative open source database replication that we offer. We have chosen to support mySQL instead of other similar alternatives, because at the time it seems to be the easier to install and start with. It also has the fewer platform dependencies and requires almost no system administrator involvement in order to set-up. The idea is to offer something that will require the minimum effort to install and give it a try for a researcher who is not an expert in the IT area and has no dedicated resources and support.It should be easy to replicate even on a normal desktop workstation with a fair amount of disk space. It also does not bind the user community to a commercial software database vendor.
The disadvantages of this options are that mySQL may not always have the sophistication and speed of a commercial database (for complex queries), we do not offer frequent incrementals and that we do not use it much, so we will not be able to offer as much support and advice.
It is also available for registered users that fill in and post a free of charge MSDSD mySQL license document (in 3 copies).
Typically a user of this replication will download and install directly the mySQL data-files of the tables he is interested in from our FTP server following the mySQL installation instructions. The tables are available in compressed myIsam format without any pre-built indexes.
For more information you may contact the PDBe group
MSDSD and flat files (PDB, mmCif, XML)
A frequently asked question about MSDSD is why the database is not available in XML and other flat file formats (XML,mmCif,clean-up PDB). The reason is that we feel that XML and other flat-files have to be based on a rigid and systematic standardisation in order to be useful. This work is done as part of the wwPDB collaboration and we would advice users to refer to the wwPDB- MSDSD is based on relational database technology and it is available on relational database technology. It is not a collection of flat files.
- It is not another data store for the PDB and does not intend to replace the PDB
- While it is partially based on mmCif terminology and organisation, it is not bound to use it when this is unsuitable
- It includes complete and consistent sections of automatically or semi-automatically derived information that are not part of the PDB
- It includes complete and consistent cross-references as well as reference information from external databases. All these are not part of the PDB
- It focuses mainly on "Assemblies", the quaternary structure that corresponds to the actual biological entity, as the starting point for determining the actual structural characteristics of proteins
MSDSD conventions
MSDSD (with some exceptions) is following a standard set of conventions in its design and architecture. Some understanding of these conventions will help anyone interested in learning the MSDSD schema, regardless of the method he chooses to use in order to use it (replication, API). For a more systematic study you will have also to consult the MSDSD reference documentation.- We use user friendly and meaningful names that are familiar to the end users instead of precise names. We will use the names CHAIN and RESIDUE instead of ENTITY_INSTANCE or COMPONENT even though that the entities that they model are not always very strictly speaking chains or residues (i.e. water groups and waters or bound molecules). This means diversion in some cases from the strict mmCif terms.
- We will follow de facto standards wherever there is no necessity to oppose them. For example we will use the PDB nomenclature and ordering for atoms and PDB style names for chains.
- Table names in sections of the model may be marked up with a common prefix (i.e. "CHEM" like in CHEM_COMP,CHEM_ATOM)
- Tables will have an abstract identifier attribute that will be used in order to implement foreign keys. Only these attributes should end with the "ID" suffix.
- The abstract identifiers are not guaranteed to remain constant in different MSDSD releases. There is always another set of naming identifiers (like ACCESSION_CODE,ASSEMBLY_SERIAL etc) for every table and these should be used by external users in order to refer to MSDSD records.
- The abstract identifier attributes of entities should have the same name as the entity and the "ID" suffix i.e. CHEM_ATOM_ID for CHEM_ATOM.
- Attributes that are external identifiers will not have the ID suffix and will be named to the CODE suffix (i.e. CIF_CODE) if they are alphanumeric, to the NO suffix (i.e. EBI_NO) when they are numeric, or the the SERIAL suffix when they are serial numbers (i.e. ASSEMBLY_SERIAL)
- Attributes that are "propagated" (denormalised) like foreign keys or foreign names should keep the same names as in the parent tables (i.e. CHEM_COMP_ID and CHEM_COMP_CODE on CHEM_ATOM) or use a consistent role name (i.e. SUPERCEDED_BY_COMP_ID - SUPERCEDED_BY_COMP_CODE).
- Usage of database or other language keywords is avoided (i.e. CLASS,TYPE,GROUP,CODE,TEXT). Table and column names should include alphanumeric characters only and the underscore (not #,$ etc)
- Names though are kept as short as possible
- Legacy names and identifiers are available where appropriate and have corresponding prefixes (i.e. PDB_CODE). Their uniqueness is not guaranteed and in most cases cannot be used as keys for reference
- Cryptic names and abbreviations are avoided i.e. NUM_RESIDUES instead of N_RESID and RELEASE_STATUS instead of REL_STATUS
- If this is not possible or in cases where attribute names are too vague: ID, CLASS, TYPE, CODE, ORDER they are prefixed with the name of the table (i.e. CHAIN_CODE, CHEM_BOND_ORDER). In cases that these attributes are propagated, the prefix is not duplicated (i.e. not CHAIN_CHAIN_CODE). The entity name should not be used as a prefix in any other case. Especially the fact that a column will be propagated should not affect the decision to prefix it with the table name.
- Boolean attributes get values 'Y'/'N' and have "FLAG" as suffix
- Counts start with the NUM prefix i.e. NUM_RESIDUES
- Extending the model with new attributes or entities is not a problem and has to be expected. Modification or removal of attributes or entities though, is strongly avoided. Inclusion of unimplemented "empty" attributes for future use is carefully considered.
- There may be a set of internal cryptic database identifier attributes usually with the INT prefix (i.e. INT_DEIC_ID) and these should not be used by external users
Sections of the PDBe search database
The PDBe search database is organised in interrelated sections. Some of these sections are in the centre of the database, while others may be decoupled and ignored for those that are not interested in them.- Ligands
- Structure
- Secondary structure
- Active sites
- External cross-references / Taxonomy
|
This is a consistent and enriched library of ligands, small molecules and monomers that are referred by each residue and atom. There is complete and consistent reference information for any small molecule and aminoacid like for example CPM 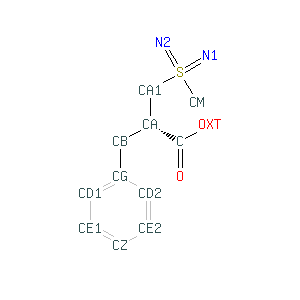 that includes detailed
information about its atoms and bonds, their standard nomenclature and
ordering, as well as their important characteristics like aromaticity and
stereochemistry. Any atom or residue in any actual structure, that does
not include and follow a reference in an atom or ligand of this dictionary,
is simply unidentified and requires cleanup. that includes detailed
information about its atoms and bonds, their standard nomenclature and
ordering, as well as their important characteristics like aromaticity and
stereochemistry. Any atom or residue in any actual structure, that does
not include and follow a reference in an atom or ligand of this dictionary,
is simply unidentified and requires cleanup. |
|
This is where the big and important volume of information is included. This section is organised in 3 different interrelated hierarchies that facilitate different points of view 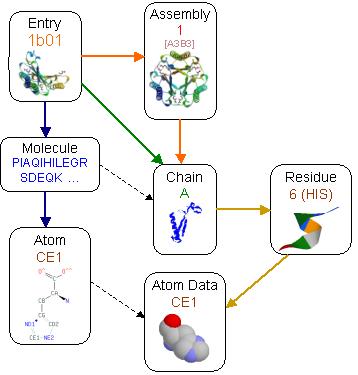 a) The sequence
point of view (denoted with blue arrows). The information in this hierarchy
is about the sequence and chemistry of the protein and does not relate
with the 3-D folding of this sequence. A molecule corresponds to the sequence
of a chain but it is possible to have more than one chain in the PDB asymmetric
unit that are slightly different foldings of the same molecule as these
were observed in the experiment. The atom is again the abstract notion
of a chemical atom that ignores alternative configurations or different
NMR models. These are useful in relationships where the actual coordinates
are not of interest, like the source organism of the molecule etc. a) The sequence
point of view (denoted with blue arrows). The information in this hierarchy
is about the sequence and chemistry of the protein and does not relate
with the 3-D folding of this sequence. A molecule corresponds to the sequence
of a chain but it is possible to have more than one chain in the PDB asymmetric
unit that are slightly different foldings of the same molecule as these
were observed in the experiment. The atom is again the abstract notion
of a chemical atom that ignores alternative configurations or different
NMR models. These are useful in relationships where the actual coordinates
are not of interest, like the source organism of the molecule etc.
b) The PDB asymmetric point of view (denoted with green and the green-orange arrows). This is the view of the observed structure as is available in the PDB entry. The asymmetric chains are also reused in assemblies but are marked with a special non-symmetric-valid flag, that specifies that are also valid regardless of the assembly where they belong. This information is more useful when different chain structures are needed regardless whether they are actually the same molecule and whether they have any interactions between them. c) The assembly point of view that corresponds to the actual quaternary biological entity. This represents what should be considered as the actual complete structure and is useful when the actual inter-chain and ligand interactions are significant. For example the assembly in entry 1b01 above form a barrel like sheet in the middle of the structure that includes strands from different chains and becomes apparent after the assembly transformation of chains. As an example the entry 1b01 has 5 chains in the asymmetric unit (A,B,C,D,E). These chains form 3 assemblies, assembly 1 with chains (A,A1,A2,B,B1,B2), assembly 2 with chains (C,C1,C2,D,D1,D2) and assembly 3 with chains (E,E1,E2,E3,E4,E5). Chains A and B from assembly 1, C and D from assembly 2 and E from assembly 3, are also marked as non symmetric valid and they may be used to extract the original PDB asymmetric unit. Additionally all bound molecules and water groups are defined in separate
chains, named after and associated to the protein chains that have the
stronger interaction with. During the process of assembly formation,
bound molecules and waters may be replicated several times, as long as
they have some form of interaction with the assembly.
|
|
This is a section of the database that keeps detailed information about the secondary structure for common things like sheets and helices up to more extended formations like bulges, hairpins and motifs. For each entry there may be one or more sets of secondary structure information from different sources. Since the secondary structure is not always available in PDB entries and its source or accuracy is not consistent, the secondary structure of all entries has been re-derived using directly the coordinates of the structure as a source to DOSS, a secondary structure prediction program - based on DSSP(W.Kabsch C. Sander(1983) Biopolymers 22:2577-2637) / Promotif [Gail Hutchinson and Janet Thornton 1996], in order to provide an consistent platform for comparisons and analysis of secondary structure. The starting point for deriving the secondary structure information is not the PDB asymmetric unit, but the actual quaternary structure (the assembly), in order to be able to identify secondary structure elements related to more than 1 chain in the assembly. For example in entry 1b01 there is a barrel like sheet in the middle of the structure that includes strands from 3-D transformed chains that originate from a single chain of the asymmetric unit |
|
Information about the active sites of the macromolecule, and the way that ligands and drugs bind to a protein. Again since the related information sometimes available in the PDB entries is not consistent and trustworthy, site information is calculated internally in PDBe [Golovin, A., Dimitropoulos, D., Oldfield, T., Rachedi, A. and Henrick, K. (2005) PROTEINS: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 58(1): 190-9.] (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/msdsite/index.jsp). The active sites of a protein chain are determined based on the contacts of the chain with a ligand. There are many ways that contacts are defined based on different types of bonds and interactions, that take into account the distance and angles of the atoms, as well as other characteristics of the ligands and residues like planes. An active site can be defined not only for a particular atom, but also for a plane of a molecule. |
|
A lot of work has also been done to provide complete and consistent cross-references with external database like Swiss-prot, SCOP, CATH, EC Enzyme, Gene ontology, Medline and NCBI taxonomy databases [Velankar, S., McNeil, P., Mittard-Runte, V., Suarez, A., Barrell, D., Apweiler, R. and Henrick.K. (2005) Nucleic Acids Res. 33 (Database Issue)]. The cross-references are established to the most suitable detailed level (for example on a residue by residue basis for Swiss-prot, since the same chain may be referenced by two different Swiss-prot entries) but are also often aggregated to facilitate data analysis on a higher level. For more details on the broader context of this effort you may refer to the eFamily web-site. |
MSDSD frequently asked SQL
-
Get the reference info including atoms and bonds of a ligand (that could be used for example to dump out a chemical file)
* SELECT CHEM_COMP_ID,CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER,FORMULA,NUM_ATOMS_ALL,FORMAL_CHARGE,STEREO_SMILES,NAME FROM CHEM_COMP WHERE CHEM_COMP_CODE='ATP' * SELECT CHEM_ATOM_ID,NAME,ELEMENT_SYMBOL,CHARGE,CHIRALITY,DEFAULT_MODEL_X,DEFAULT_MODEL_Y,DEFAULT_MODEL_Z FROM CHEM_ATOM WHERE CHEM_COMP_CODE='ATP' /* or CHEM_COMP_ID=794 /* /* optinally: AND ELEMENT_SYMBOL!='H' for non-hydrogen */ ORDER BY ORDERING; * SELECT CHEM_BOND_ID,CHEM_ATOM_1_NAME,CHEM_ATOM_2_NAME,CHEM_BOND_TYPE,EXTENDED_TYPE,STEREOCHEM FROM CHEM_BOND WHERE CHEM_COMP_CODE='ATP' /* or CHEM_COMP_ID=794 / ORDER BY CHEM_ATOM_1_ORDERING,CHEM_ATOM_2_ORDERING;
-
Get the assemblies of an entry
* SELECT ASSEMBLY_ID,ASSEMBLY_SERIAL,ASSEMBLY_TYPE,ASSEMBLY_CLASS,ASSEMBLY_FORM,ASSEMBLY_TITLE,NUM_CHAINS,SCORE FROM ASSEMBLY WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0'; ASSEMBLY_ID ASSEMBLY_SERIAL ASSEMBLY_TYPE ASSEMBLY_CLASS ASSEMBLY_FORM NUM_CHAINS SCORE -15203 0 0 17668 1 DIMERIC HE [AB] 2 -8 17669 2 TETRAMERIC HE [A2B2] 4 -10
Note: Assemblies with assembly serial 0 are not real biological assemblies. The serve for legacy purposes us placeholders for
data in the asymmetric unit (waters and ligands) that do not seem to be able to fit in a real assembly (problematic PDB data) -
Get the chains in all assemblies of an entry (this is just for demonstration - not a actual useful query)
SELECT CHAIN_ID,ASSEMBLY_SERIAL,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_TYPE,ASSOCIATED_CHAIN_CODE,NON_ASSEMBLY_VALID, PDB_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,CHAIN_INCR_1_LETTER, NUM_RESIDUES,MOLECULE_CODE,CHAINMOL_SERIAL,MOLECULE_NAME FROM CHAIN WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' ORDER BY ASSEMBLY_SERIAL,DECODE(CHAIN_TYPE,'C',1,'B',2,3),CHAIN_CODE; -93483 0 AW W Y A 0 1 3 5 Solvent 38473 1 A C Y A A 0 215 1 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) 38474 1 B C Y B B 0 232 2 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN) 26194066 1 AW W A N D 0 191 3 1 Solvent 26193928 1 AW1 W B N C 0 239 3 2 Solvent 38475 2 C C Y C C 0 215 1 3 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) 38476 2 C1 C N C A 0 215 1 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) 38477 2 D C Y D D 0 232 2 3 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN) 38478 2 D1 C N D B 0 232 2 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN) 26193936 2 AW W C N E 0 332 3 3 Solvent 26193942 2 AW1 W D N F 0 418 3 4 Solvent
- Get the chains of an assembly
SELECT CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_TYPE,ASSOCIATED_CHAIN_CODE,PDB_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER, NUM_RESIDUES,MOLECULE_CODE,MOLECULE_NAME FROM CHAIN WHERE ASSEMBLY_ID=17669 ORDER BY CHAIN_CODE; AW W C E 332 3 Solvent AW1 W D F 418 3 Solvent C C C C 215 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) C1 C C A 215 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) D C D D 232 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN) D1 C D B 232 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN)
-
Get the chains of the asymmetric unit (original PDB file)
SELECT CHAIN_ID,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_TYPE,PDB_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,NUM_RESIDUES,MOLECULE_CODE,MOLECULE_NAME FROM CHAIN WHERE ENTRY_ID=15203 /* or ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' */ and NON_ASSEMBLY_VALID='Y' ORDER BY CHAIN_CODE; 38473 A C A A 215 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) -93483 AW W A 1 3 Solvent 38474 B C B B 232 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN) 38475 C C C C 215 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) 38477 D C D D 232 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN)
-
Get a single (ideally representative) chain per molecule
SELECT CHAIN_ID,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_TYPE,PDB_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,NUM_RESIDUES,MOLECULE_CODE,MOLECULE_NAME FROM CHAIN WHERE ENTRY_ID=15203 /* or ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' */ and chainmol_serial=1 ORDER BY CHAIN_CODE; 26194066 AW W A 191 3 Solvent 38473 A C A A 215 1 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (LIGHT CHAIN) 38474 A C A B 232 2 IGM-KAPPA COLD AGGLUTININ (HEAVY CHAIN)
-
Get the residues of a chain
SELECT RESIDUE_ID,CHAIN_CODE,SERIAL,CHEM_COMP_ID,CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, PDB_SEQ,PDB_INSERT_CODE,PDB_CODE FROM RESIDUE WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' AND ASSEMBLY_SERIAL=1 AND CHAIN_CODE='A'
-
Get residues where the 3 letter code has been changed in the MSDSD (usually due to obsolete-superceded 3 letter codes
SELECT RESIDUE_ID,ACCESSION_CODE,CHAIN_CODE,SERIAL,CHEM_COMP_ID,CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, PDB_SEQ,PDB_INSERT_CODE,PDB_CODE FROM RESIDUE WHERE PDB_CODE!=CODE_3_LETTER AND NON_ASSEMBLY_VALID='Y'
-
Get the residues and bound molecules that have not yet been associated with a reference ligand (to be cleaned)
SELECT RESIDUE_ID,ACCESSION_CODE,CHAIN_CODE,SERIAL,CHEM_COMP_ID,CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, PDB_SEQ,PDB_INSERT_CODE,PDB_CODE FROM RESIDUE WHERE CHEM_COMP_ID IS NULL
-
Get the data to dump the "ATOM" lines of a PDB file for the original asymmetric unit file
SELECT ATOM_DATA_ID,MODEL_SERIAL,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,CHAIN_PDB_CODE, RESIDUE_SERIAL,RESIDUE_PDB_SEQ,RESIDUE_PDB_INSERT_CODE, CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, CHEM_ATOM_NAME,CHEM_ATOM_NAME_PDB_LS, ORIG_X,ORIG_Y,ORIG_Z,ALT_CODE,OCCUPANCY FROM ATOM_DATA WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' AND NON_ASSEMBLY_VALID='Y' ORDER BY MODEL_SERIAL,CHAIN_CODE,RESIDUE_SERIAL,CHEM_ATOM_ORDERING -
Get the data to dump the PDB "ATOM" lines of an assembly
SELECT ATOM_DATA_ID,MODEL_SERIAL,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,CHAIN_PDB_CODE, RESIDUE_SERIAL,RESIDUE_PDB_SEQ,RESIDUE_PDB_INSERT_CODE, CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, CHEM_ATOM_NAME,CHEM_ATOM_NAME_PDB_LS, X,Y,Z,ALT_CODE,OCCUPANCY FROM ATOM_DATA WHERE ASSEMBLY_ID=17668 ORDER BY MODEL_SERIAL,CHAIN_CODE,RESIDUE_SERIAL,CHEM_ATOM_ORDERING -
Get the data of a single (ideally the representative) NMR model for an NMR entry
SELECT ATOM_DATA_ID,CHAIN_CODE,CHAIN_CODE_1_LETTER,CHAIN_PDB_CODE, RESIDUE_SERIAL,RESIDUE_PDB_SEQ,RESIDUE_PDB_INSERT_CODE, CHEM_COMP_CODE,CODE_3_LETTER, CHEM_ATOM_NAME,CHEM_ATOM_NAME_PDB_LS, X,Y,Z,ALT_CODE,OCCUPANCY FROM ATOM_DATA WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1olg' and MODEL_SERIAL=1 ORDER BY CHAIN_CODE,RESIDUE_SERIAL,CHEM_ATOM_ORDERING -
Query for mySQL that pre-formats directly in the PDB format
(kindly contributed)
SELECT CONCAT( RPAD("ATOM", 6, " "), LPAD(SERIAL, 5, " "), " ", LPAD(CHEM_ATOM_NAME, 4, " "), IF(ALT_CODE IS NULL, " ", ALT_CODE), CODE_3_LETTER, " ", IF(CHAIN_PDB_CODE IS NULL, " ", CHAIN_PDB_CODE), LPAD(RESIDUE_SERIAL, 4, " "), IF(RESIDUE_PDB_INSERT_CODE IS NULL, " ", RESIDUE_PDB_INSERT_CODE), REPEAT(" ", 3), LPAD(X, 8, " "), LPAD(Y, 8, " "), LPAD(Z, 8, " "), LPAD(OCCUPANCY, 6, " "), REPEAT(" ", 6), REPEAT(" ", 6), RPAD(CHAIN_CODE, 4, " ") ) AS atom_lines FROM ATOM_DATA WHERE (ACCESSION_CODE = "1olg") AND (ASSEMBLY_SERIAL = 1) AND (MODEL_SERIAL = 1) ORDER BY CHAIN_CODE, RESIDUE_SERIAL, CHEM_ATOM_ORDERING, SERIAL; -
Get the helices of the original asymmetric unit of an entry
SELECT ACCESSION_CODE,CHAIN_CODE,MODEL_SERIAL,HELIX_ID,HELIX_SERIAL,NUM_RESIDUES, LINEARITY,BEG_RESIDUE_SERIAL,BEG_CHEM_COMP_CODE,END_RESIDUE_SERIAL,END_CHEM_COMP_CODE FROM HELIX WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' AND NON_ASSEMBLY_VALID='Y'
-
Get the actual and the observed aminoacid sequence string of the chains of an entry
* SELECT ACCESSION_CODE,CHAIN_CODE,RES_SEQ FROM CHAIN_ALL_SEQ WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0' * SELECT ACCESSION_CODE,CHAIN_CODE,RES_SEQ FROM CHAIN_OBS_SEQ WHERE ACCESSION_CODE='1dn0'