UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase
Bacterial UDP-glucose dehydrogenase is essential for the formation of the antiphagocytic capsule that protects many virulent bacteria from the host's immune system. The homodimeric enzyme is composed of an N-terminal NAD+ dinucleotide binding domain and a C-terminal UDP-sugar binding domain connected by a long central alpha helix.
The enzyme catalyses the NAD+ dependent oxidation of UDP-glucose to UDP-glucuronic acid. In mammals this is the substrate for UDP-glucuronosyl transferases in the liver. UDP-glucuronosyl transferases catalyse the formation of glucuronide conjugates with various substances e.g. bilirubin - aiding its excretion.
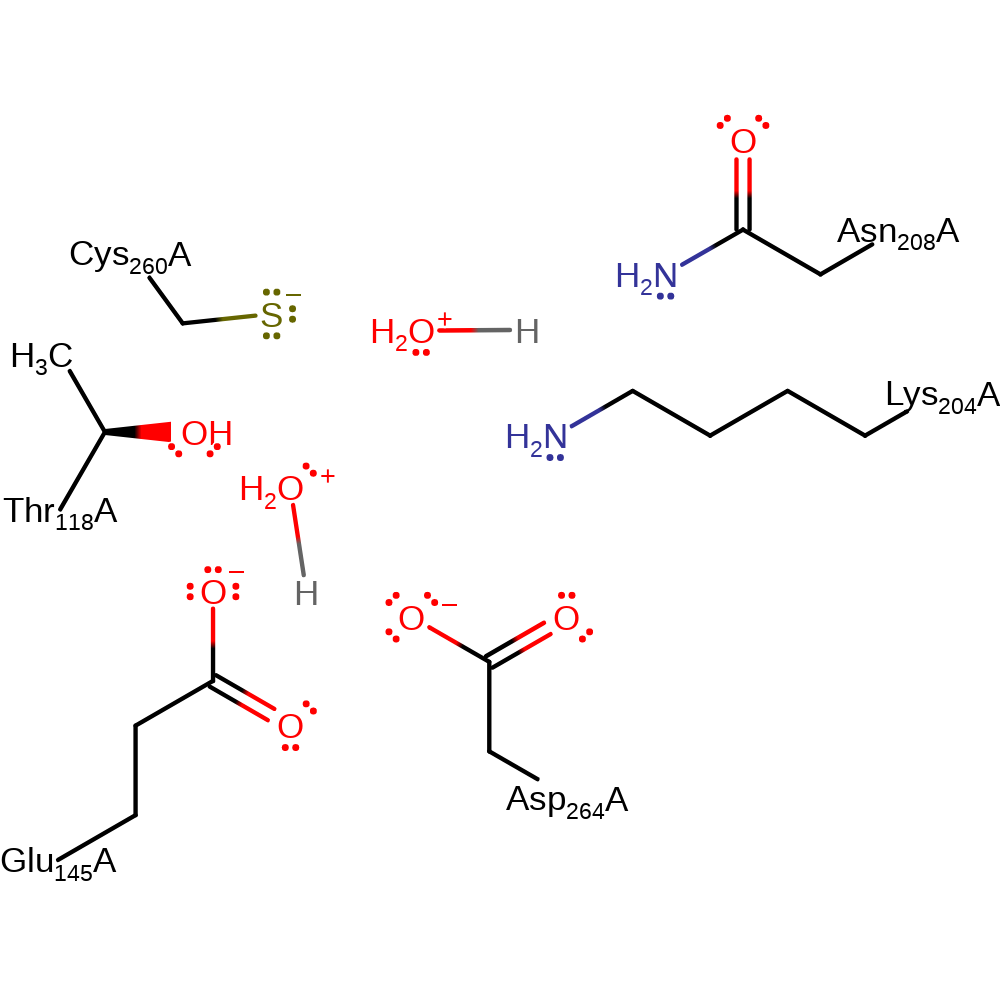
The active site contains residues contributed from the N- and C-terminal domains as well as from the central alpha-helix. Thr118 from the N-terminal forms a hydrogen bond to an ordered active site water molecule, that may be critical for the catalytic mechanism. Ser117 and Pro120 are also probably essential for proper orientation of the catalytic Thr118. The central alpha-helix contributes two active site residues; Lys204 and Asn208. Glu141 forms a hydrogen bond to the key catalytic residue Lys204. The C-terminal contributes two residues; Cys260 and Asp264, both having direct roles in the enzyme mechanism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0C0F4
 (1.1.1.22)
(1.1.1.22)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptococcus pyogenes (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dli
- THE FIRST STRUCTURE OF UDP-GLUCOSE DEHYDROGENASE (UDPGDH) REVEALS THE CATALYTIC RESIDUES NECESSARY FOR THE TWO-FOLD OXIDATION
(2.31 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1040.10
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1dli)
(see all for 1dli)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.22)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In this proposal, the primary C6'' hydroxyl of UDP-glucose is oxidised with the transfer of the pro-R hydride to C4 (NC4) on the si face of the nicotinamide ring of NAD+. This step is initiated by the transfer of a proton from the alcohol by water, activated by Asp264. Then, Cys260 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the newly formed carbonyl carbon. Collapse of the new oxyanion leads to the elimination of a second hydride ion. In the cleavage step, Glu145 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl, carbon, eliminating cysteine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dli) | ||
| Cys260 | Cys260A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. Thought to be negatively charged due to the optimum pH of the active site being around 9. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Asp264 | Asp264A | Acts as a general acid/base, activating the water molecule that performs the first proton abstraction of the mechanism. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu145 | Glu145A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from the water molecule that is responsible for the final hydrolysis step. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys204, Thr118, Asn208 | Lys204A, Thr118A, Asn208A | Act to stabilise the reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, proton relay, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Campbell RE et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 7012-7023. The first structure of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase reveals the catalytic residues necessary for the two-fold oxidation. DOI:10.2210/pdb1dlj/pdb. PMID:10841783.
- Chen YY et al. (2011), J Struct Biol, 175, 300-310. Conformational change upon product binding to Klebsiella pneumoniae UDP-glucose dehydrogenase: A possible inhibition mechanism for the key enzyme in polymyxin resistance. DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2011.04.010. PMID:21536136.
- Rocha J et al. (2011), J Bacteriol, 193, 3978-3987. Structure of Burkholderia cepacia UDP-Glucose Dehydrogenase (UGD) BceC and Role of Tyr10 in Final Hydrolysis of UGD Thioester Intermediate. DOI:10.1128/jb.01076-10. PMID:21602353.
- Ge X et al. (2004), Eur J Biochem, 271, 14-22. Active site residues and mechanism of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase. PMID:14686915.
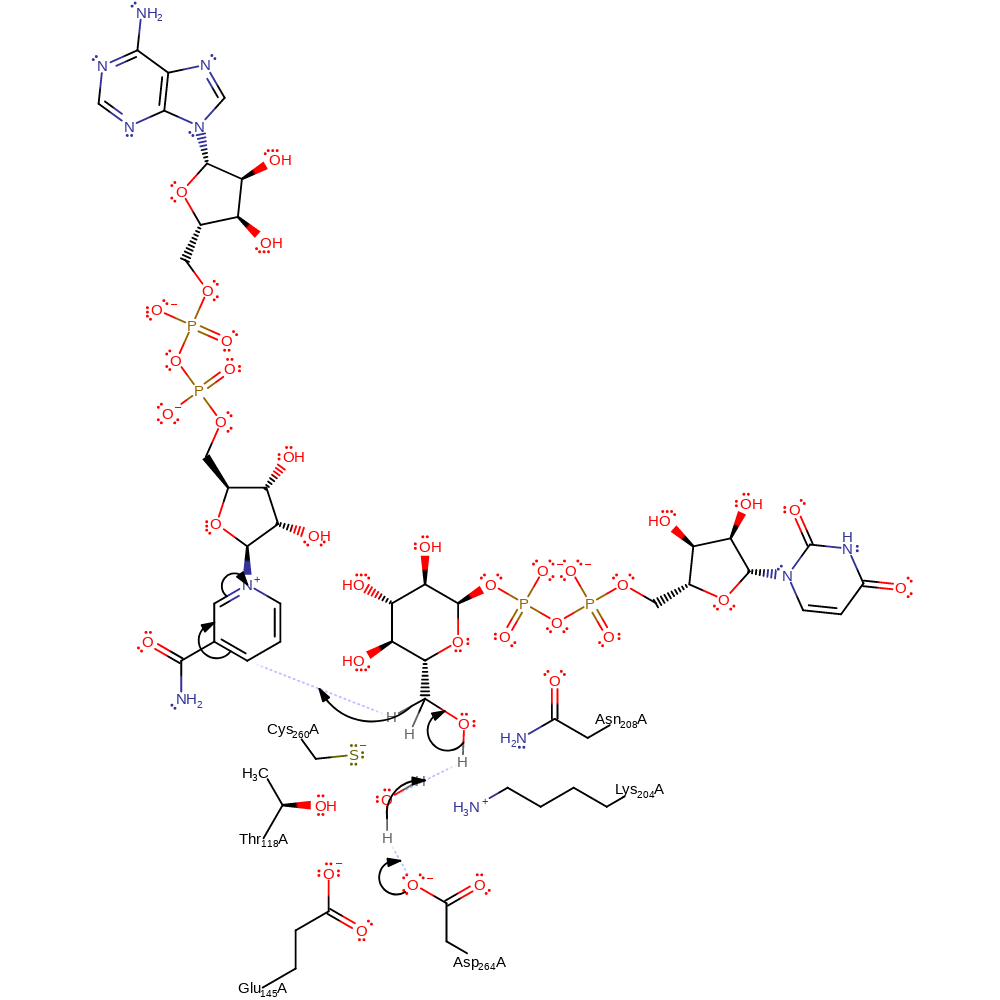
Step 1. Asp264 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the CH3OH group of UDP, which causes the elimination of a hydride which adds to NAD
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, proton relay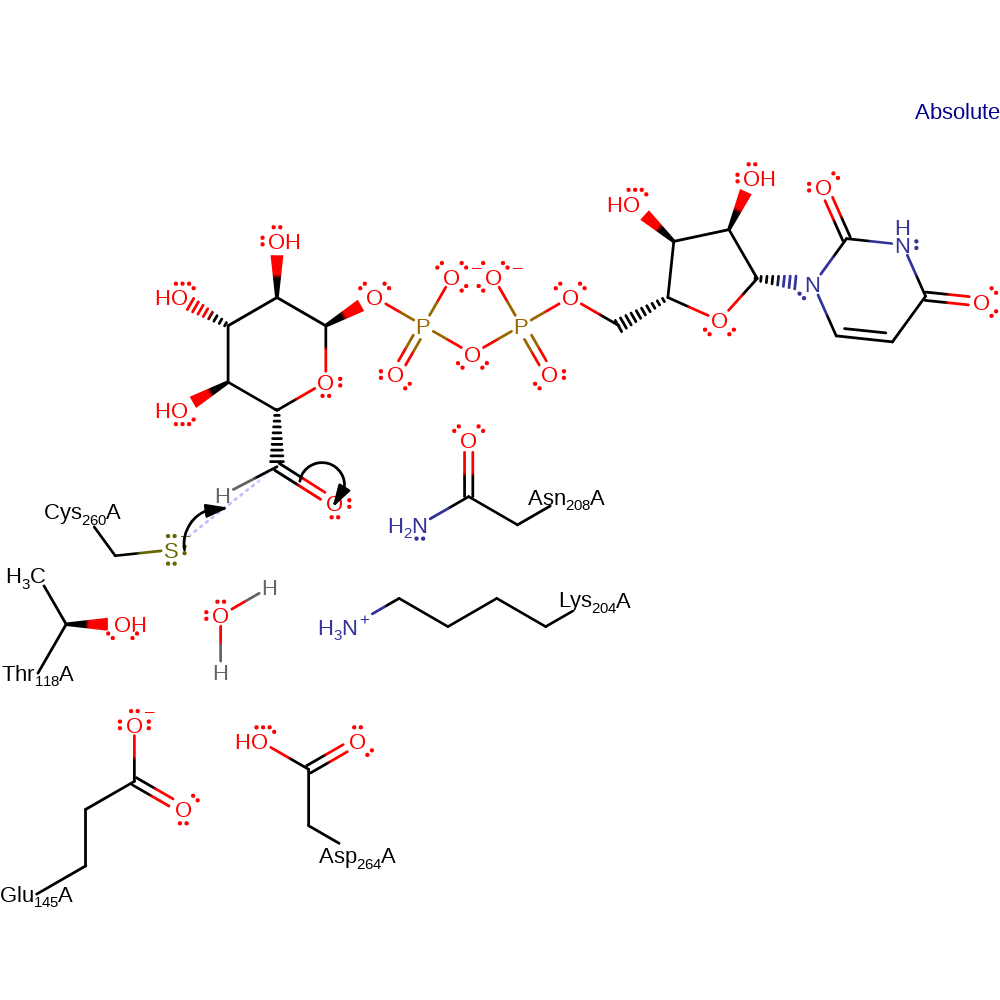
Step 2. Cys260 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the formed carbonyl carbon in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys260A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation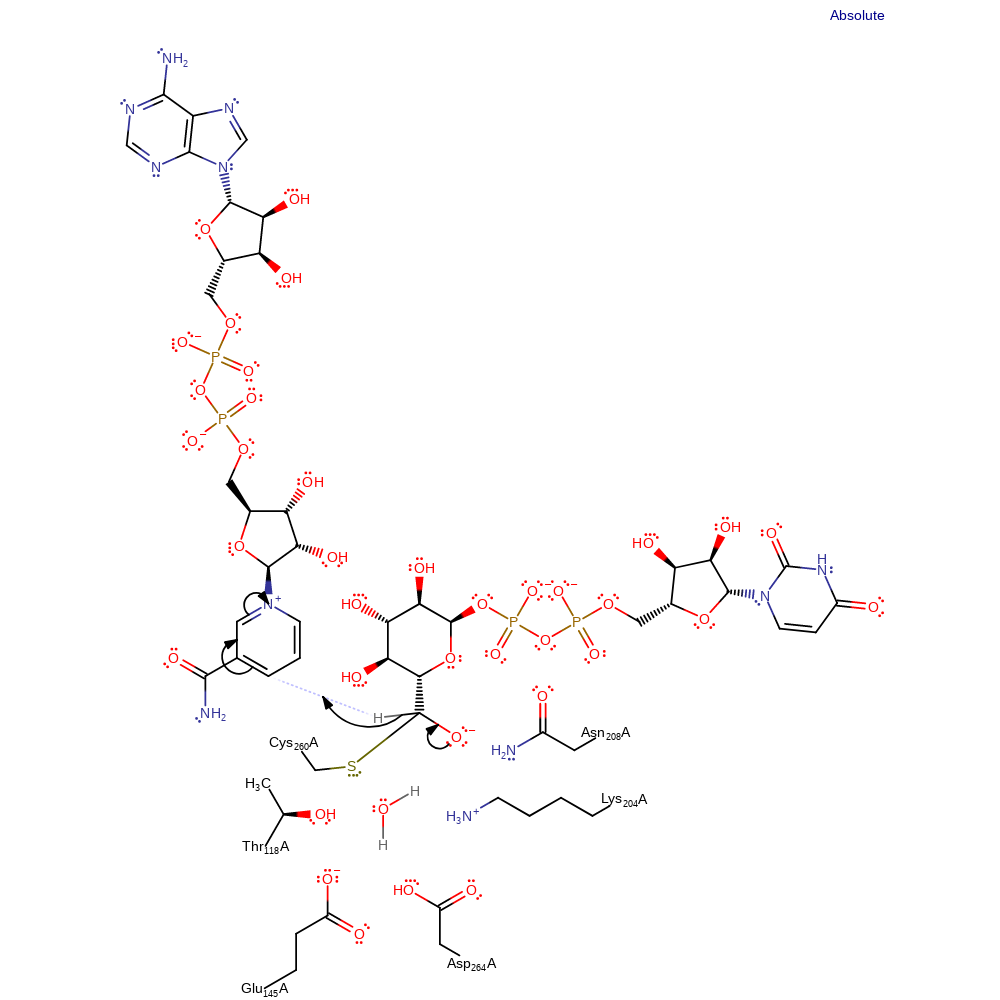
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating a second hydride, which adds to a second molecule of NAD.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys260A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition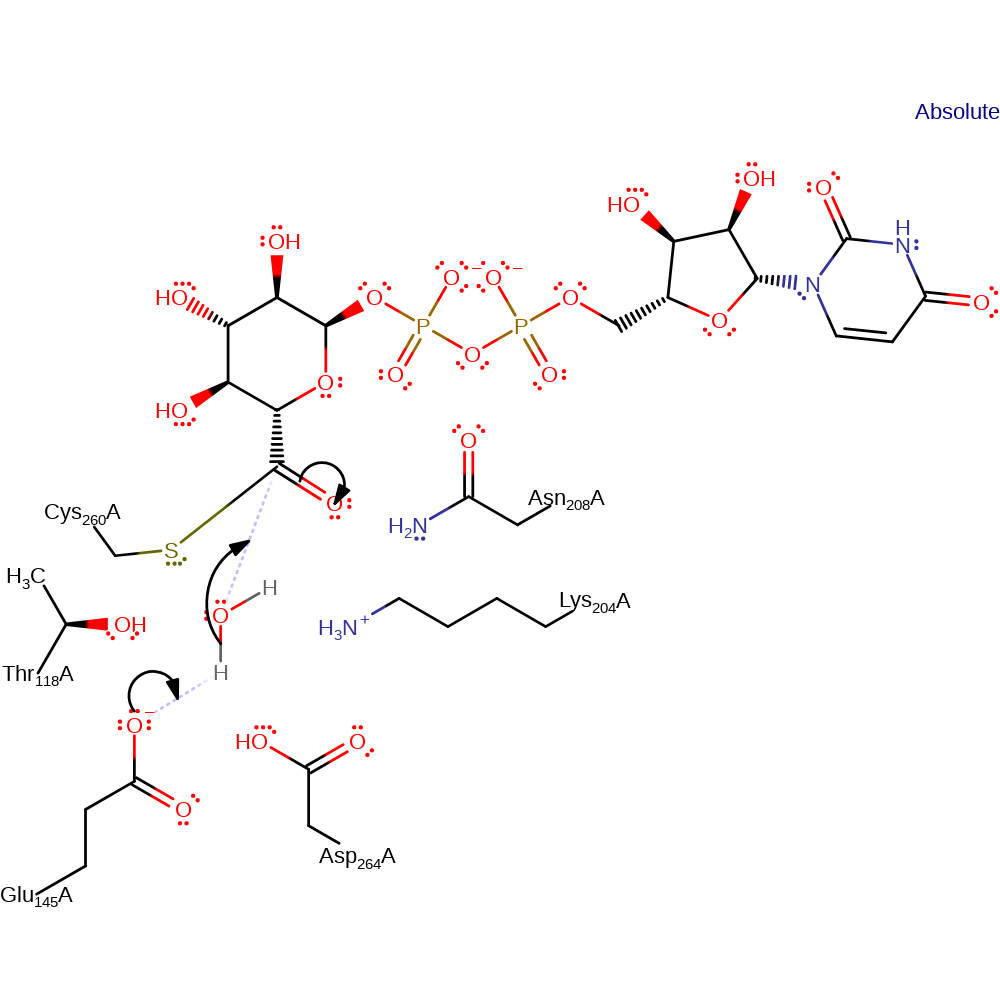
Step 4. Glu145 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently bound substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys260A | covalently attached |
| Glu145A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys260A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage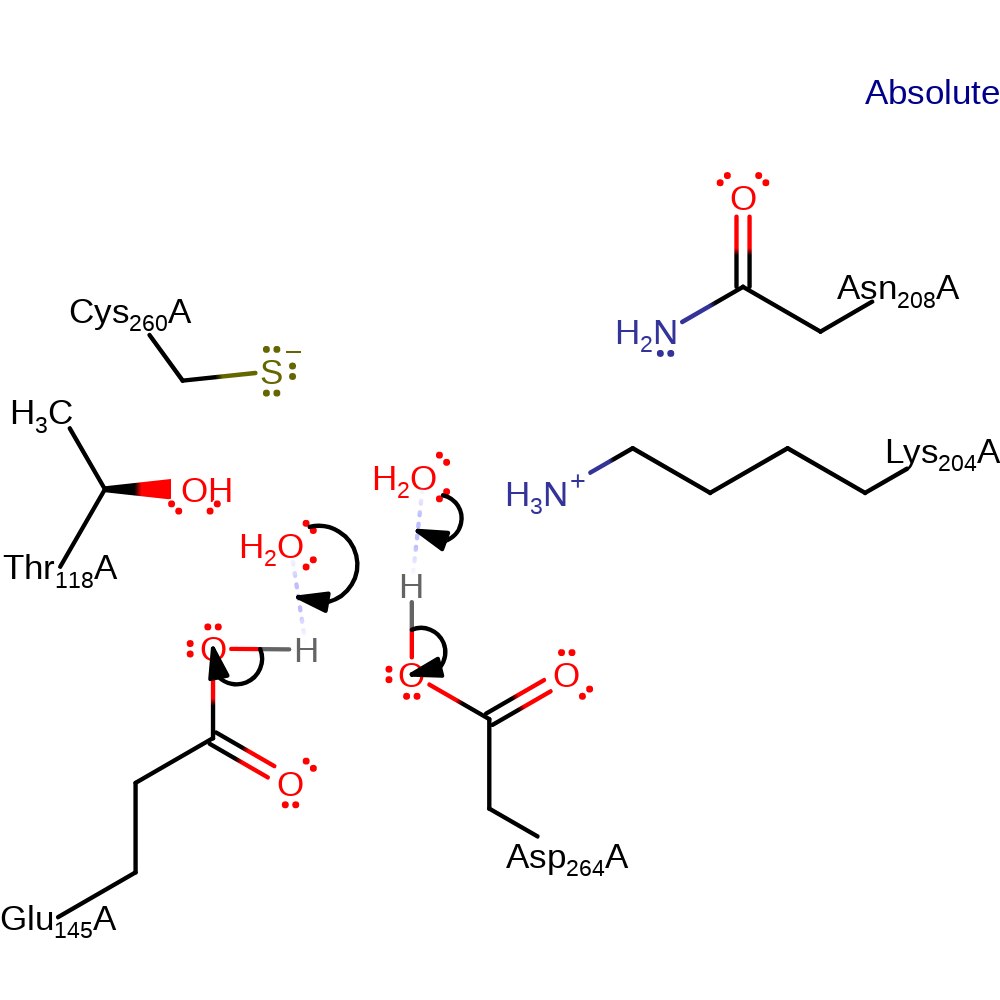
Step 6. In an inferred return step, two water molecules deprotonate Glu145 and Asp264.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp264A | proton donor |
| Glu145A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
In this proposal, the primary C6'' hydroxyl of UDP-glucose is oxidised with the transfer of the pro-R hydride to C4 (NC4) on the si face of the nicotinamide ring of NAD+. This step is initiated by the transfer of a proton from the alcohol by Lys204. Then, Cys260 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the newly formed carbonyl carbon. Collapse of the new oxyanion leads to the elimination of a second hydride ion. In the cleavage step, Glu145 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl, carbon, eliminating cysteine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dli) | ||
| Lys204 | Lys204A | Acts as a general acid/base, responsible for the initial proton abstraction. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Cys260 | Cys260A | Acts as a catalytic nucleophile. Thought to be negatively charged due to the optimum pH of the active site being around 9 | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Asp264 | Asp264A | Activates the catalytic water through hydrogen bonding. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu145 | Glu145A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting a proton from the water molecule that is responsible for the final hydrolysis step. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Thr118, Asn208 | Thr118A, Asn208A | Act to stabilise the reactive intermediates. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Campbell RE et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 7012-7023. The first structure of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase reveals the catalytic residues necessary for the two-fold oxidation. DOI:10.2210/pdb1dlj/pdb. PMID:10841783.
- Chen YY et al. (2011), J Struct Biol, 175, 300-310. Conformational change upon product binding to Klebsiella pneumoniae UDP-glucose dehydrogenase: A possible inhibition mechanism for the key enzyme in polymyxin resistance. DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2011.04.010. PMID:21536136.
- Ge X et al. (2004), Eur J Biochem, 271, 14-22. Active site residues and mechanism of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase. PMID:14686915.
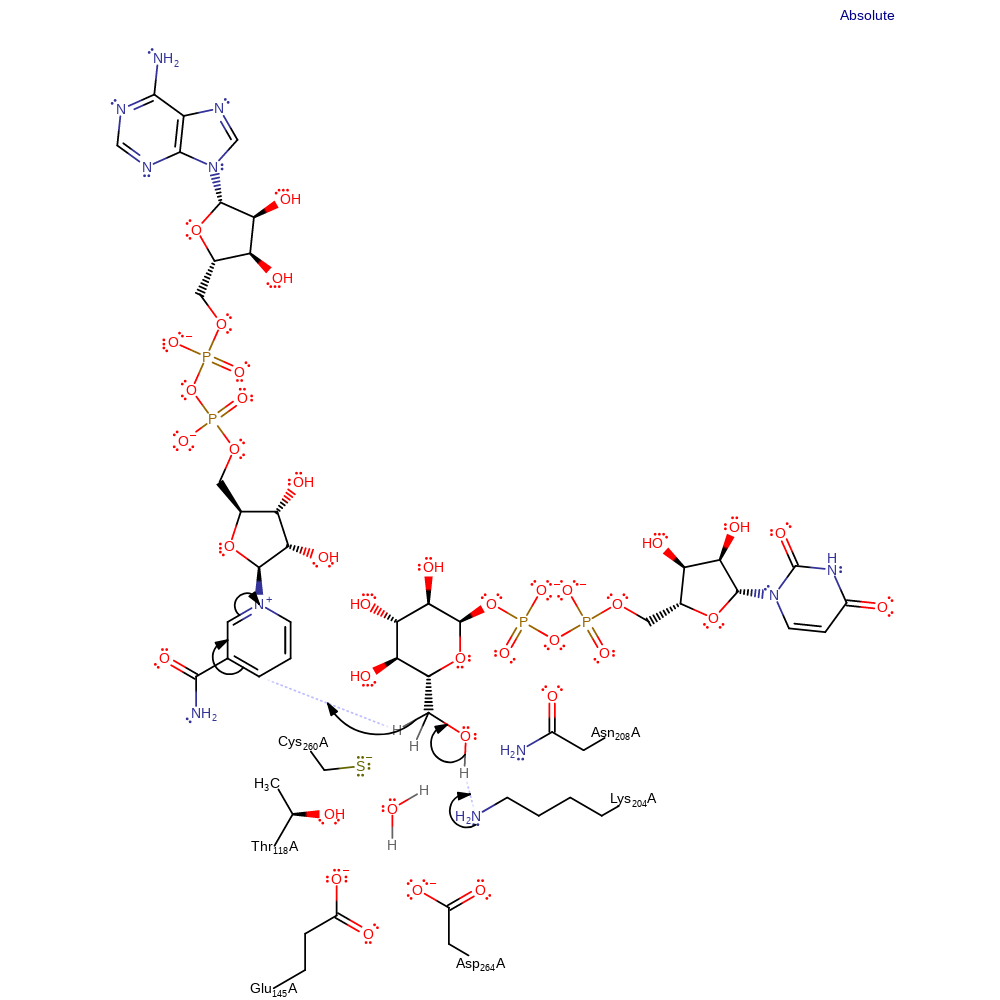
Step 1. Lys204 deprotonates the CH3OH group of UDP, which causes the elimination of a hydride which adds to NAD.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys204A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall product formed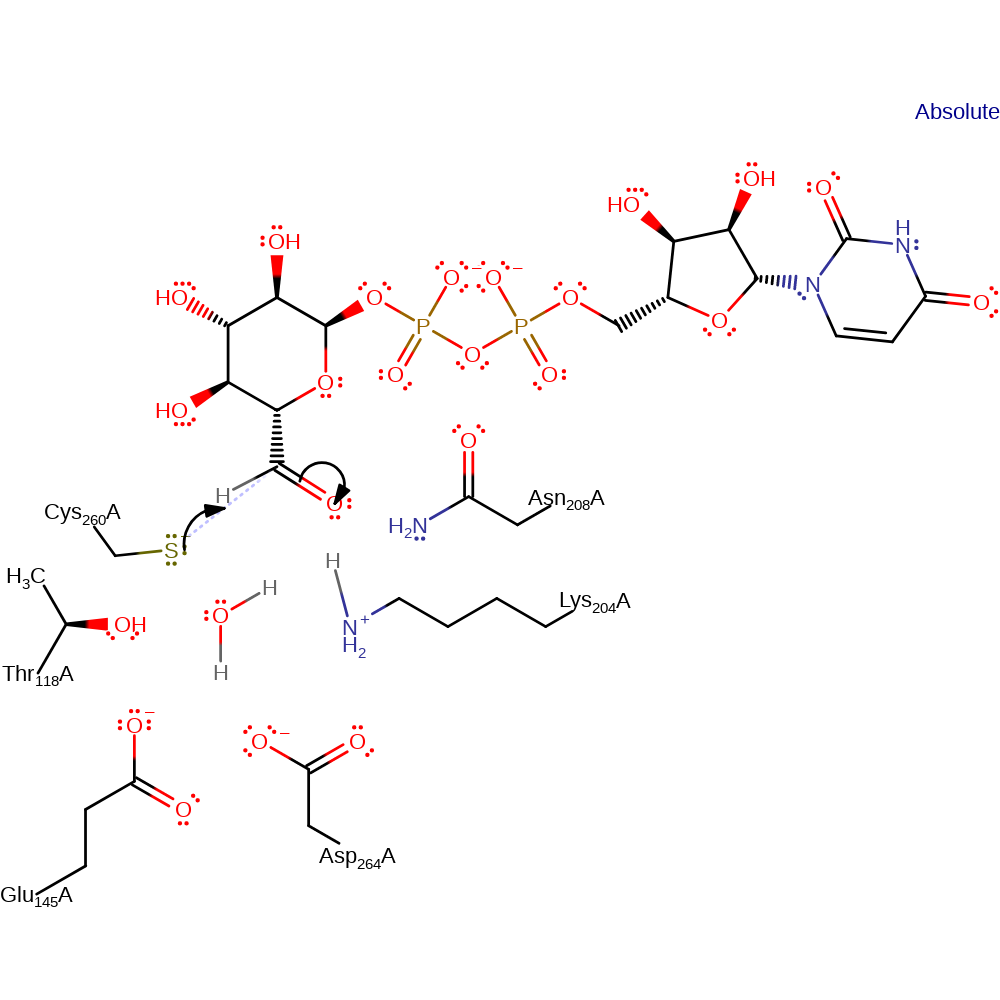
Step 2. Cys260 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the formed carbonyl carbon in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys260A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation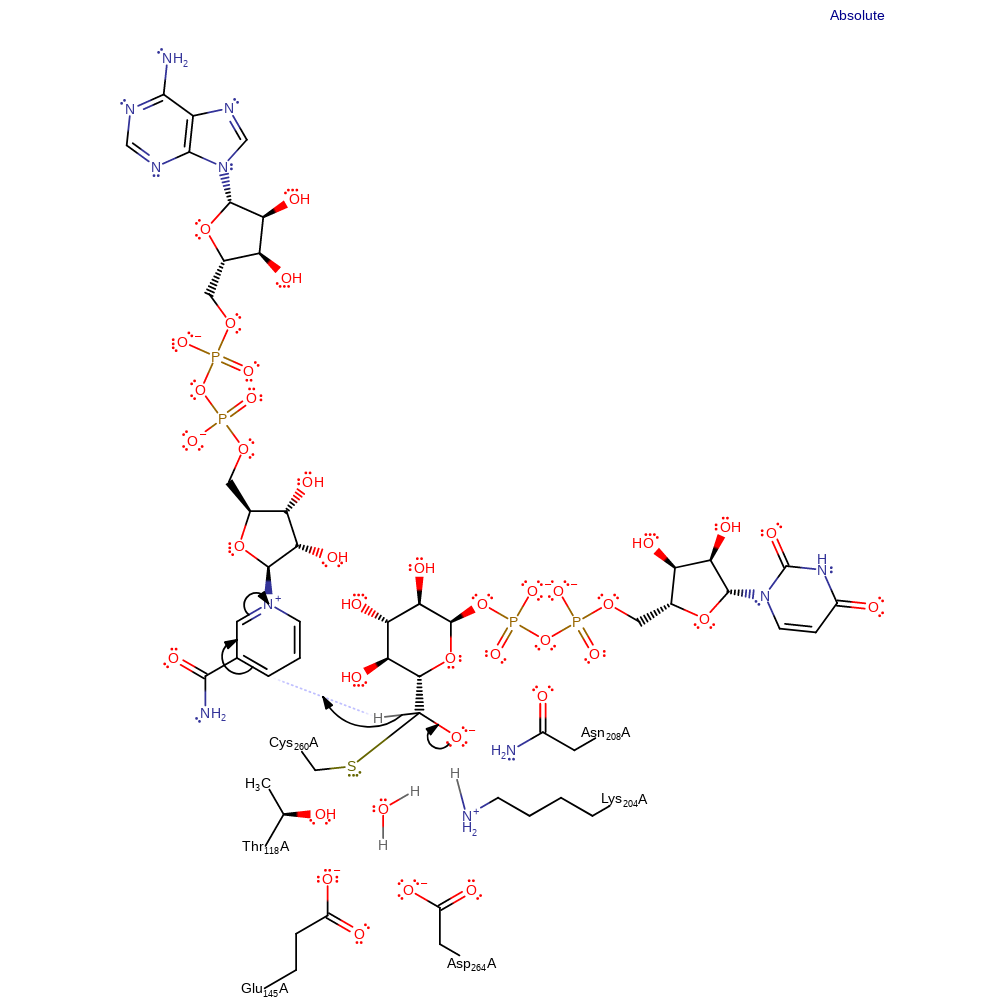
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating a second hydride, which adds to a second molecule of NAD.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys260A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition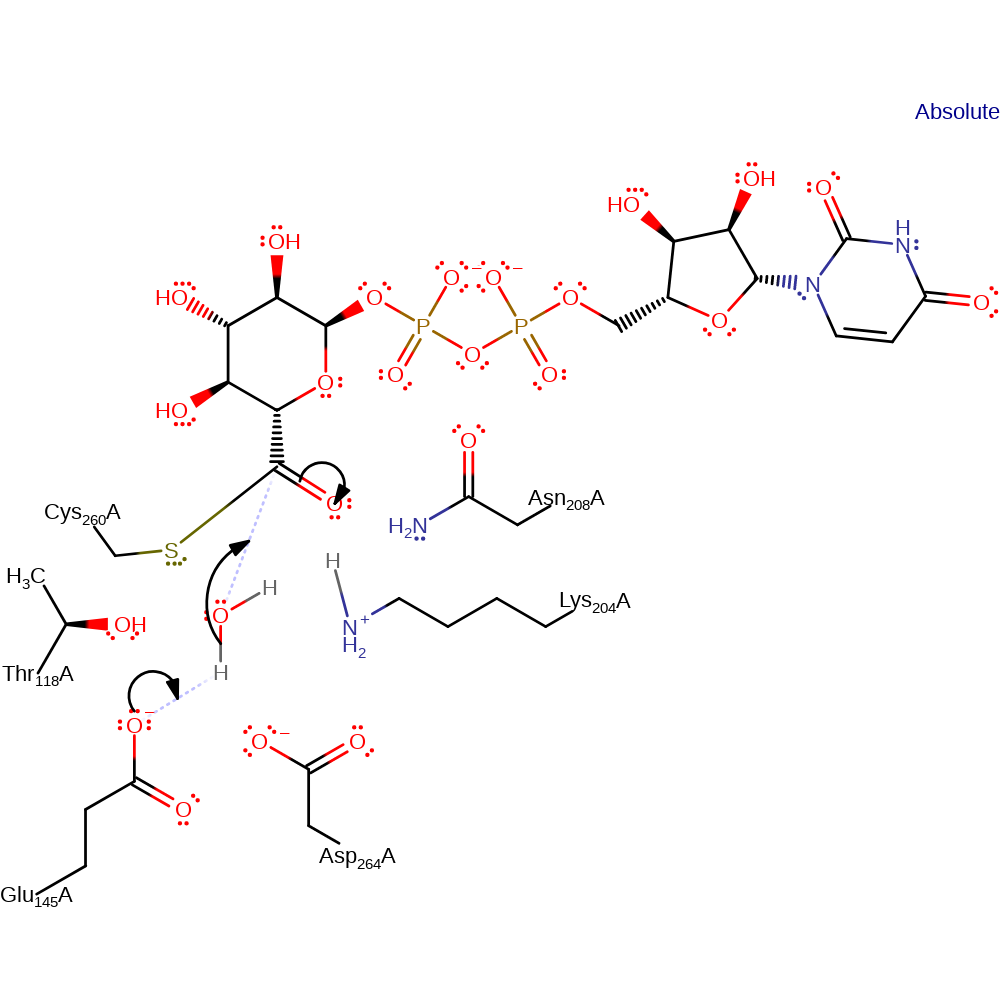
Step 4. Glu145 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently bound substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys260A | covalently attached |
| Glu145A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys204A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn208A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys260A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
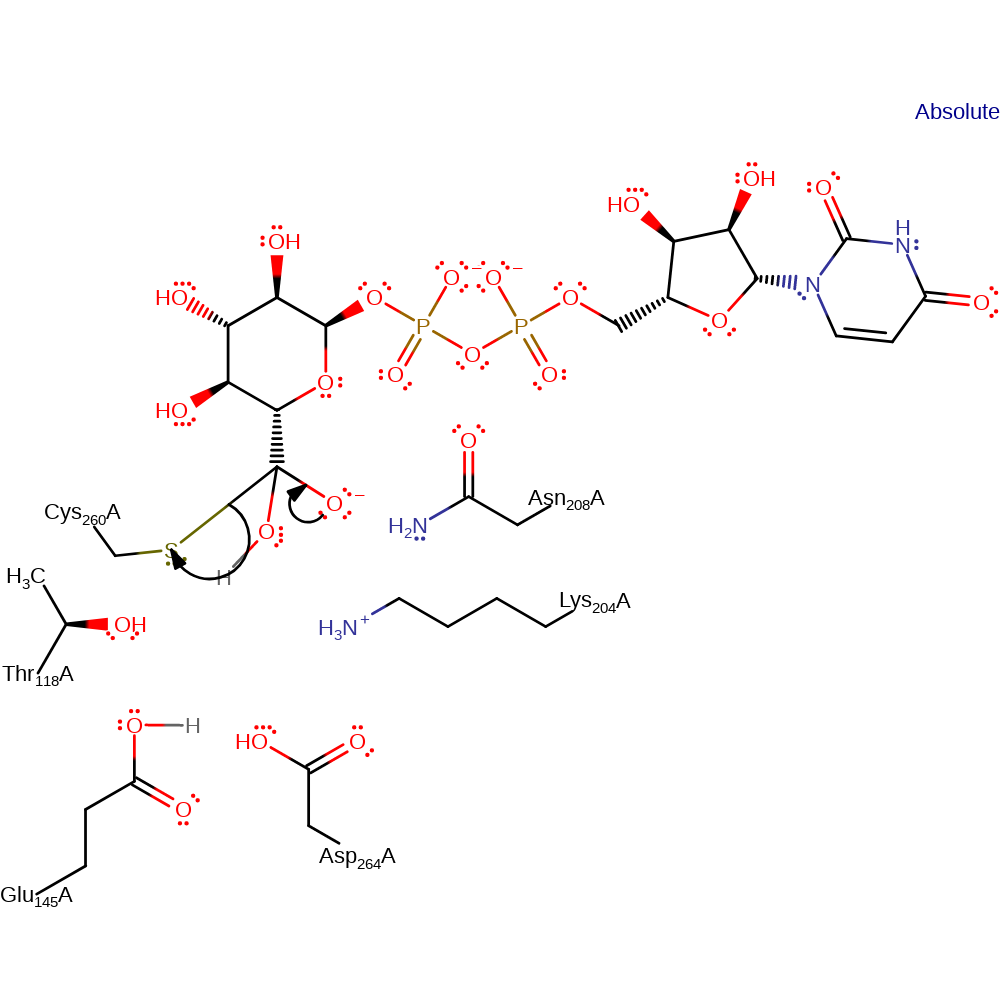
Step 6. In an inferred return step, two water molecules deprotonate Glu145 and Asp264.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp264A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr118A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu145A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| Lys204A | proton donor |






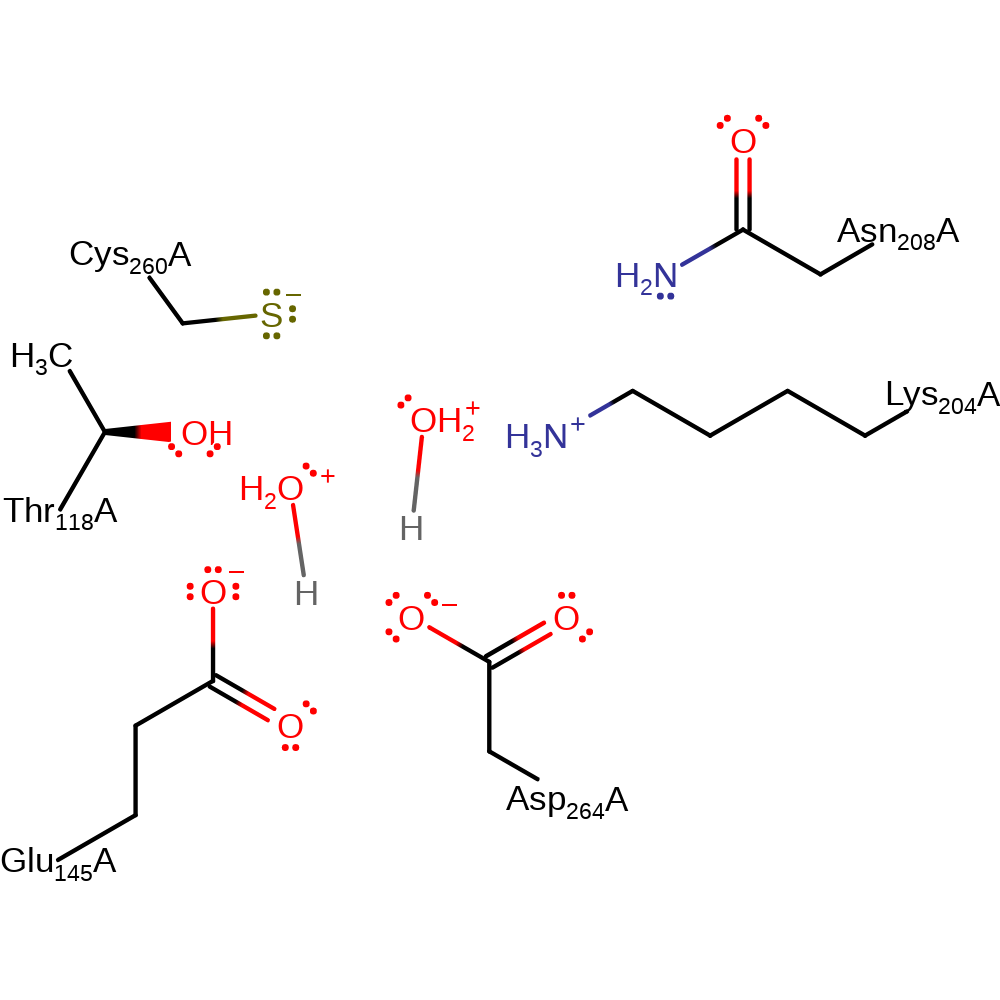 Download:
Download: 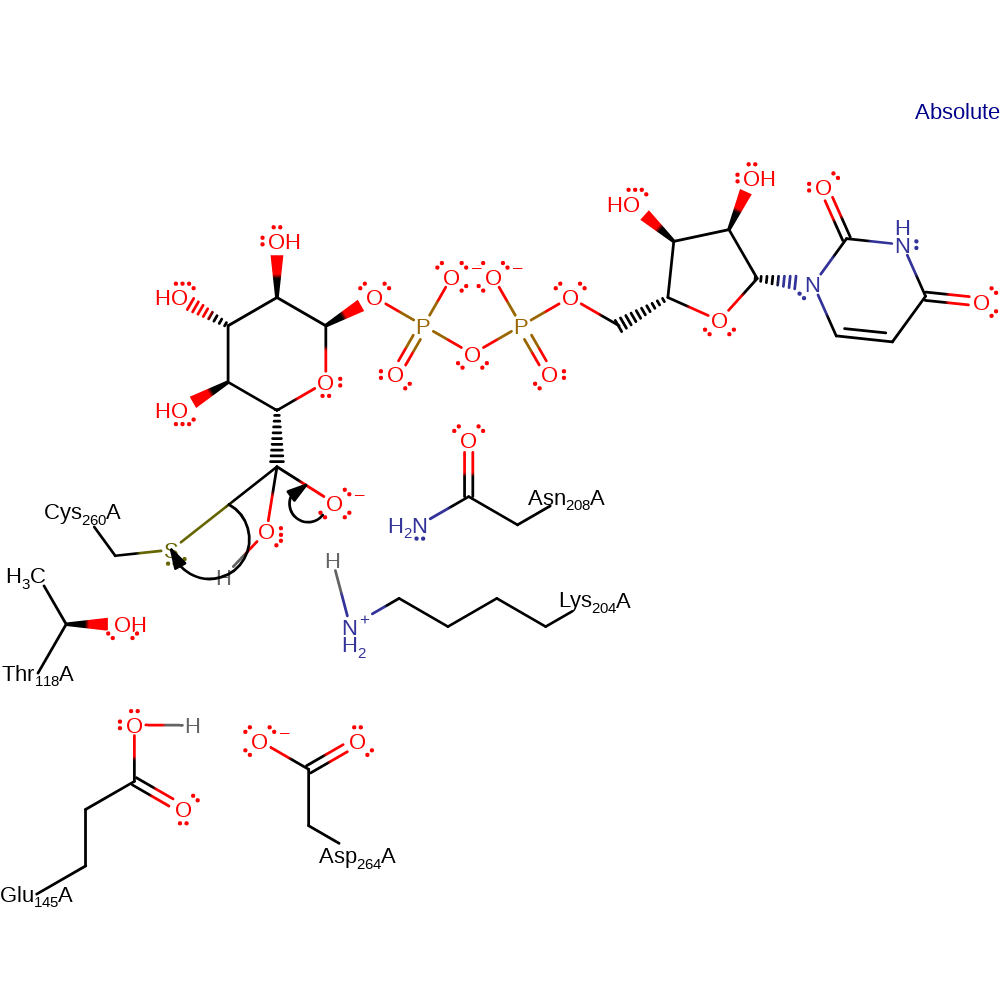
 Download:
Download: