Carboxypeptidase D
Carboxypeptidase D is a serine protease which specifically removes basic or hydrophobic residues from the C-terminus of the substrate protein.
Carboxypeptidase D is a member of the alpha beta hydrolase family and contains a Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad typical of the family.
In humans, mutations arising in this enzyme result in genetic disorders such as galactosialidosis, a disease associated with incorrect protein degradation in the lysosome.
Carboxypeptidase D from yeast and wheat have had their structures determined, The wheat catalytic triad is made up of residues from both subunits of the homodimer whilst yeast carboxypeptidase D is a monomer, however, both have similar active site geometries.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08819
 (3.4.16.6)
(3.4.16.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Triticum aestivum (bread wheat)

- PDB
-
1whs
- STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF L-BENZYLSUCCINATE WITH WHEAT SERINE CARBOXYPEPTIDASE II AT 2.0 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 3.40.50.11320
3.40.50.11320  (see all for 1whs)
(see all for 1whs)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.16.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Carboxypeptidase D uses a catalytic triad to activate serine 146 as a nucleophile to attack the scissile peptide bond. Histidine 397 and aspartate 338 from the neighbouring subunit complete the triad. The backbone amides of glycine 53 and tyrosine 147 make up the oxyanion hole to stabilise the tetrahedral intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1whs) | ||
| Ser158 | Ser146(153)A | Acts as a nucleophile in the acylation step. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
| Gly62 (main-N), Tyr159 (main-N) | Gly53(57)A (main-N), Tyr147(154)A (main-N) | The main chain amide forms part of the oxyanion hole. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp361 | Asp338(75)B | Part of the Ser-His-Asp triad that activates Ser146 for nucleophilic attack. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| His413 | His397(127)B | Part of the Ser-His-Asp triad that activates Ser146 for nucleophilic attack. His397 acts as a general acid/base, deprotonating Ser146 and furnishes the proton to the first product. It then deprotonates water for the step in which Ser146 is regenerated. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Bullock TL et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 11127-11134. Structure of the Complex of L-Benzylsuccinate with Wheat Serine Carboxypeptidase II at 2.0-.ANG. Resolution. DOI:10.1021/bi00203a009. PMID:7727364.
- Mortensen UH et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 508-517. Site-directed mutagenesis on (serine) carboxypeptidase Y. A hydrogen bond network stabilizes the transition state by interaction with the C-terminal carboxylate group of the substrate. DOI:10.1021/bi00168a016. PMID:7904479.
- Stennicke HR et al. (1994), Protein Eng, 7, 911-916. Effects of introduced aspartic and glutamic acid residues on the Pi substrate specificity, pH dependence and stability of carboxypeptidase Y. DOI:10.1093/protein/7.7.911. PMID:7971953.
- Liao DI et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 9796-9812. Refined atomic model of wheat serine carboxypeptidase II at 2.2-.ANG. resolution. DOI:10.1021/bi00155a037. PMID:1390755.
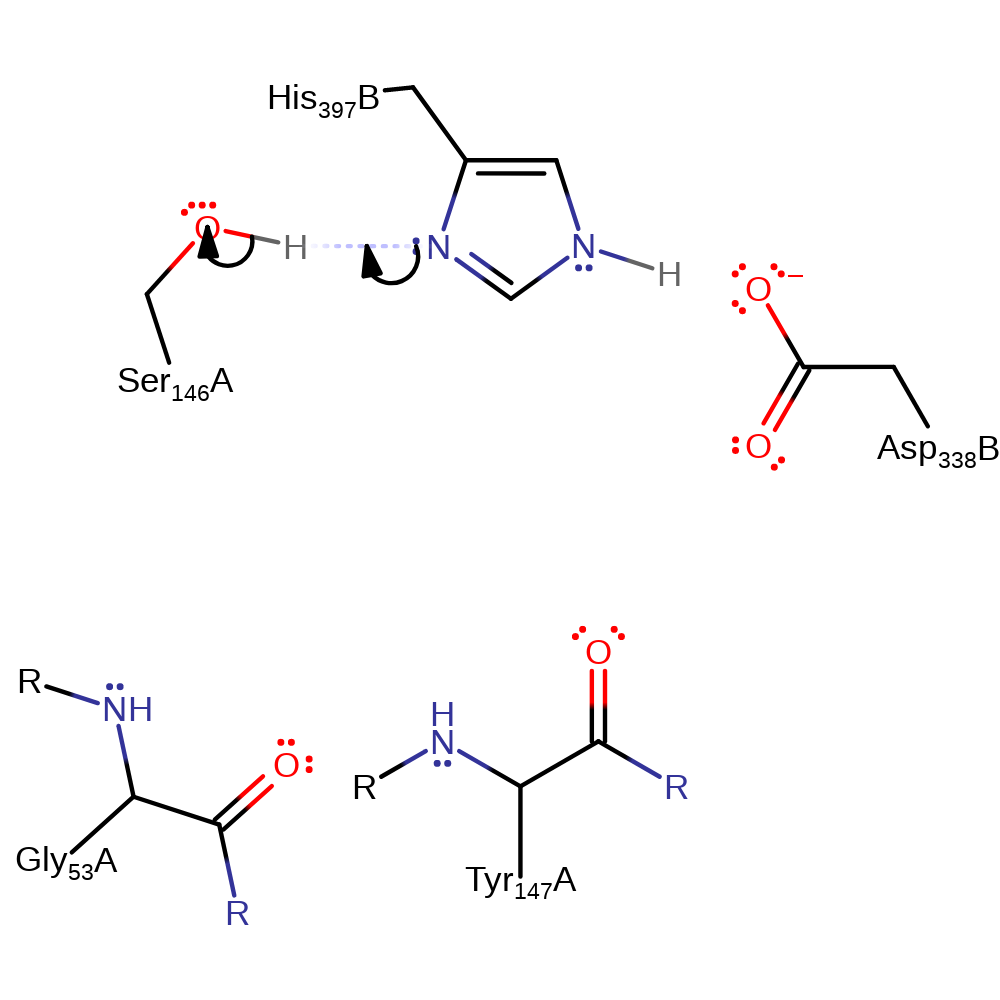
Step 1. His397, of the Ser146-His397-Asp338 triad, deprotonates Ser146.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp338(75)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Ser146(153)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His397(127)B | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
| Ser146(153)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer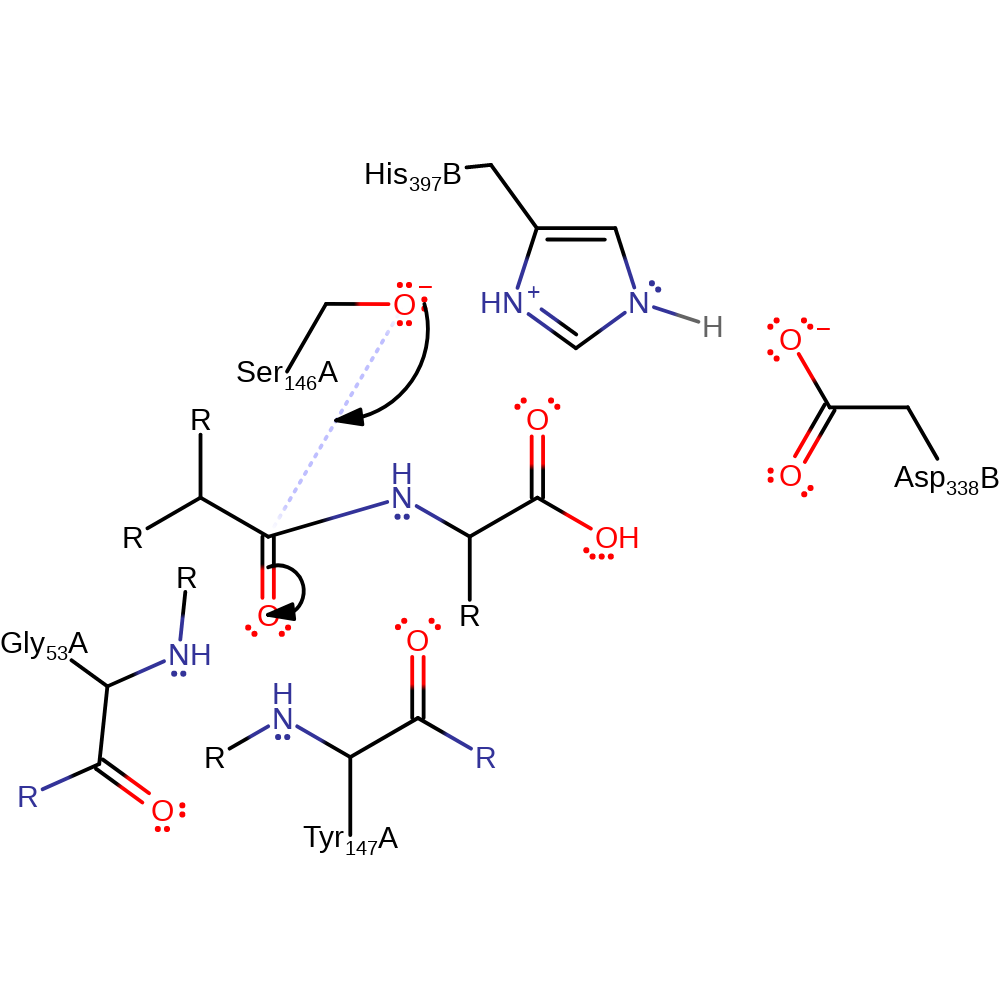
Step 2. Ser146 attacks the carbonyl carbon of the substrate in a nucleophilic addition, resulting in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly53(57)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp338(75)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser146(153)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His397(127)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr147(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser146(153)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation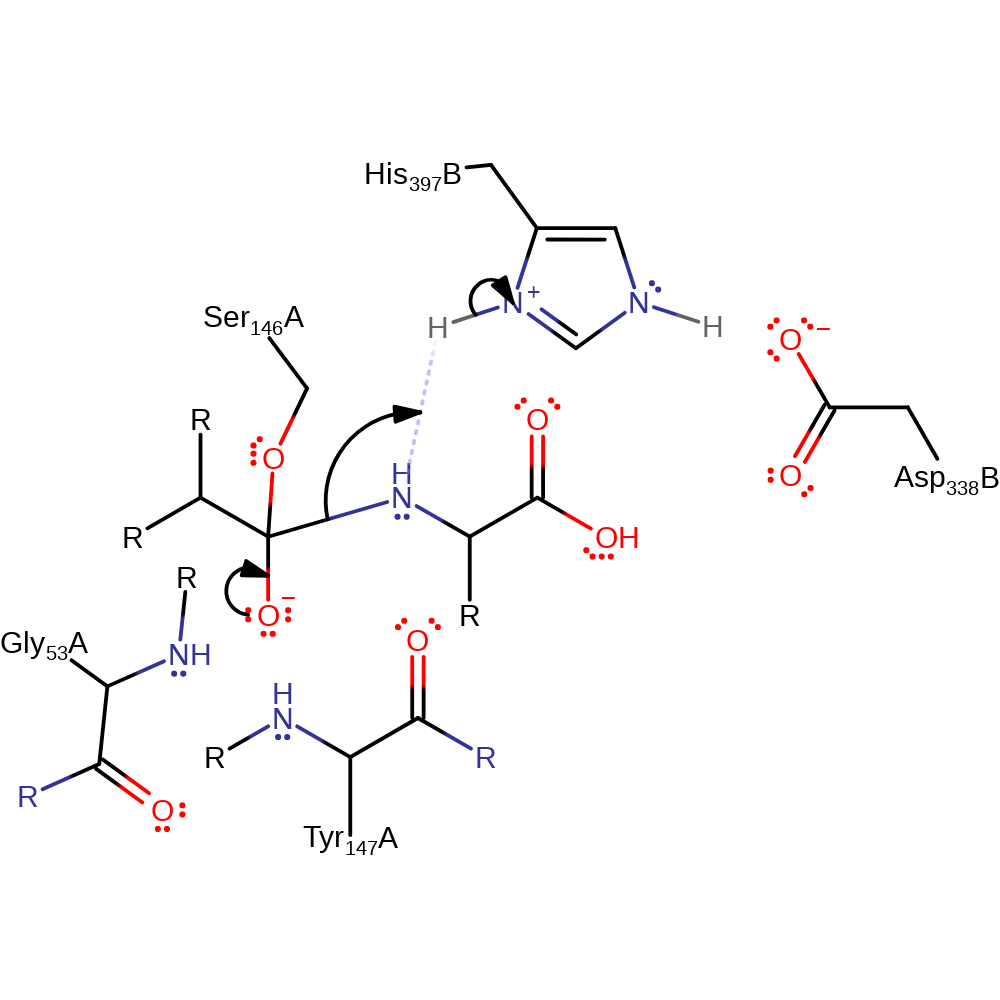
Step 3. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, cleaving the C-N bond, the nitrogen of which deprotonates His397.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly53(57)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp338(75)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Ser146(153)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His397(127)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr147(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His397(127)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation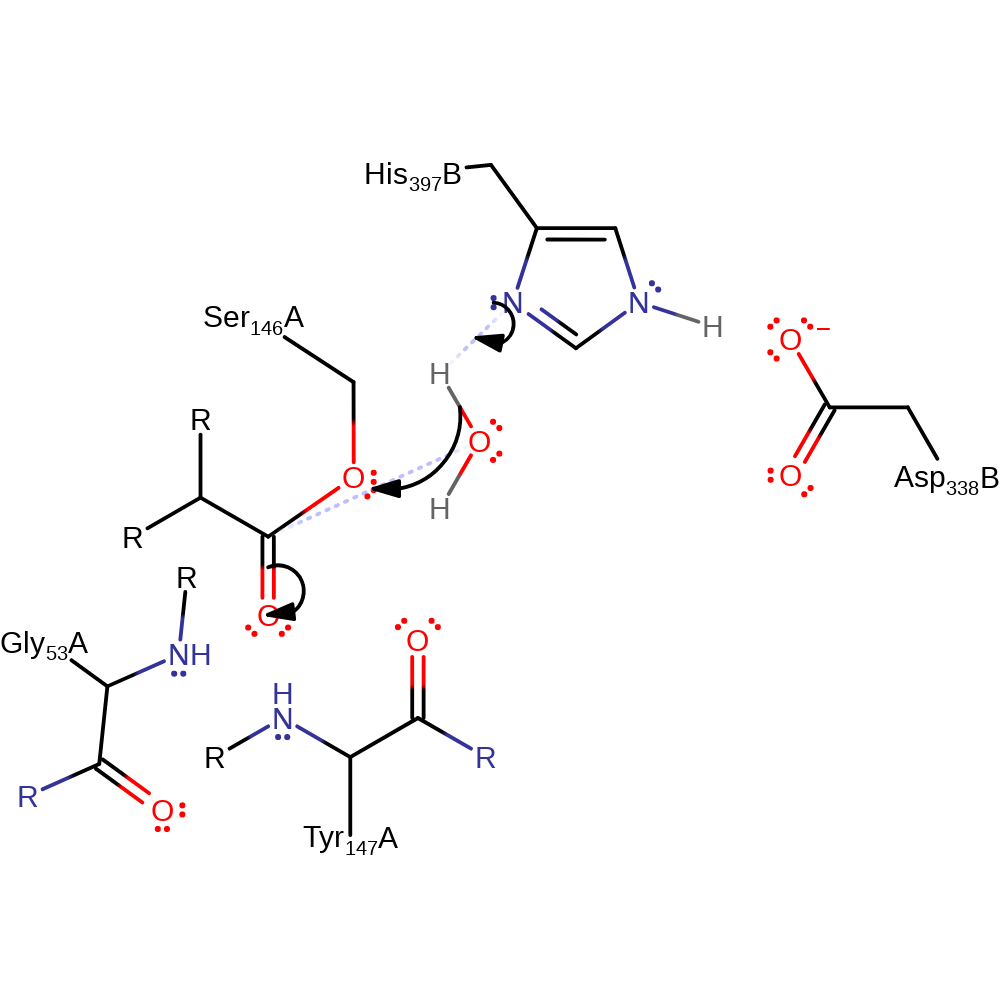
Step 4. His397 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-enzyme substrate, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly53(57)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp338(75)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Ser146(153)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His397(127)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr147(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His397(127)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation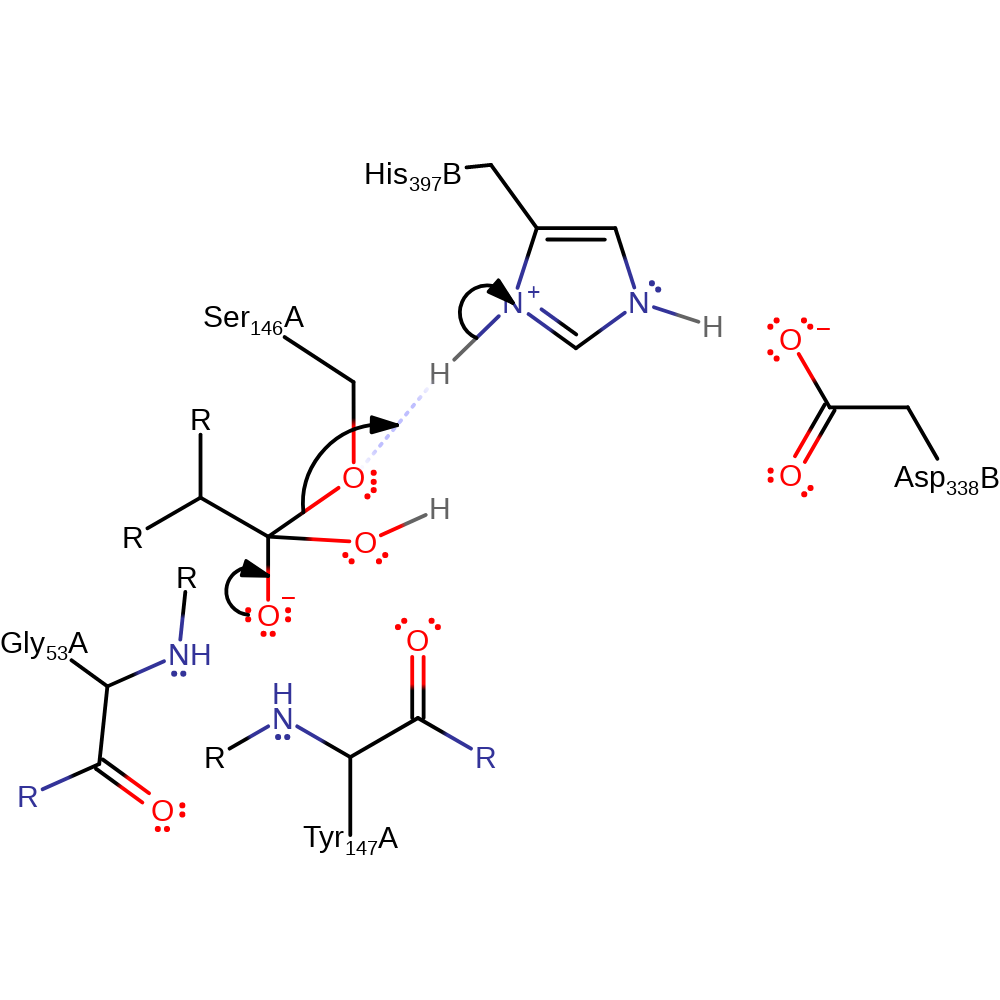
Step 5. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating Ser146, which deprotonates His397.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly53(57)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp338(75)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| Ser146(153)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His397(127)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr147(154)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His397(127)B | proton donor |
| Ser146(153)A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |



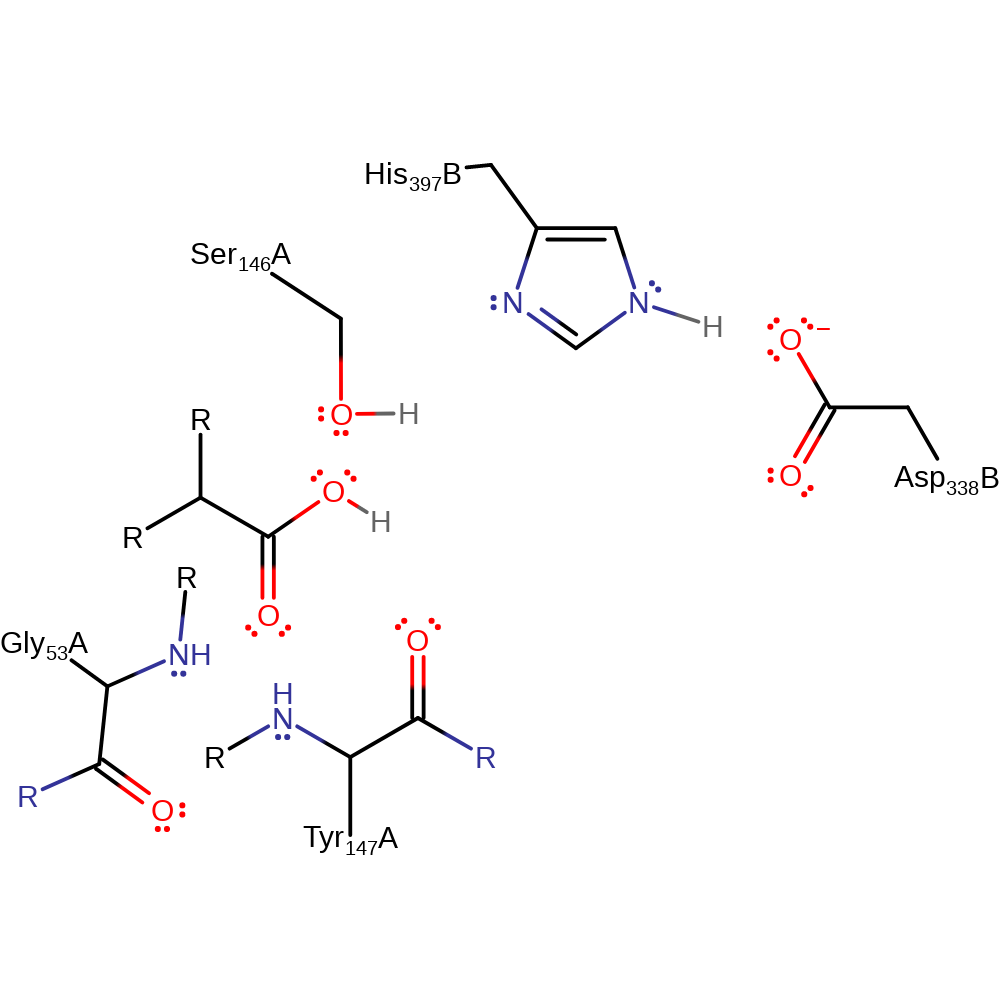 Download:
Download: