Vanadium-dependent bromoperoxidase (organic molecule bromination)
V-BPO, isolated from Ascophyllum nodosum, is a vanadium-dependent haloperoxidase.
It catalyses the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide to form hypohalides, which can go on to react with organic substrates in halogenation reactions. In this entry, we show one of the side reactions of the vanadium-dependent haloperoxidases: bromination of phenols, the reaction produces 4-bromophenol in higher yields than the 2,4-dibromophenol. The enzyme is known to halogenate many other organic substrates including phenols, indoles, terpenes, and pyrroles.
V-BPO has the ability to oxidise bromide and, to a lesser extent, chloride and iodide.
V-BPO contains a vanadium(V) ion with a trigonal bipyramidal coordination sphere. It is coordinated to His486 and a hydroxide in the axial positions, and two oxygen atoms and a hydroxide in the equatorial positions.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P81701
 (1.11.1.18)
(1.11.1.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Ascophyllum nodosum (Knotted wrack)

- PDB
-
1qi9
- X-RAY SIRAS STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF A VANADIUM-DEPENDENT HALOPEROXIDASE FROM ASCOPHYLLUM NODOSUM AT 2.0 A RESOLUTION
(2.05 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.606.10
 (see all for 1qi9)
(see all for 1qi9)
- Cofactors
- Vanadate(3-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.11.1.18)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
An oxygen of hydrogen peroxide attacks the vanadium centre and causes the elimination of the axial hydroxide, which then deprotonates the bound peroxide to form water. The second oxygen of the peroxide ligand then attacks the vanadium centre and causes the elimination of an equatorial oxygen, which then abstracts the second peroxide proton. This forms a side-on vanadium-peroxo species. Bromide attacks one of the oxygens of the peroxo group, causing the O-O bond to break and leading to the formation of an axial vanadium-OBr complex.
The substrate hydrocarbon then binds in the active site and is bromonated by the activated O-Br species.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qi9) | ||
| Lys341 | Lys341A | Lys341 is thought to polarise the vanadium-bound peroxo group and increase its susceptibility to attack by bromide. Lys341 forms a hydrogen bond to His411 and this is thought to modulate its polarising power. This is thought to be partially responsible for the selectivity of the enzyme for bromide over chloride. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His411 | His411A | His411 forms a hydrogen bond to Lys341, buffering its polarising power towards the peroxo group. This is thought to be partially responsible for the selectivity of the enzyme for bromide over chloride. | increase basicity, increase electrophilicity |
| His418 | His418A | His418 increases the nucleophilicity of the axial hydroxide, thus making it more able to abstract a proton from hydrogen peroxide. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His486 | His486A | His486 coordinates to the vanadate ion and is thought to be necessary for the formation of the vanadium-peroxo intermediate. It is thought that it is responsible for the lengthening and possible weakening of the axial V-O bond. | activator, metal ligand |
| Asp490 | Asp490A | Helps activate and position the vanadate binding His486. | activator |
| Arg349, Ser416, Arg480, Gly417 (main-N) | Arg349A, Ser416A, Arg480A, Gly417A (main-N) | Forms the positive binding site for the cofactor; activating and stabilising it. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, dehydration, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aromatic bimolecular electrophilic addition, inferred reaction step, aromatic bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Wischang D et al. (2012), Tetrahedron, 68, 9456-9463. Bromination of phenols in bromoperoxidase-catalyzed oxidations. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2012.08.081.
- Frank A et al. (2016), Chembiochem, 17, 2028-2032. Characterization of a Cyanobacterial Haloperoxidase and Evaluation of its Biocatalytic Halogenation Potential. DOI:10.1002/cbic.201600417. PMID:27542168.
- Rehder D (2015), Metallomics, 7, 730-742. The role of vanadium in biology. DOI:10.1039/c4mt00304g. PMID:25608665.
- Wischang D et al. (2013), Dalton Trans, 42, 11926-. Vanadate-dependent bromoperoxidases from Ascophyllum nodosum in the synthesis of brominated phenols and pyrroles. DOI:10.1039/c3dt51582f. PMID:23881071.
- Littlechild J et al. (2009), J Inorg Biochem, 103, 617-621. Vanadium containing bromoperoxidase – Insights into the enzymatic mechanism using X-ray crystallography. DOI:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.01.011. PMID:19230976.
- Weyand M et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 293, 595-611. X-ray structure determination of a vanadium-dependent haloperoxidase from Ascophyllum nodosum at 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3179. PMID:10543953.
- Butler A (1998), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2, 279-285. Vanadium haloperoxidases. DOI:10.1016/s1367-5931(98)80070-7.
- Tschirret-Guth RA et al. (1994), J Am Chem Soc, 116, 411-412. Evidence for organic substrate binding to vanadium bromoperoxidase. DOI:10.1021/ja00080a063.
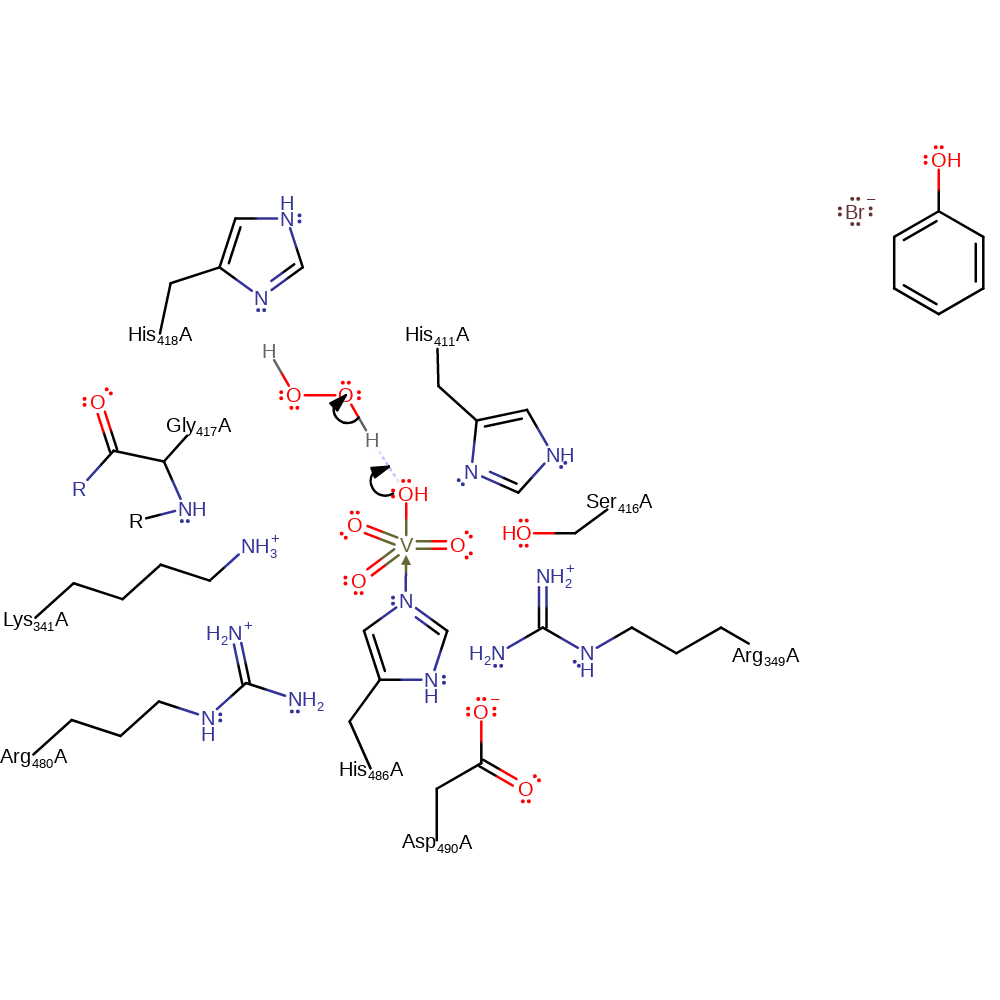
Step 1. The axial hydroxide of the vanadate cofactor deprotonates hydrogen peroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | metal ligand |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His411A | increase basicity |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
| His486A | activator |
Chemical Components
proton transfer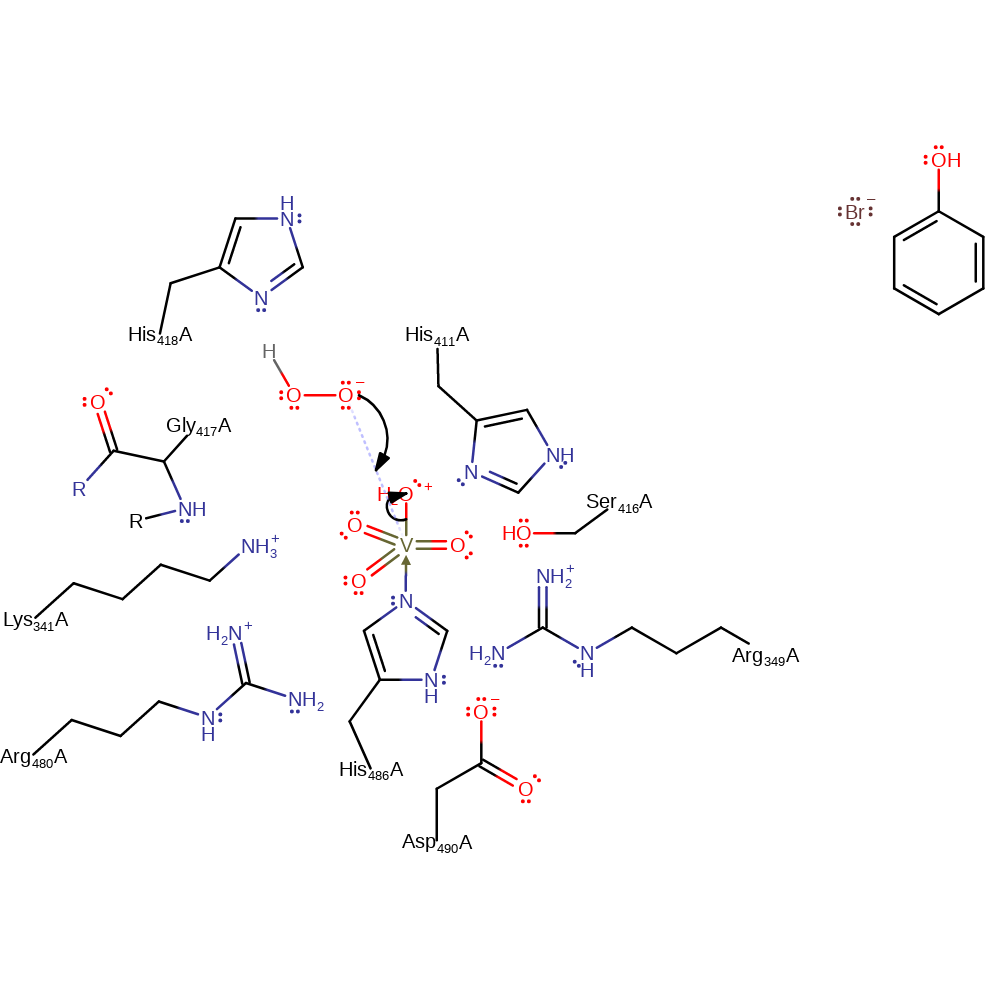
Step 2. The activated hydrogen peroxide initiates a nucleophilic attack on the vanadate in a substitution reaction, eliminating water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | activator |
| Asp490A | activator |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His486A | metal ligand |
| His411A | increase electrophilicity |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, dehydration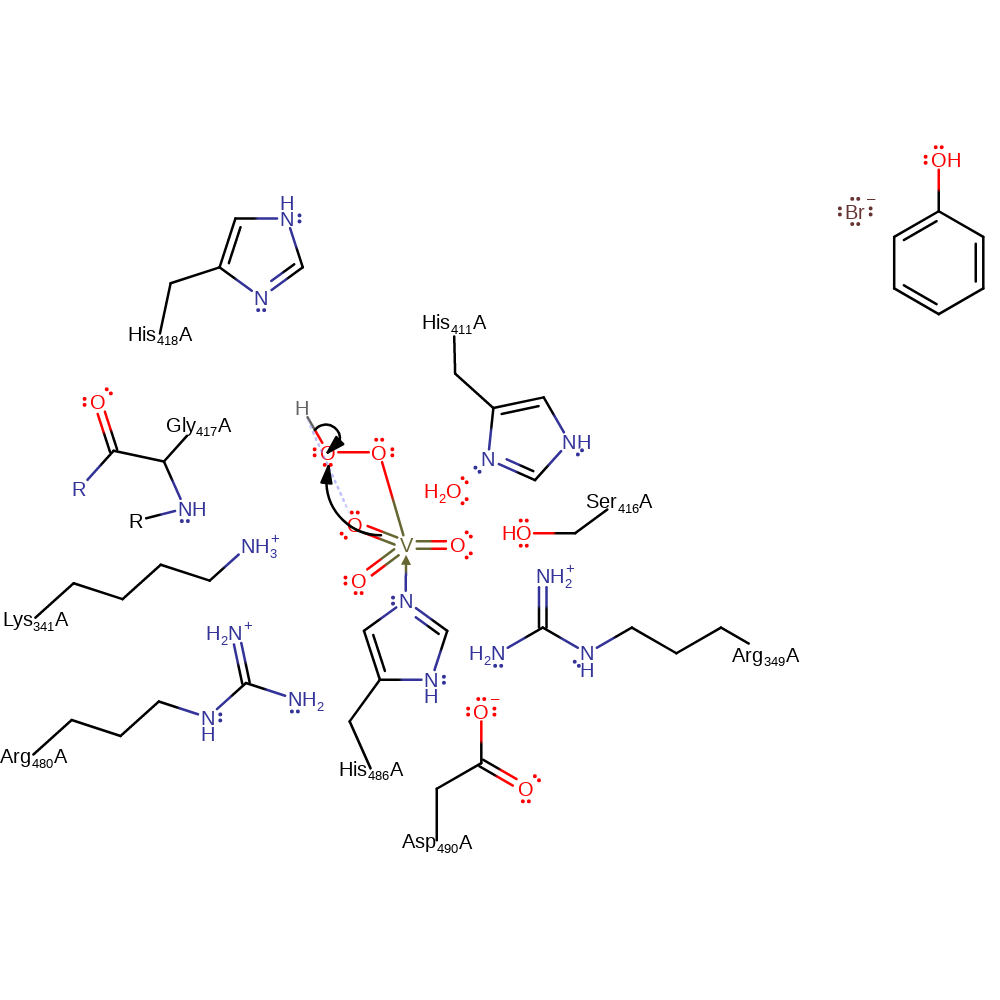
Step 3. One of the equatorial oxo groups deprotonates the attached hydrogen peroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
| His486A | activator |
| His486A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer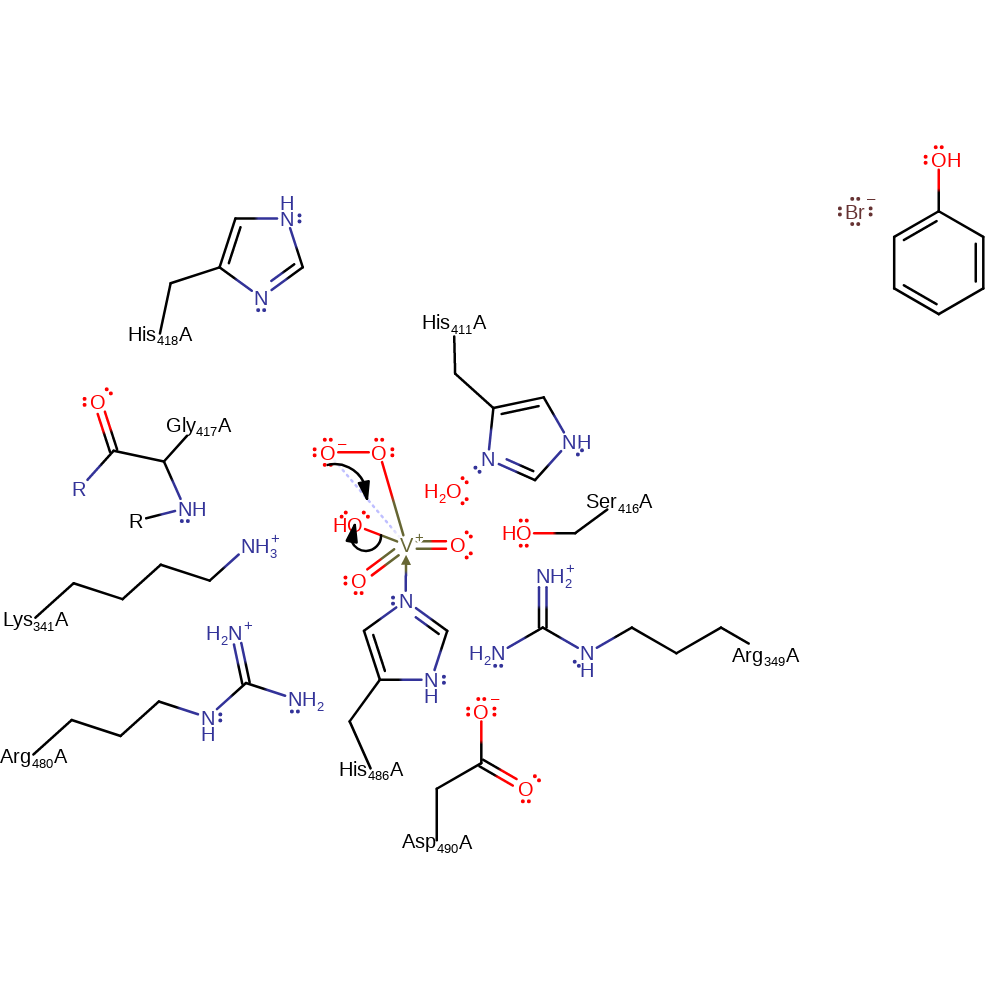
Step 4. The peroxide initiates a nucleophilic attack on the vanadate in a substitution reaction, eliminating hydroxide and forming a three membered ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | activator |
| Asp490A | activator |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His486A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitutionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
| His486A | activator |
| His486A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | activator |
| Asp490A | activator |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular electrophilic addition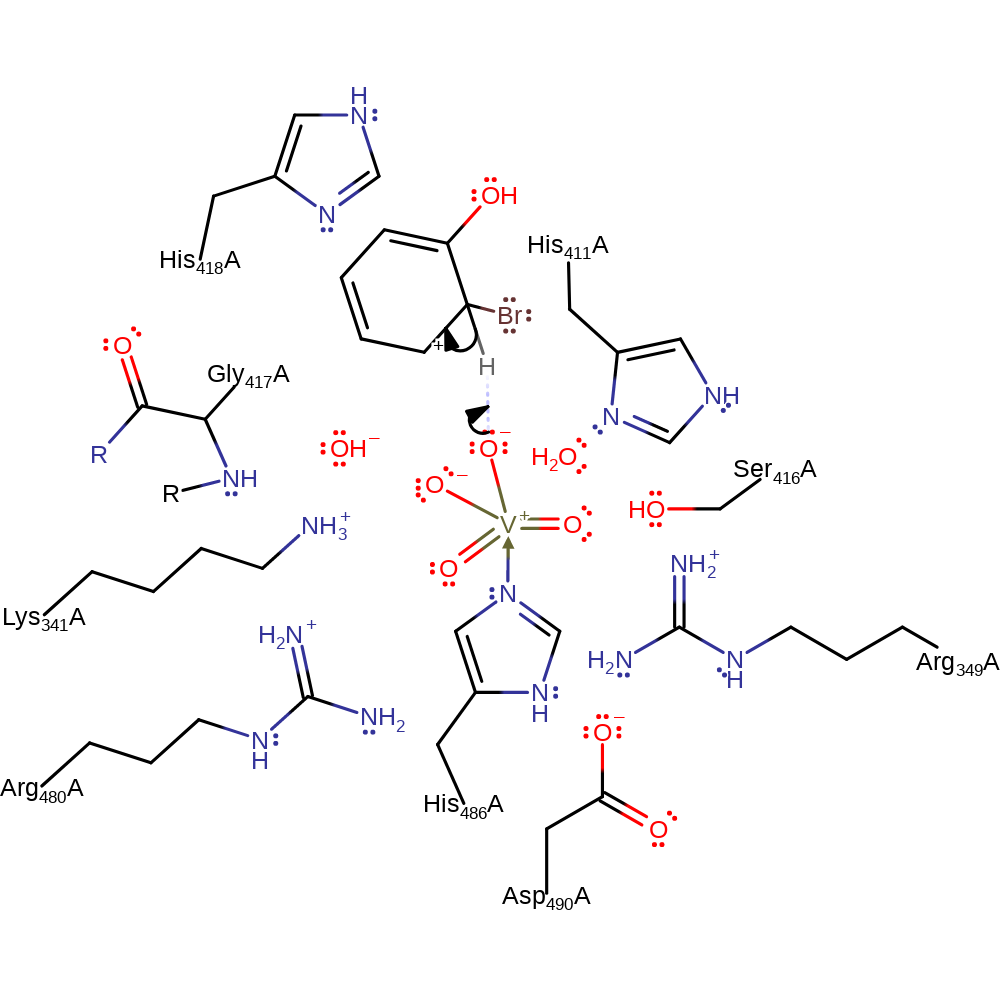
Step 7. The highly active oxo species of the vanadate cofactor abstracts the proton from the intermediate, regenerating both the cofactor and the aromaticity of the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
| His486A | activator |
| His486A | metal ligand |







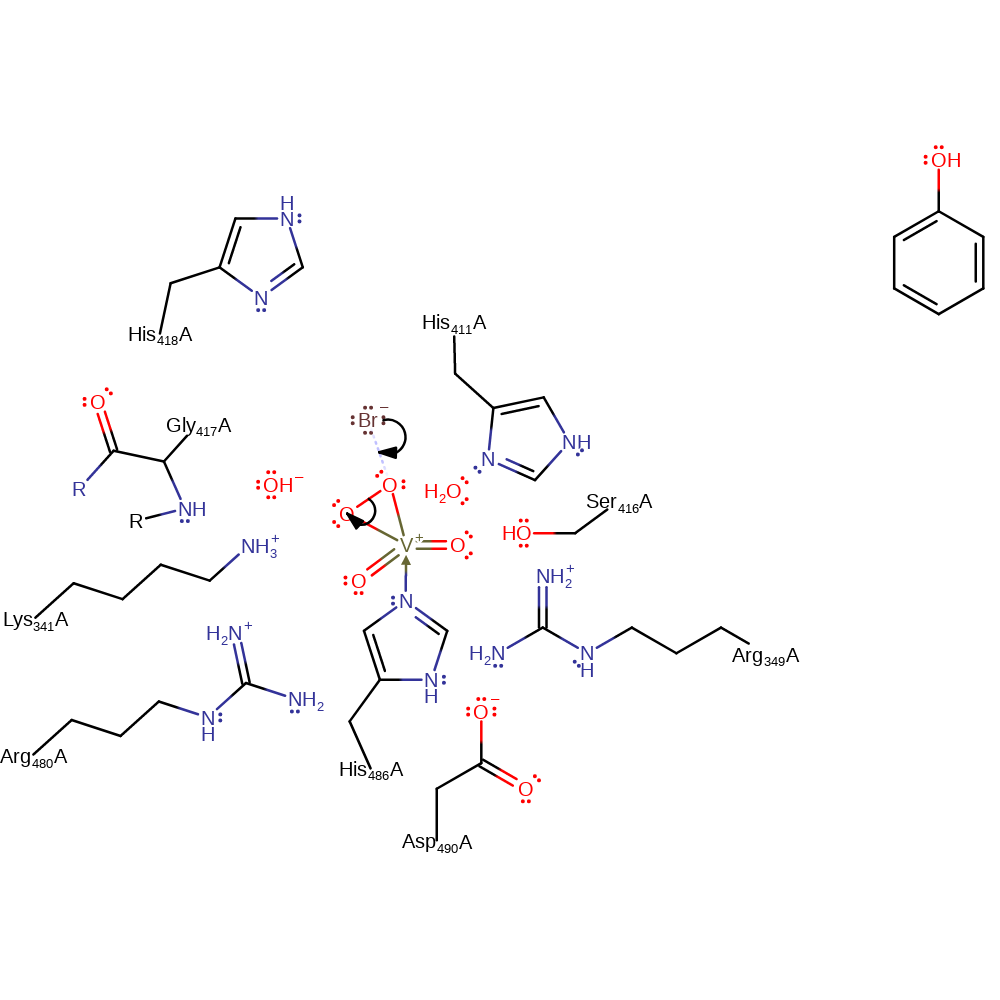
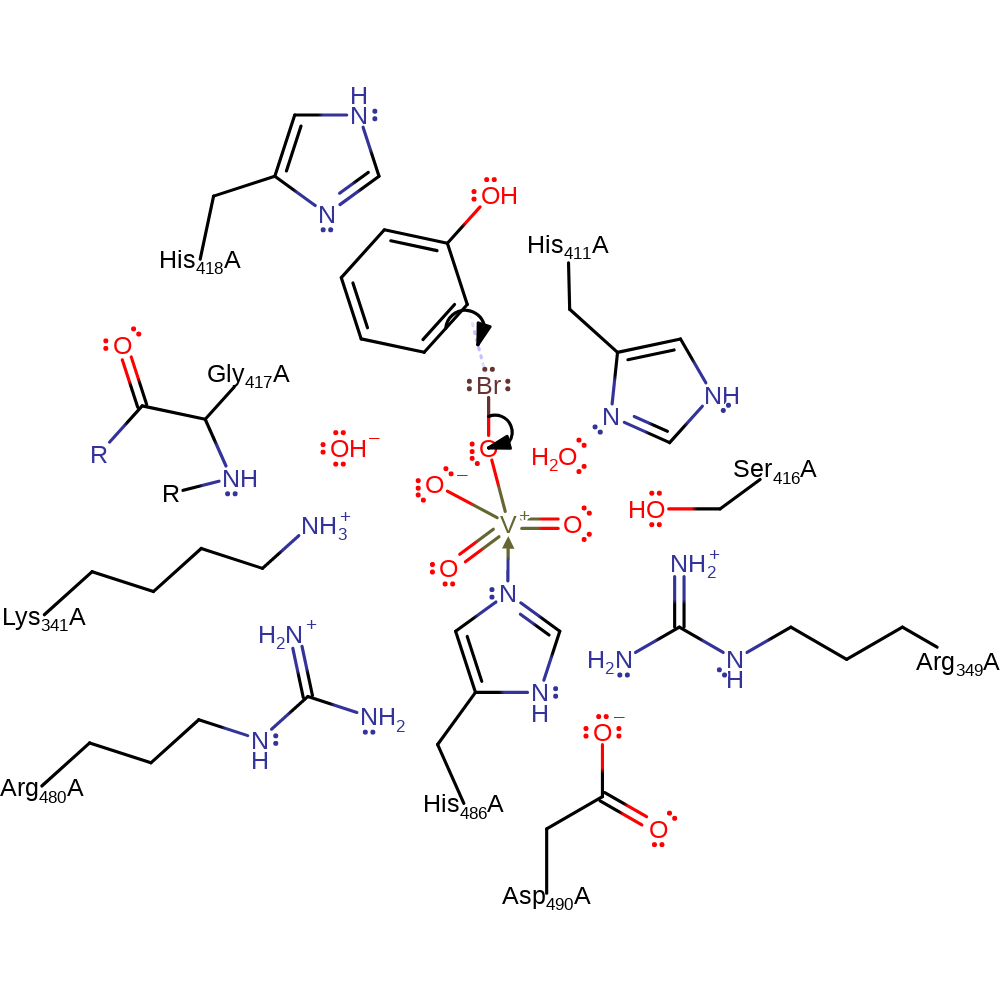
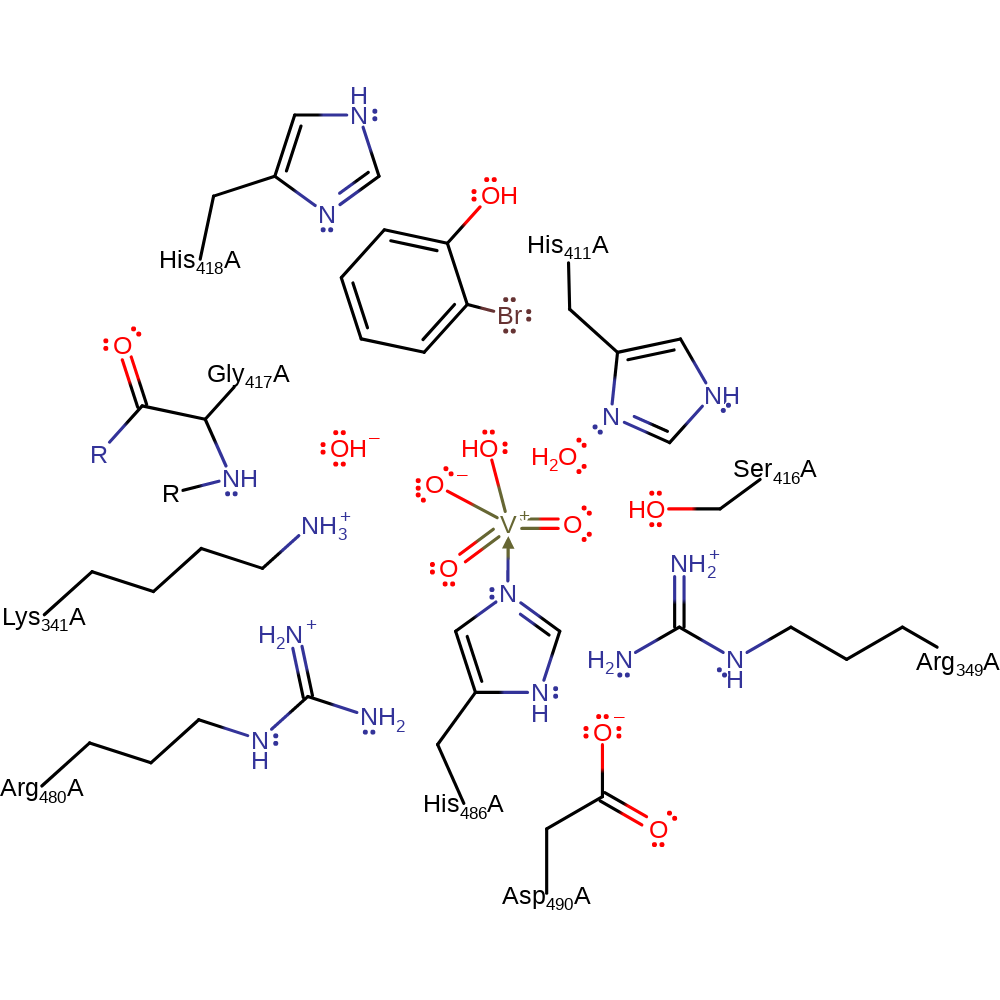 Download:
Download: