Thymidylate synthase
Thymidylate synthase (TS) is an essential enzyme for the de novo synthesis of thymidine 5'-monophosphate (dTMP) via the addition of a methyl group to 2'-deoxyuridine 5'monophosphate (dUMP) from folate. TS is a highly conserved enzyme. dTMP is a nucleotide required for DNA synthesis, and therefore, it is an important drug target, especially for anticancer and antineoplastic drugs. TS also plays a role in regulating tissue folate levels.
TS is a bisubstrate enzyme in which the cofactor, CH2 H4 folate, serves as both the one-carbon donor to the substrate dUMP and, subsequently, as the reductant. A one-carbon unit and hydride are transferred from different sites on the cofactor, and large contributions to the catalytic power of TS are achieved through the dynamic alignment and realignment of reactants at these chemical steps.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00469
 (2.1.1.45)
(2.1.1.45)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Lactobacillus casei (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1lcb
- LACTOBACILLUS CASEI THYMIDYLATE SYNTHASE TERNARY COMPLEX WITH DTMP AND H2FOLATE
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.572.10
 (see all for 1lcb)
(see all for 1lcb)
- Cofactors
- Water (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.45)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Active site closure upon the binding of the substrates correctly aligns the reactants, allowing the reaction to proceed correctly [PMID:12525150]. Asp-221 is the only residue whose side chain hydrogen bonds directly to the pterin ring of the cofactor. D221 variants that cannot form this hydrogen bond either do not form a covalent ternary complex form the ternary complex with a much higher Kd. Crystallography has shown that the hydrogen bond is critical for excluding nonproductive cofactor binding modes in the ternary complex. In the structure of D221N, for example, where the hydrogen bond acceptor, Asp, is replaced with the donor, Asn, the pterin ring of the cofactor binds in a flipped conformation and cannot condense with dUMP [PMID:12525151]. The cofactor in this reaction plays a duel role, first it is a one-carbon donor and then it is a reductant of the transferred methylene at different steps in the reaction. It is regenerated stereospecifically by dihyrdofolate reductase and serine hydroxymethyltransferases in the thymidylate synthase cycle [PMID:2223755].
The mechanism proceeds as follows: Cys198 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ene carbon of dUMP in a Michael (1,4) addition reaction. It is polarised by Arg218. The oxyanion formed deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Glu60. Glu60 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the hydroxyl group, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the activated (by Asp221) methylenetetrahydrofolate at the CH2=N carbon. Tyr146 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the carbon newly connected to the methylenetetrahydrofolate. This causes the formation of a C=C and the oxyanion formed deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Glu60. Glu60 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the hydroxyl group, eliminating the negatively charged dihydrofolate. The negatively charged nitrogen of dihydrofolate eliminates a hydride ion, which adds to the CH2=C group of the covalently attached methyl-dUMP, causing the elimination of Cys198.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1lcb) | ||
| Trp82 | Trp82A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates. | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198 | Cys198A | Acts as a nucleophile by attacking the C6 atom of dUMP. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Glu60 | Glu60A | Transfers a proton to and from the O4 atom of dUMP in various steps of the mechanism. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg218 | Arg218A | Activates Cys 198 for nucleophilic attack. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp221 | Asp221A | Activates the co-substrate CH2H4PteGlu by protonating the N5 atom. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146 | Tyr146A | Abstracts a proton from C5 of dUMP via a water molecule. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, decyclisation, inferred reaction step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton relay, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bimolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Stroud RM et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 239-247. Conformational Dynamics along an Enzymatic Reaction Pathway: Thymidylate Synthase, “the Movie”†. DOI:10.1021/bi020598i. PMID:12525150.
- Kaiyawet N et al. (2015), J Chem Theory Comput, 11, 713-722. High-Level QM/MM Calculations Support the Concerted Mechanism for Michael Addition and Covalent Complex Formation in Thymidylate Synthase. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/ct5005033.
- Kanaan N et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 3704-3713. A Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of the Catalytic Mechanism of the Thymidylate Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi061953y. PMID:17328531.
- Finer-Moore JS et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 248-256. Lessons and Conclusions from Dissecting the Mechanism of a Bisubstrate Enzyme: Thymidylate Synthase Mutagenesis, Function, and Structure†. DOI:10.1021/bi020599a. PMID:12525151.
- Saxl RL et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 4544-4551. Modification ofEscherichia coliThymidylate Synthase at Tyrosine-94 by 5-Imidazolylpropynyl-2‘-deoxyuridine 5‘-Monophosphate†. DOI:10.1021/bi0268089. PMID:12693951.
- Chiericatti G et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 9038-9042. Aspartate 221 of Thymidylate Synthase Is Involved in Folate Cofactor Binding and in Catalysis†. DOI:10.1021/bi9802770. PMID:9636048.
- Hyatt DC et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 4585-4594. Use of Strain in a Stereospecific Catalytic Mechanism: Crystal Structures ofEscherichia coliThymidylate Synthase Bound to FdUMP and Methylenetetrahydrofolate†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi962936j. PMID:9109668.
- Carreras CW et al. (1995), Annu Rev Biochem, 64, 721-762. The Catalytic Mechanism and Structure of Thymidylate Synthase. DOI:10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.003445. PMID:7574499.
- Finer-Moore JS et al. (1990), Biochemistry, 29, 6977-6986. Pairwise specificity and sequential binding in enzyme catalysis: thymidylate synthase. DOI:10.1021/bi00482a005. PMID:2223755.
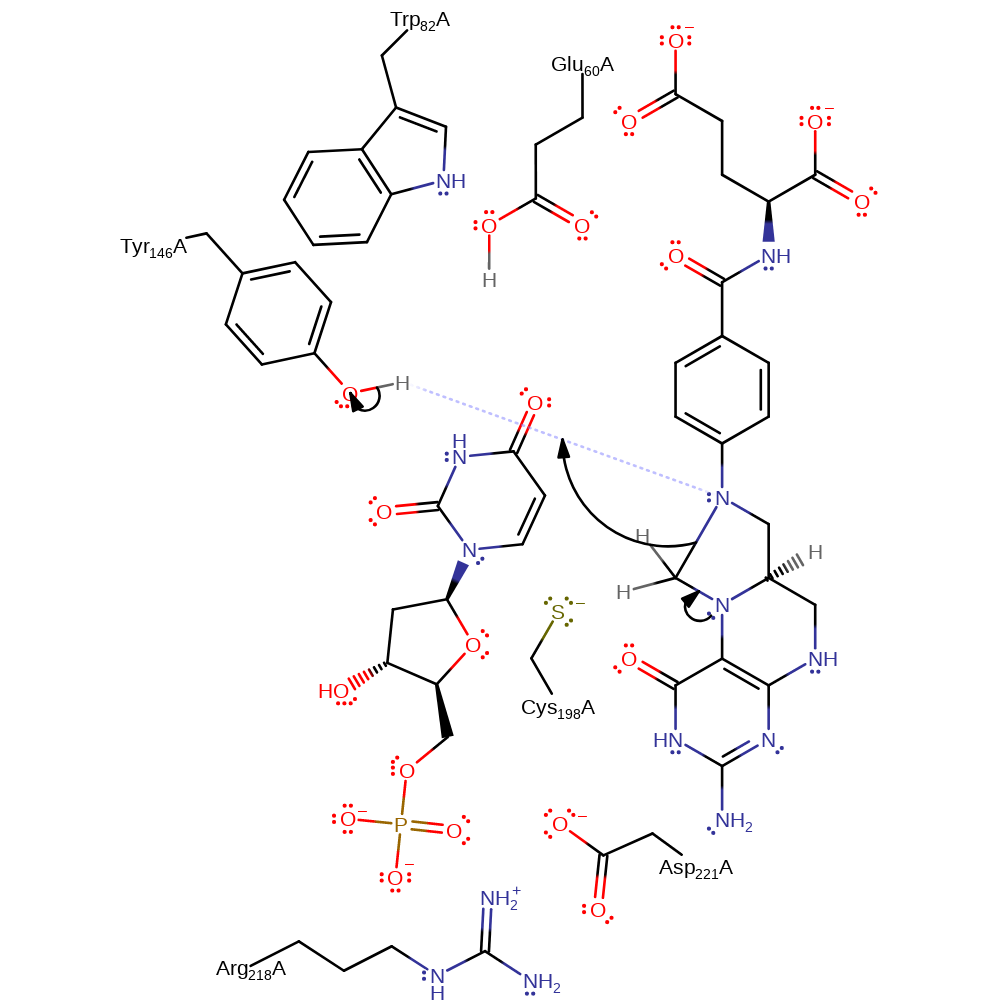
Step 1. The methylenetetrahydrofolate undergoes decyclisation, the secondary amine released deprotonates Tyr146.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, decyclisation, inferred reaction step
Step 2. Cys198 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ene carbon of dUMP in a Michael (1,4) addition reaction. The oxyanion formed deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Glu60.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu60A | proton donor |
| Cys198A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton relay, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. Glu60 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the hydroxyl group, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the activated methylenetetrahydrofolate at the CH2=N carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Cys198A | covalently attached |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu60A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, intermediate formation
Step 4. Tyr146 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the carbon newly connected to the methylenetetrahydrofolate. This causes the formation of a C=C and the oxyanion formed deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates Glu60.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, activator |
| Cys198A | covalently attached |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu60A | proton donor |
| Tyr146A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 5. Glu60 deprotonates water, which deprotonates the hydroxyl group, eliminating the negatively charged dihydrofolate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, activator |
| Cys198A | covalently attached |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu60A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 6. The negatively charged nitrogen of dihydrofolate eliminates a hydride ion, which adds to the CH2=C group of the covalently attached methyl-dUMP, causing the elimination of Cys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
The molecular mechanism is developed in nine steps (ten with the inferred return step), three more steps than in mechanism 1, this is due not only to the fact that some of the steps, initially supposed to be concerted-like reactions, take place through stable intermediates but also to a more detailed description of the chemical transformations.
In the first step, Cys146 transfers a hydrogen to a water molecule that acts as a base in an exothermic reaction. Three water molecules, present in the X-ray structure of the protein obtained by Stroud et al., contribute to the transfer of a proton from Cys146 through three transition state structures. The protein environment favors, thermodynamically, the transfer of a proton to the water molecule.
The protonated water molecule acts as a general acid catalyst in step 2, transferring a hydrogen to N10 of the CH2H4folate cofactor and facilitating the opening of the imidazolidine ring followed by the formation of the activated form of the cofactor, the iminium ion 5-CH2H4folate.
In the next step (step 4), a nucleophilic attack at C6 of dUMP by the basic deprotonated Cys146 and the concomitant formation of a bond between C5 of dUMP and the iminium ion take place in a concerted way.
Step 5 is an E2 elimination of the thiol anion (Cys146) at C6 and the proton at C5, forming an intermediate double bond. The only general base that can abstract the proton is the water molecule (W40), which is hydrogen bonded to Tyr94. The following step (step 6) involves the protonation of N5 (folate) that turns the tetrahydropterin into a much better leaving group. Afterwards, the formation of the protonated pyrazine ring facilitates the scission of the methylene bridge established between the substrate and the cofactor, which takes place with a concomitant trans-diaxial nucleophilic attack of the negatively charged Cys46 on C6 of the folate (step 7). This concerted step leads to the elimination of H4folate and to the cleavage of the covalent bond between the pteridine ring and the exo-methyline dUMP intermediate. Subsequently, the favourable three-dimensional orientation of the pterin ring of the cofactor and the pyrimidine of the substrate prepares the system for a transfer of hydride from H4folate to dUMP in step 8, releasing the Cys146 in a single concerted but very asynchronous step. The protonated Cys is regenerated in the reverse of the first step (inferred).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1lcb) | ||
| Trp82 | Trp82A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates. | van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198 | Cys198A | Acts as a nucleophile by attacking the C6 atom of dUMP. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg218 | Arg218A | Helps activate the Cys for the initial deprotonation event. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| Asp221 | Asp221A | Helps guide the steric outcome of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu60, Tyr146 | Glu60A, Tyr146A | Help activate catalytic site water molecules. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, bimolecular elimination, hydride transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Kanaan N et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 3704-3713. A Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study of the Catalytic Mechanism of the Thymidylate Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi061953y. PMID:17328531.
- Kaiyawet N et al. (2015), J Chem Theory Comput, 11, 713-722. High-Level QM/MM Calculations Support the Concerted Mechanism for Michael Addition and Covalent Complex Formation in Thymidylate Synthase. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/ct5005033.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg218A | increase acidity |
| Cys198A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, decyclisation
Step 4. Cys198 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the ene carbon of dUMP in an addition reaction, which adds to the CH2 group of the THF intermediate..
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Arg218A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 5. Activated water deprotonates the intermediate, resulting in the elimination of Cys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular eliminationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp82A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg218A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp221A | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 7. Cys198 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the intermediate, which eliminates the protonated THF product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp82A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg218A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp221A | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys198A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 8. The nitrogen of dihydrofolate eliminates a hydride ion, which adds to the CH2=C group of the covalently attached methyl-dUMP, causing the elimination of Cys198.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp221A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp82A | hydrogen bond donor, van der waals interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys198A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 9. The activated water deprotonates the positively charged THF product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp82A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg218A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp221A | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 10. Cys198 deprotonates the acidified water molecule in an inferred return step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg218A | increase acidity |
| Trp82A | electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu60A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr146A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg218A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp221A | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys198A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: 



 Download:
Download: