Malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating)
Malic enzymes are found in most living organisms, including bacteria and humans. They catalyse the conversion of L-malate to pyruvate with the concomitant reduction of the cofactor NAD+ or NADP+. In mammals three isoforms have been identified, a cytosolic NADP+ dependent enzyme, a mitochondrial NADP+ dependent enzyme and a mitochondrial NAD+ dependent enzyme. Each has a specific role, for example the mitochondrial NAD+ dependent enzyme is important for the metabolism of glutamine for energy production in rapidly proliferating tissues and tumours.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P23368
 (1.1.1.38)
(1.1.1.38)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1do8
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A CLOSED FORM OF HUMAN MITOCHONDRIAL NAD(P)+-DEPENDENT MALIC ENZYME
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.10380
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1do8)
(see all for 1do8)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.38)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalysis by malate enzymes generally proceeds in two steps - dehydrogenation of the malate to produce oxaloacetate and then decarboxylation to produce pyruvate. A bound metal divalent cation (Mg2+ or Mn2+) polarises the C2 hydroxyl of malate for dehydrogenation and stabilises the C2 enolic oxygen for decarboxylation. Lys183 is the most likely candidate for a general acid to protonate the enol-pyruvate product of decarboxylation. Tyr112 plays a vital role in the dehydrogenation reaction although the structural basis for such a role is yet to be determined. Many other residues are involved in substrate binding and stabilisation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1do8) | ||
| Arg165, Asn421 | Arg165(145)A, Asn421(401)A | Acts as an electrostatic stabiliser throughout the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys183, Tyr112, Asp278 | Lys183(163)A, Tyr112(92)A, Asp278(258)A | Acts as a general acid/base at various points during the reaction. Initial protonation state is regenerated via an inferred return step. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp279, Asp256, Glu255 | Asp279(259)A, Asp256(236)A, Glu255(235)A | Binds the Mn(II) ion. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, bimolecular elimination, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, proton relay, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Yang Z et al. (2000), Nat Struct Biol, 7, 251-257. Structure of a closed form of human malic enzyme and implications for catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1038/73378. PMID:10700286.
- Tao X et al. (2003), Structure, 11, 1141-1150. Crystal Structures of Substrate Complexes of Malic Enzyme and Insights into the Catalytic Mechanism. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(03)00168-0. PMID:12962632.
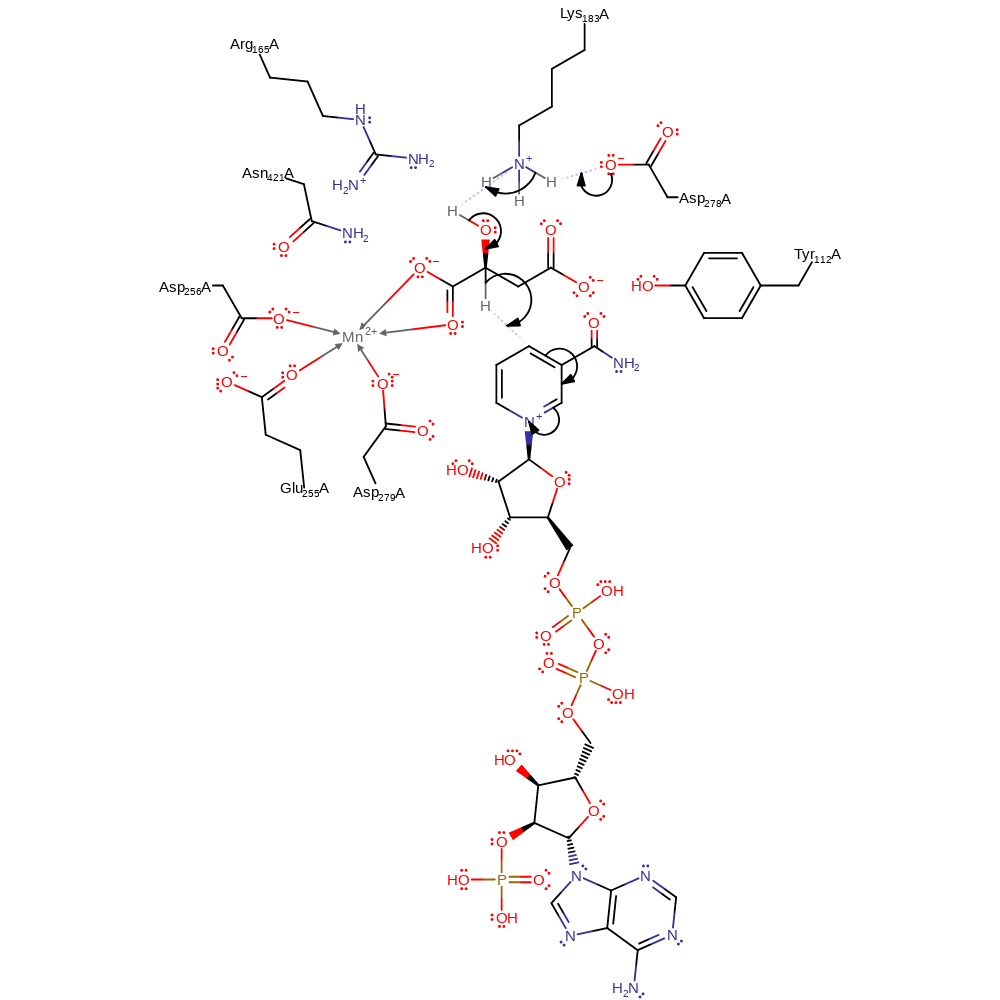
Step 1. Asp278 deprotonates Lys183, which deprotonates the hydroxyl group of malate, which eliminates a hydride ion that is added to NADP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp278(258)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys183(163)A | proton relay, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn421(401)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg165(145)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr112(92)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp256(236)A | metal ligand |
| Glu255(235)A | metal ligand |
| Asp279(259)A | metal ligand |
| Asp278(258)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys183(163)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 2. The reduced intermediate decarboxylates with concomitant double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn421(401)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp278(258)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg165(145)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys183(163)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr112(92)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp256(236)A | metal ligand |
| Glu255(235)A | metal ligand |
| Asp279(259)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation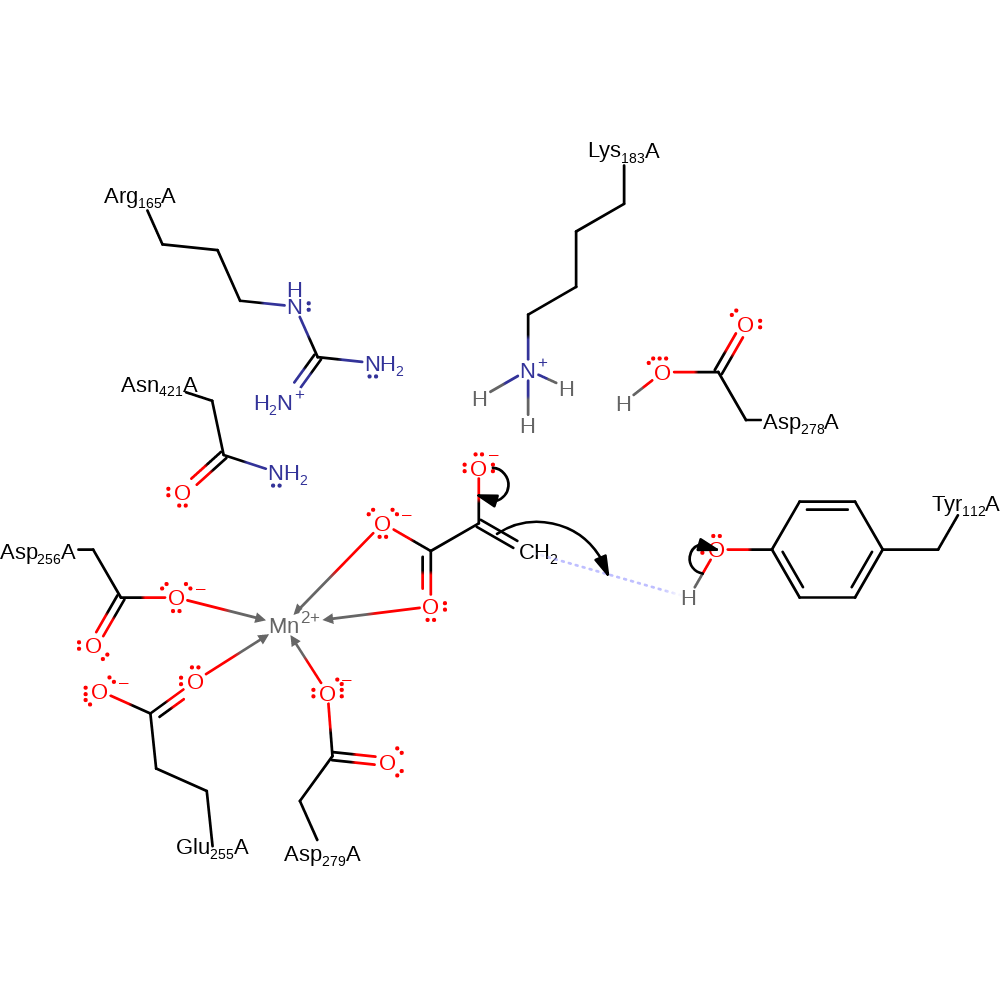
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, reducing the C=C with concomitant deprotonation of Tyr112.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp278(258)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr112(92)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys183(163)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn421(401)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg165(145)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp256(236)A | metal ligand |
| Glu255(235)A | metal ligand |
| Asp279(259)A | metal ligand |
| Tyr112(92)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, proton transfer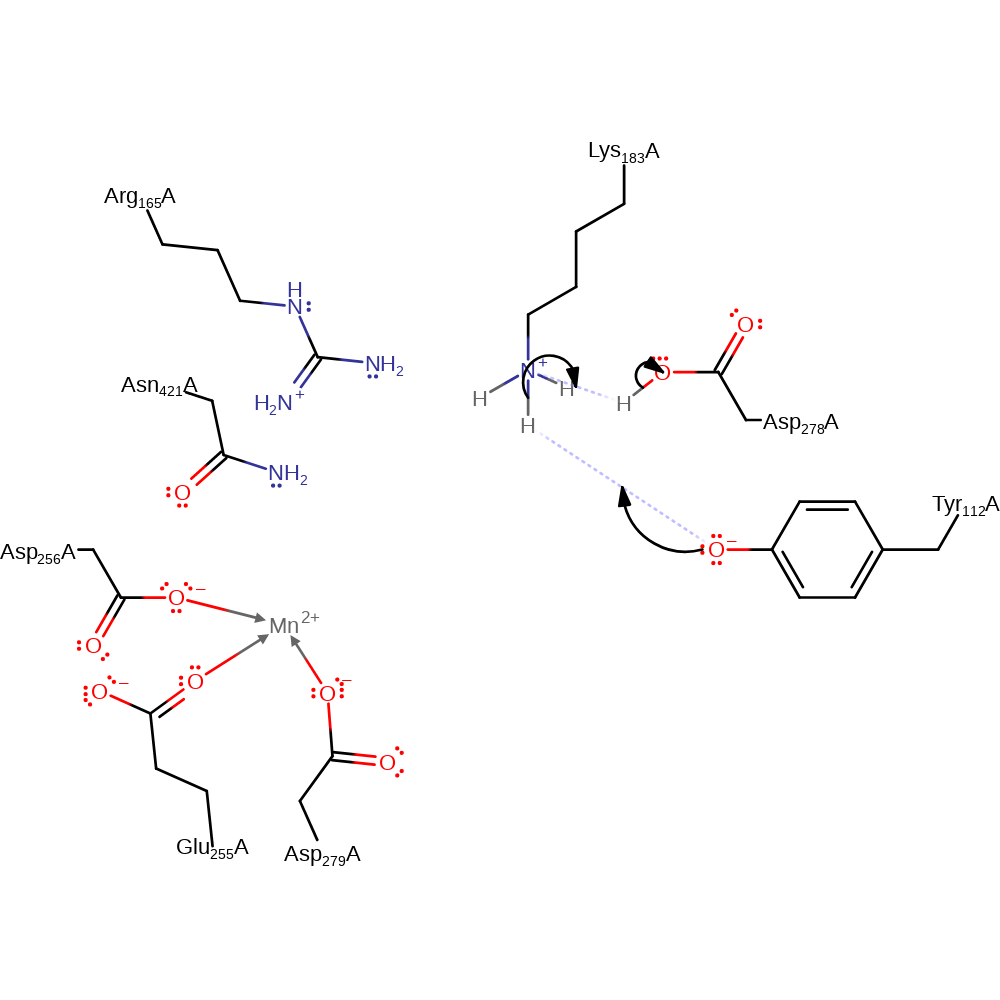
Step 4. Tyr112 deprotonates Lys183 which deprotonates Asp278 in an inferred return step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys183(163)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp278(258)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Tyr112(92)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp256(236)A | metal ligand |
| Glu255(235)A | metal ligand |
| Asp279(259)A | metal ligand |
| Lys183(163)A | proton relay |
| Asp278(258)A | proton donor |
| Tyr112(92)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys183(163)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |





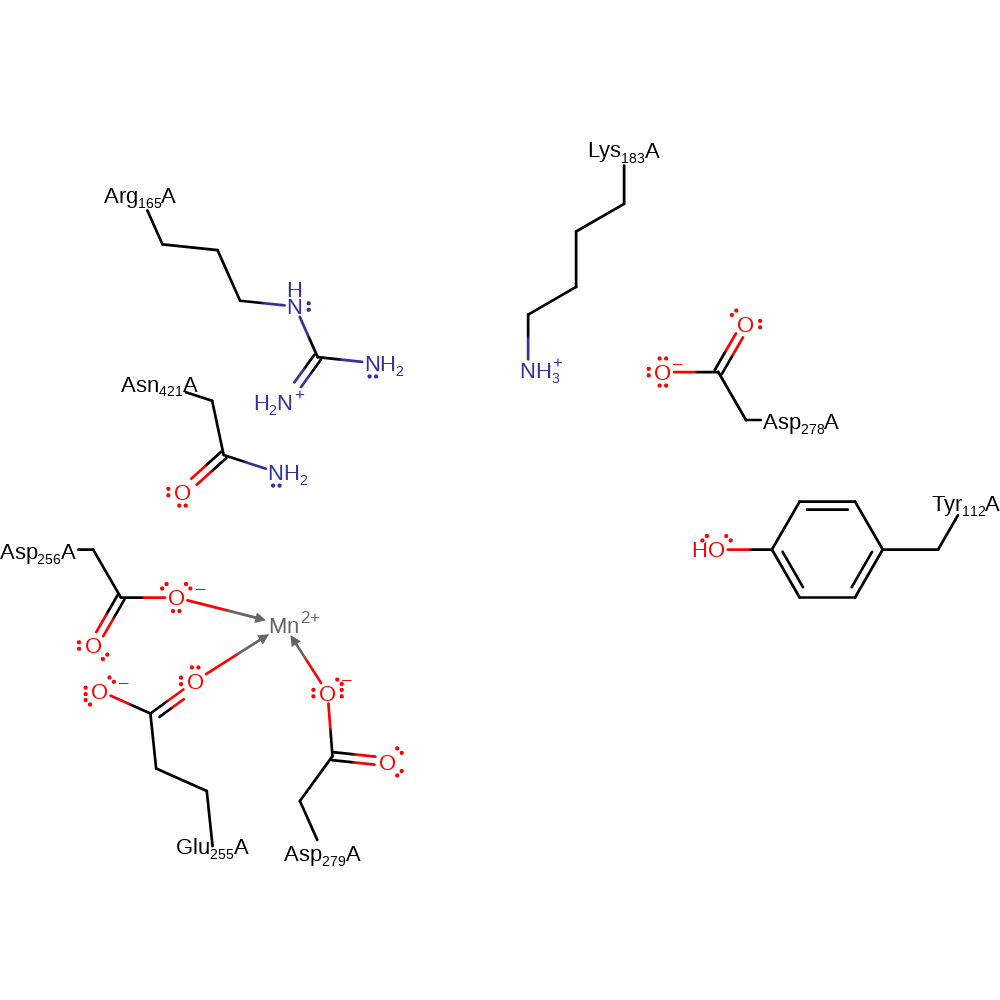 Download:
Download: