Deoxyribonuclease (pyrimidine dimer)
Endonuclease V removes pyrimidine dimers in DNA induced by UV radiation. The enzyme first associates with the DNA and locates the damaged site by a scanning mechanism. It catalyses 2 reactions to remove DNA pyrimidine dimers: (1)cleavage of glycosidic bond by pyrimidine dimer glycosylase activity, which hydrolyses the N-glycosyl bond of the 5'-thymidine in the thymine dimer site and (2)incision of the phosphodiester bond at the apyrimidinic site via a beta-elimination reaction by the apurinic/apyrimidinic(AP) endonuclease activity.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P04418
 (3.2.2.17, 4.2.99.18)
(3.2.2.17, 4.2.99.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterobacteria phage T4 (Virus)

- PDB
-
1vas
- ATOMIC MODEL OF A PYRIMIDINE DIMER SPECIFIC EXCISION REPAIR ENZYME COMPLEXED WITH A DNA SUBSTRATE: STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR DAMAGED DNA RECOGNITION
(2.75 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.440.10
 (see all for 1vas)
(see all for 1vas)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.25.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The glycosylase step proceeds by an SN2 mechanism. The neutral N-terminus(Thr2) performs a nucleophilic attack on ribose C1' of the 5'-thymine of the dimer. The susceptibility of C1' to nucleophilic attack is enhanced by a hydrogen bond between Glu23 and O4' of the ribose. The transition state is stabilised by the hydrogen bond as well. The positively charged Arg22 and Arg26 provides favourable electrostatic interactions to the transition state and hence stabilising it. Glu23 protonates ribose O4', leading to the opening of the ribose ring and the formation of the protonated Schiff base, the product of the glycosylase reaction, which is stabilised by Glu23.
The AP endonuclease step proceeds via a beta-elimination mechanism. Glu23 acts as a base to remove the pro-S 2'-hydrogen of the opened ribose, leading to the cleavage of the phosphodiester bond. It is followed by the hydrolysis of the Schiff base by a water molecule, leading to the dissociation of the enzyme and the formation of an alpha-beta-unsaturated aldehyde.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1vas) | ||
| Thr2 (N-term) | Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | The N-terminal of Thr 2 acts as a nucleophile to attack the ribose C1' of the 5'-thymine of the dimer. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleophile, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Arg22 | Arg22(21)A(C) | Stabilises the transition state of the glycosylase reaction by forming favourable electrostatic interaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg26 | Arg26(25)A(C) | Stabilises the transition state in the glycosylase reaction by providing favourable electrostatic interaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu23 | Gln23(22)A(C) | In the glycosylase reaction, it hydrogen bonds to ribose O4' to increase the electrophilicity of ribose C1' to enhance the nucleophilic attack of Thr 2 on C1' The hydrogen bond stabilises the transition state as well. It protonates the ribose O4', leading to the opening of the ribose ring and the formation of the Schiff base, which is stabilised again by Glu 23. In the AP endonuclease reaction, it acts as a base to remove the pro-S 2'-hydrogen of the opened ribose, leading to the cleavage of the phosphodiester bond. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, proton relay, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decyclisation, schiff base formed, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate collapse, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Fuxreiter M et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 9577-9589. Role of Active Site Residues in the Glycosylase Step of T4 Endonuclease V. Computer Simulation Studies on Ionization States†. DOI:10.1021/bi9901937. PMID:10423235.
- Golan G et al. (2006), J Mol Biol, 362, 241-258. Structure of T4 pyrimidine dimer glycosylase in a reduced imine covalent complex with abasic site-containing DNA. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.059. PMID:16916523.
- Vassylyev DG et al. (1995), Cell, 83, 773-782. Atomic model of a pyrimidine dimer excision repair enzyme complexed with a dna substrate: Structural basis for damaged DNA recognition. DOI:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90190-6. PMID:8521494.
- Schrock RD 3rd et al. (1993), J Biol Chem, 268, 880-886. Site-directed mutagenesis of the NH2 terminus of T4 endonuclease V. The position of the alpha NH2 moiety affects catalytic activity. PMID:8419366.
- Doi T et al. (1992), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 89, 9420-9424. Role of the basic amino acid cluster and Glu-23 in pyrimidine dimer glycosylase activity of T4 endonuclease V. DOI:10.1073/pnas.89.20.9420. PMID:1409651.
- Morikawa K et al. (1992), Science, 256, 523-526. X-ray structure of T4 endonuclease V: an excision repair enzyme specific for a pyrimidine dimer. DOI:10.1126/science.1575827. PMID:1575827.
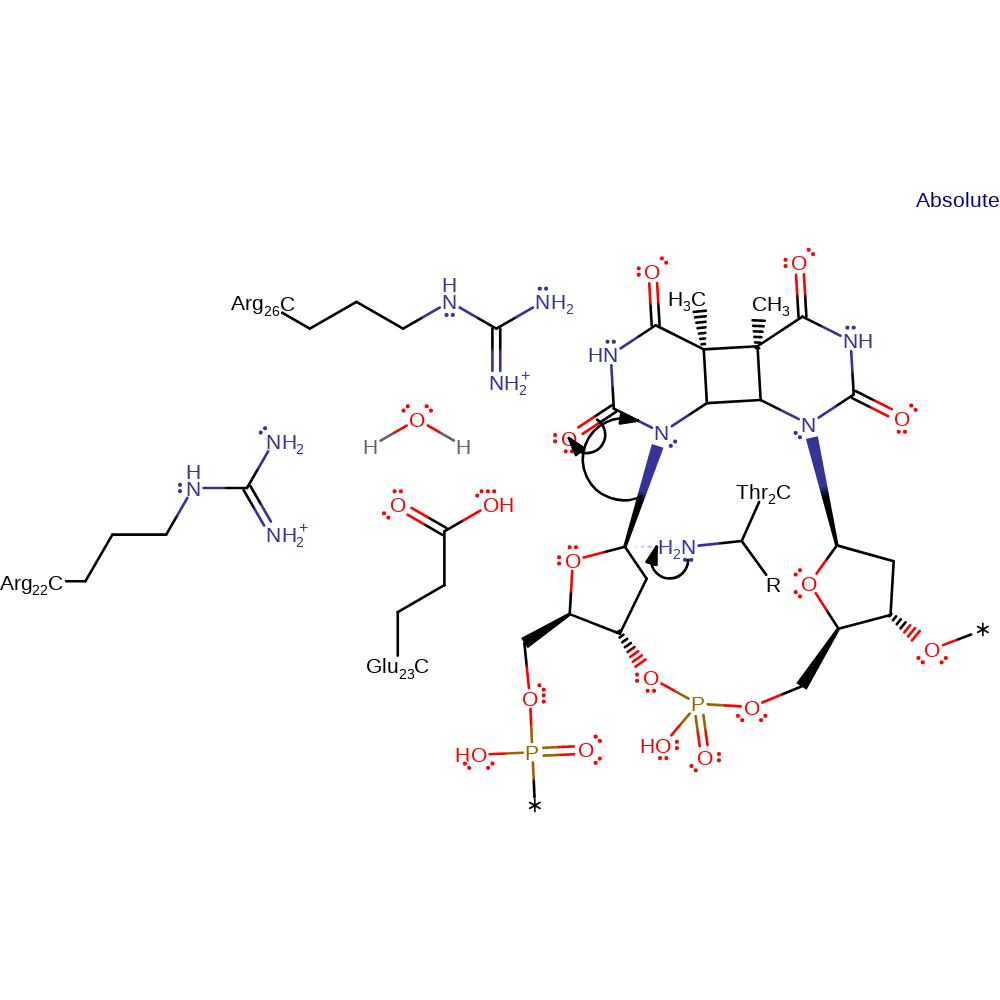
Step 1. The N-terminus of the enzyme, Thr2, attacks the C1 carbon of the deoxyribose ring at the 5' end of the DNA molecule in a nucleophilic substitution, cleaving the bond to the damaged base
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation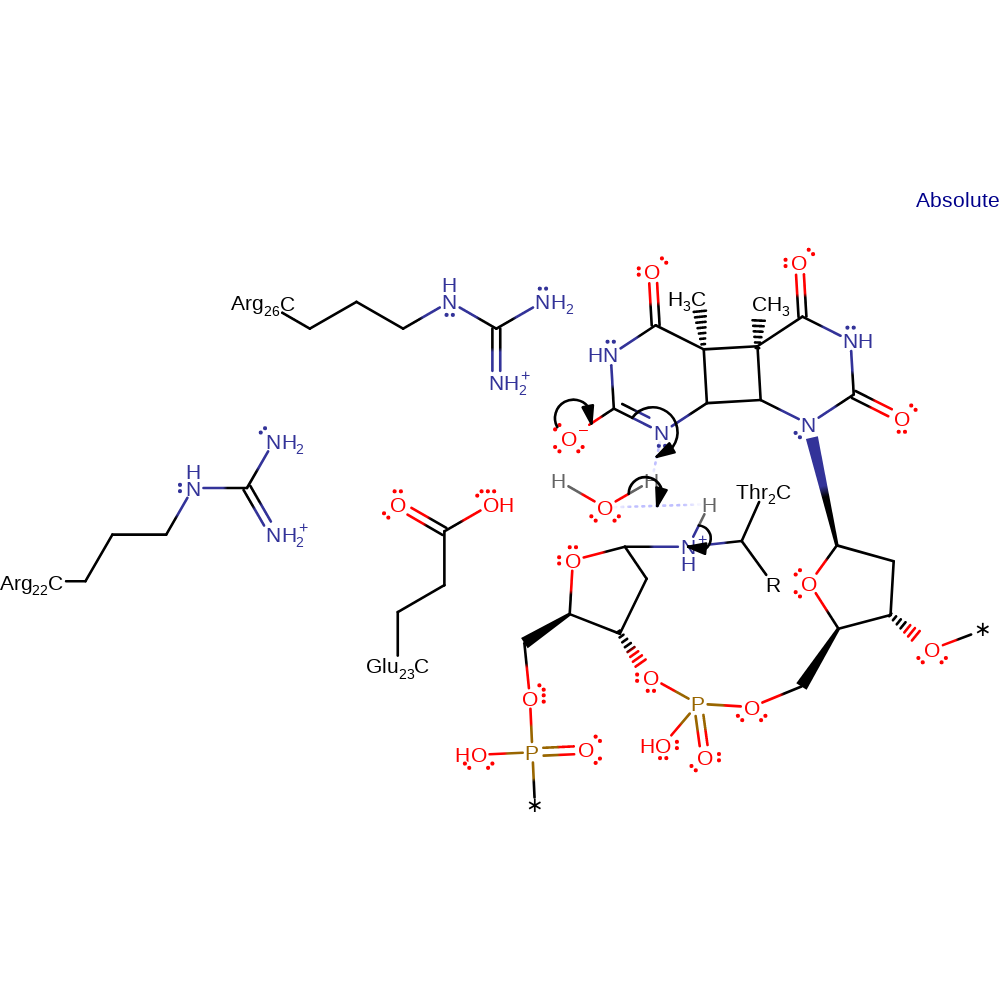
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an isomerisation which causes the nitrogen of the base to deprotonate water, which in turn deprotonates the N-terminal Thr2.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay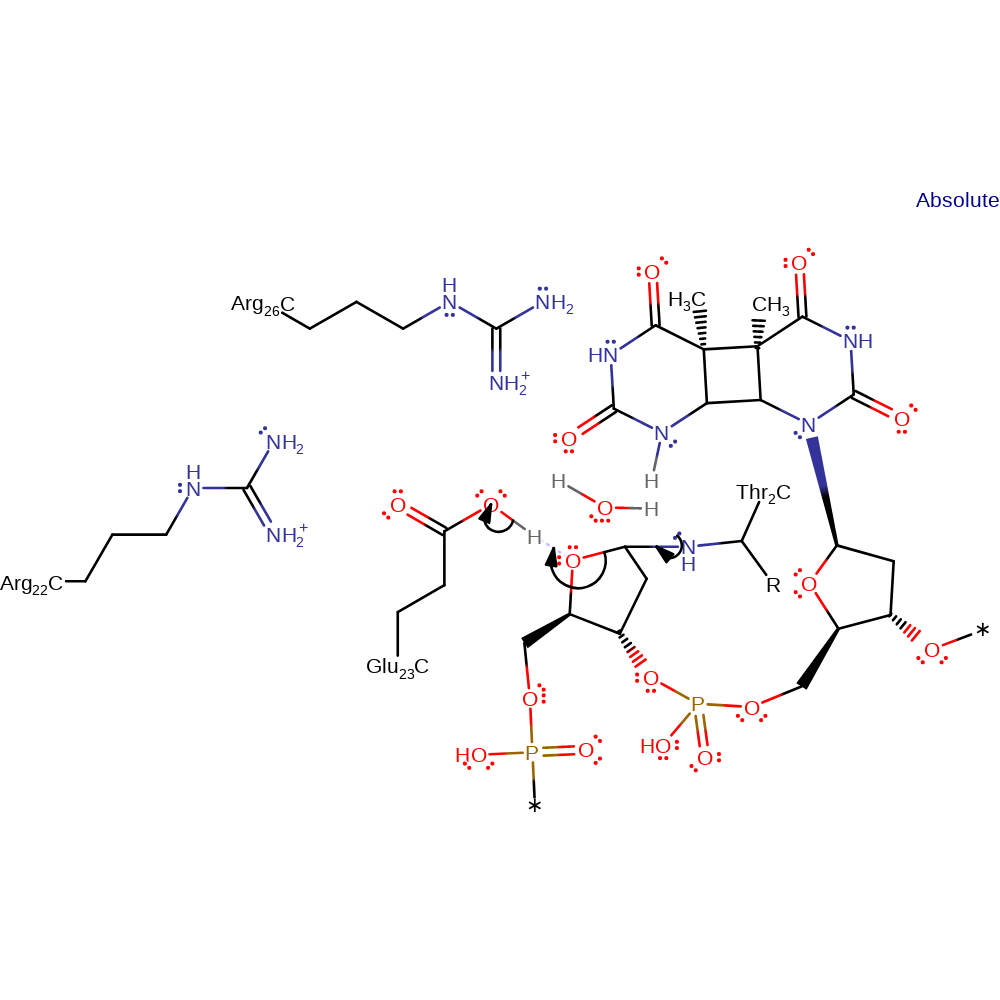
Step 3. The lone pair on the N-terminal Thr2 initiates an elimination, cleaving the C1-O bond of the deoxyribose ring, which in turn deprotonates Glu23
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | proton donor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, decyclisation, intermediate formation, schiff base formed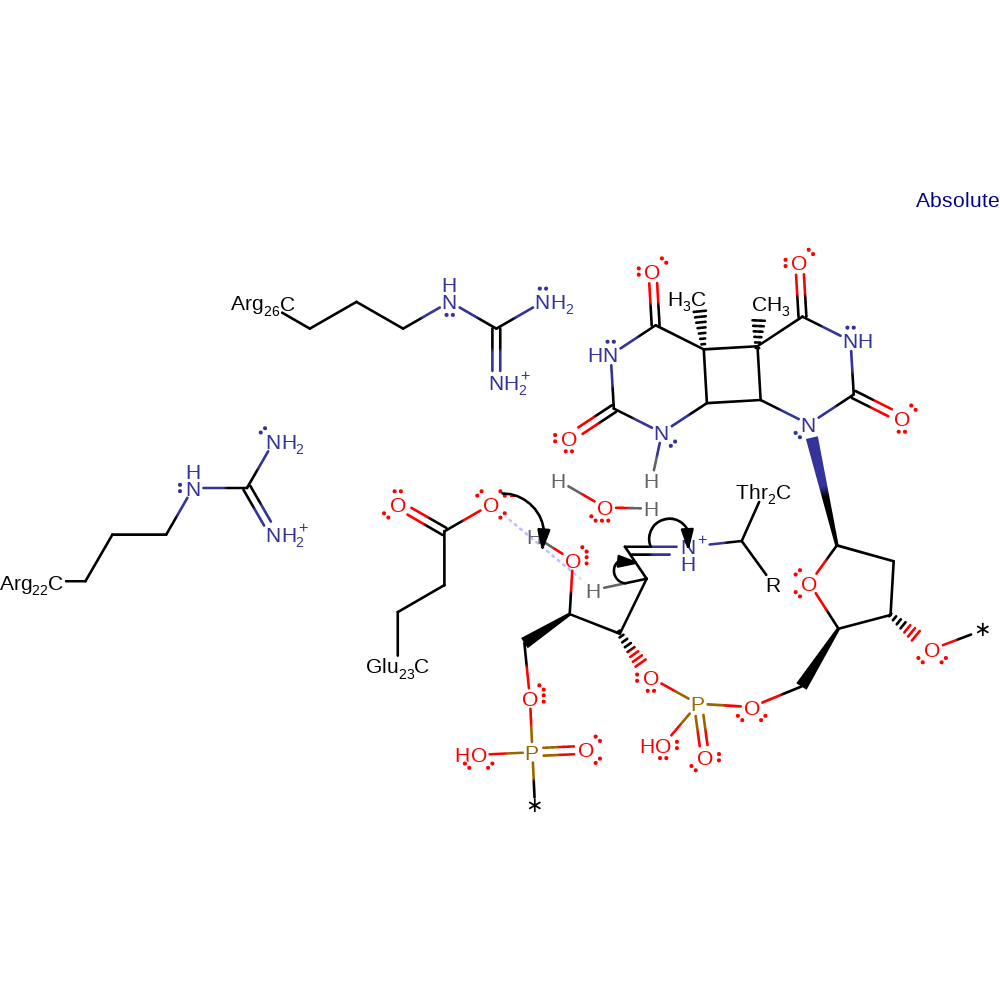
Step 4. Glu23 deprotonates the C2 of the deoxyribose ring, causing a double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | proton acceptor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation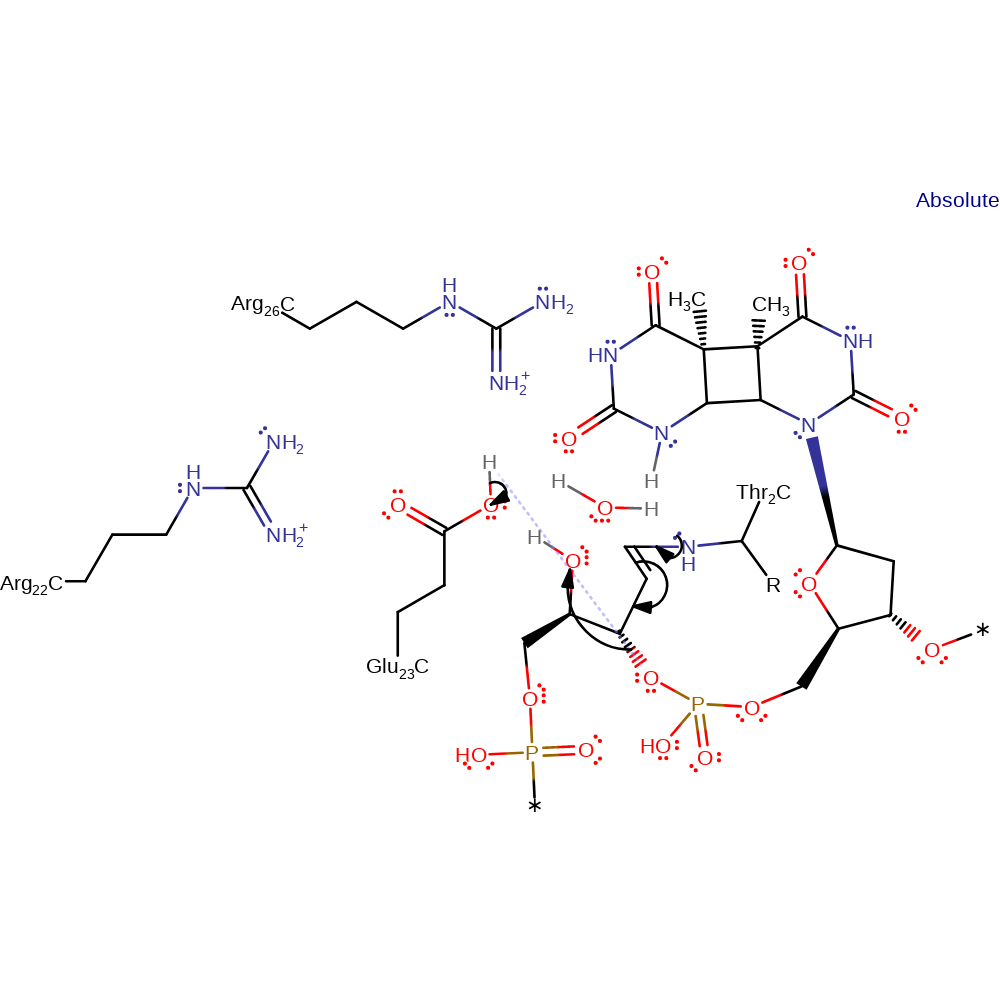
Step 5. The lone pair on the N-terminal Thr2 initiates an elimination of the phosphate, which in turn deprotonates Glu23
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | proton donor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed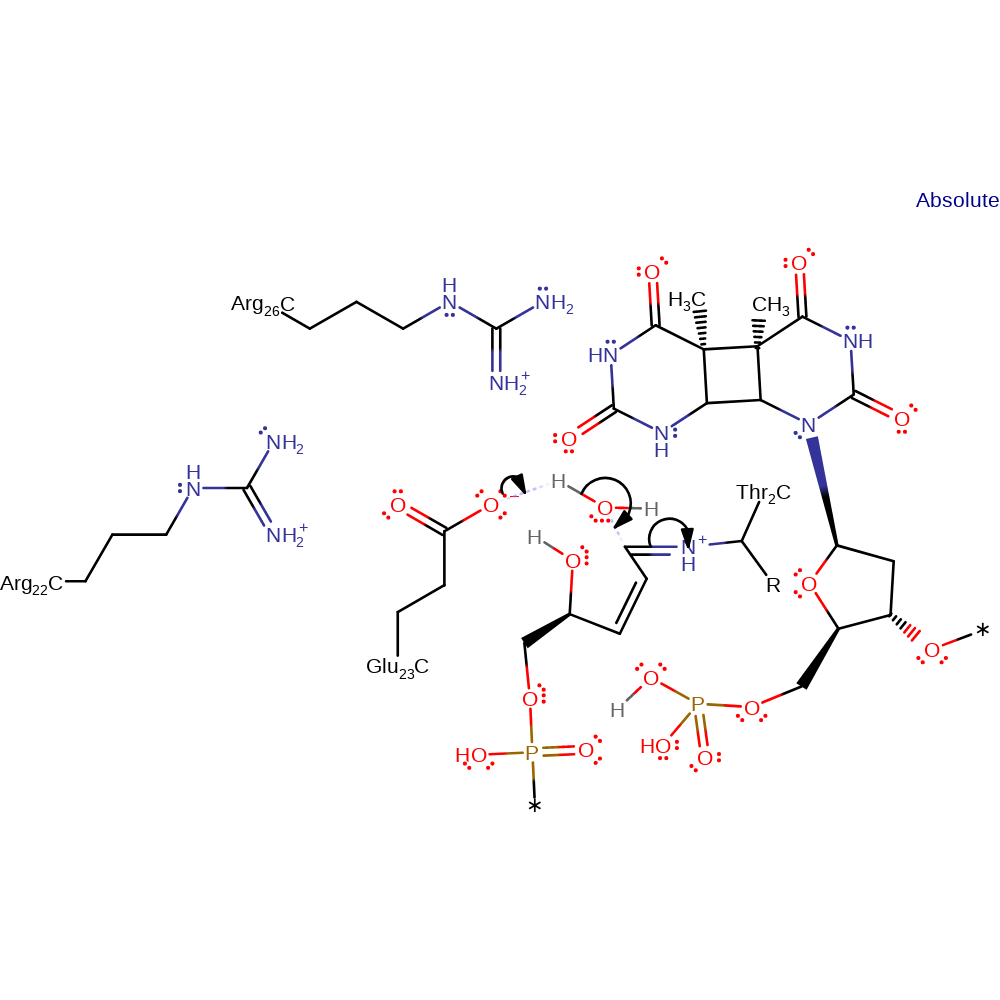
Step 6. Glu23 deprotonates water, which attacks the C1 bound to the N-terminal Thr2 in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln23(22)A(C) | proton acceptor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 7. The N-terminal Thr2 deprotonates the newly formed alcohol group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation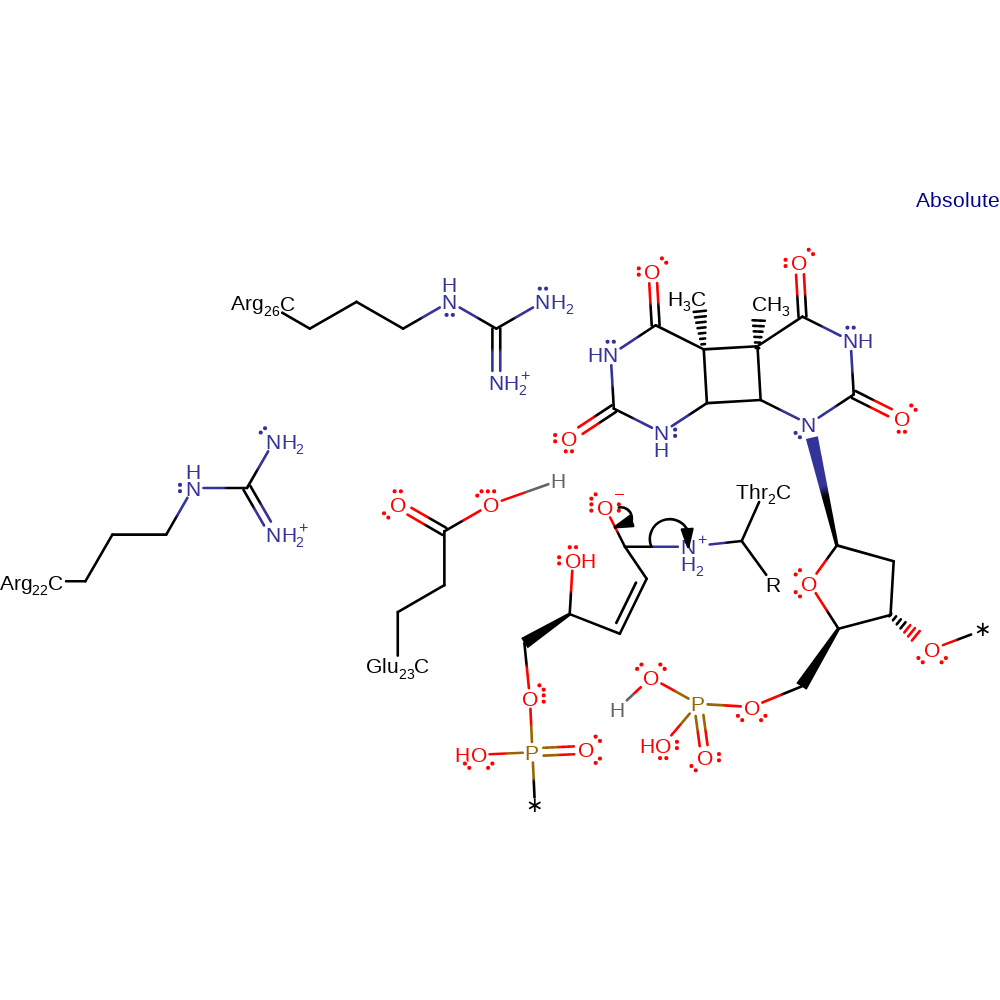
Step 8. The oxyanion initiates an elimination of the N-terminal Thr2, regenerating the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg22(21)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg26(25)A(C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr2(1)A(C) (N-term) | nucleofuge |




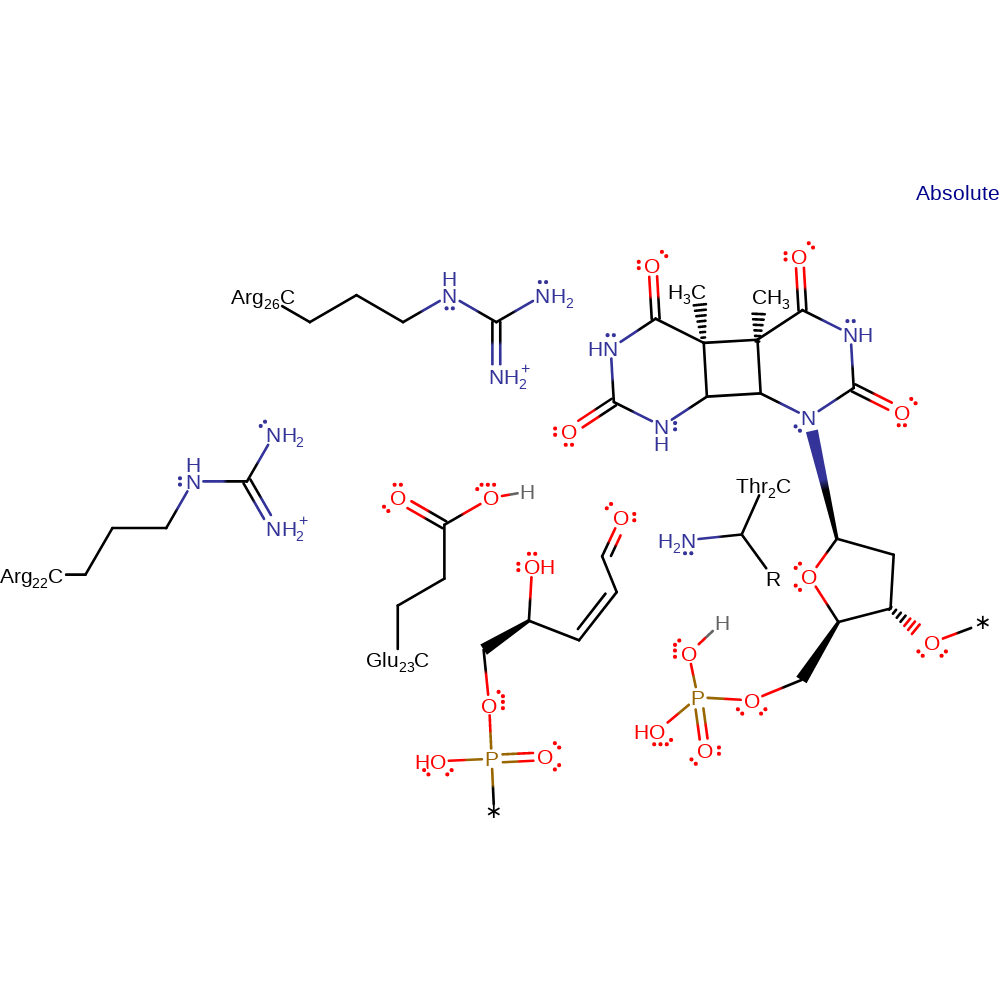 Download:
Download: