Serine hydroxymethyltransferase
serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a PLP-dependent protein that catalyses the reversible interconversion of serine and glycine with tetrahydrofolate serving as the one-carbon carrier. This reaction serves as the major source of one-carbon groups required for the biosynthesis of purines, thymidylate, methionine and many neurotransmitters.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P07511
 (2.1.2.1)
(2.1.2.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
1ls3
- Crystal Structure of the Complex between Rabbit Cytosolic Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase and TriGlu-5-formyl-tetrahydrofolate
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 (see all for 1ls3)
(see all for 1ls3)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.2.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The THF-dependent reaction is thought to proceed via a retroaldol mechanism. The serine substrate first forms the external aldimine by displacing Lys229 from the internal aldimine. Glu57 abstracts the C3-OH proton, initiating the loss of formaldehyde from the intermediate leaving behind the glycine-quinoid aldimine. This rearranges to form the glycine aldimine. This intermediate is broken down by nucleophilic attack of Lys229 at the imine functionality, displacing glycine and reforming the internal aldimine, the enzyme resting state. The released formaldehyde reacts with the THF cofactor to form 5,10-methylene-H4-folate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ls3) | ||
| Lys257 | Lys229(256)A | In the enzyme ground state, Lys229 is covalently attached to the PLP cofactor. During catalysis, it is elminated and acts as a general acid/base, before initiating the final transaldimination reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Glu75 | Glu57(74)B | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Thr254, Asp228 | Thr226(253)A, Asp200(227)A | Acts to stabilise the PLP cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg263 | Arg235(262)A | Activates Tyr55. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr73 | Tyr55(72)B | Tyr55 is indispensable for a correct positioning of the cofactor and for the maintenance of the structure of several loops involved in substrate and cofactor binding. Also thought to act as the general acid/base in the proton transfers that occur during the transaldimination reaction. | steric locator |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, dehydration, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, cyclisation, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Szebenyi DM et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 6865-6876. Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase: Role of Glu75 and Evidence that Serine Is Cleaved by a Retroaldol Mechanism†. DOI:10.1021/bi049791y. PMID:15170323.
- Milano T et al. (2015), Protein Eng Des Sel, 28, 415-426. Conserved water molecules in bacterial serine hydroxymethyltransferases. DOI:10.1093/protein/gzv026. PMID:25986490.
- Gandhi S et al. (2015), Exp Parasitol, 149, 16-23. Arg-265: A critical residue of L.donovani cytosolic SHMT in maintaining the binding of THF and catalysis. DOI:10.1016/j.exppara.2014.12.004. PMID:25499510.
- Chiba Y et al. (2012), FEBS J, 279, 504-514. Mechanism for folate-independent aldolase reaction catalyzed by serine hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08443.x. PMID:22141341.
- Florio R et al. (2011), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1814, 1489-1496. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase: A model enzyme for mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary studies. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.10.010. PMID:21059411.
- Pai VR et al. (2009), Biochem J, 418, 635-642. Structural and functional studies ofBacillus stearothermophilusserine hydroxymethyltransferase: the role of Asn341, Tyr60and Phe351in tetrahydrofolate binding. DOI:10.1042/bj20081739. PMID:19046138.
- Pang CK et al. (2009), Mol Biochem Parasitol, 168, 74-83. Catalytic and ligand-binding characteristics of Plasmodium falciparum serine hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.06.011. PMID:19591883.
- Vivoli M et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 12034-12046. Role of a Conserved Active Site Cation−π Interaction inEscherichia coliSerine Hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/bi901568b. PMID:19883126.
- Florio R et al. (2009), FEBS J, 276, 132-143. The role of evolutionarily conserved hydrophobic contacts in the quaternary structure stability of Escherichia coli serine hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06761.x. PMID:19019081.
- Bhatt AN et al. (2008), J Biochem, 144, 295-303. Characterization of Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate-Binding Domain and Folding Intermediate of Bacillus subtilis Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase: an Autonomous Folding Domain. DOI:10.1093/jb/mvn067. PMID:18483062.
- Rajaram V et al. (2007), FEBS J, 274, 4148-4160. Structure determination and biochemical studies onBacillus stearothermophilusE53Q serine hydroxymethyltransferase and its complexes provide insights on function and enzyme memory. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05943.x. PMID:17651438.
- Bhavani S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 6929-6937. Role of Lys-226 in the Catalytic Mechanism ofBacillus StearothermophilusSerine HydroxymethyltransferaseCrystal Structure and Kinetic Studies†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi047800x. PMID:15865438.
- Schirch V et al. (2005), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 9, 482-487. Serine hydroxymethyltransferase revisited. DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.08.017. PMID:16125438.
- Fu TF et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 31088-31094. Role of Proline Residues in the Folding of Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m303779200. PMID:12773539.
- Trivedi V et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 17161-17169. Crystal Structure of Binary and Ternary Complexes of Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase from Bacillus stearothermophilus: INSIGHTS INTO THE CATALYTIC MECHANISM. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m111976200. PMID:11877399.
- Scarsdale JN et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 296, 155-168. Crystal structure at 2.4 Å resolution of E. coli serine hydroxymethyltransferase in complex with glycine substrate and 5-formyl tetrahydrofolate. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3453. PMID:10656824.
- Rao JV et al. (2000), Eur J Biochem, 267, 5967-5976. The role of Glu74 and Tyr82 in the reaction catalyzed by sheep liver cytosolic serine hydroxymethyltransferase. DOI:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01667.x. PMID:10998057.
- Contestabile R et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 7492-7500. Role of tyrosine 65 in the mechanism of serine hydroxymethyltransferase. PMID:10858298.
- Delle Fratte S et al. (1994), Eur J Biochem, 225, 395-401. The function of arginine 363 as the substrate carboxyl-binding site in Escherichia coli serine hydroxymethyltransferase. PMID:7925461.
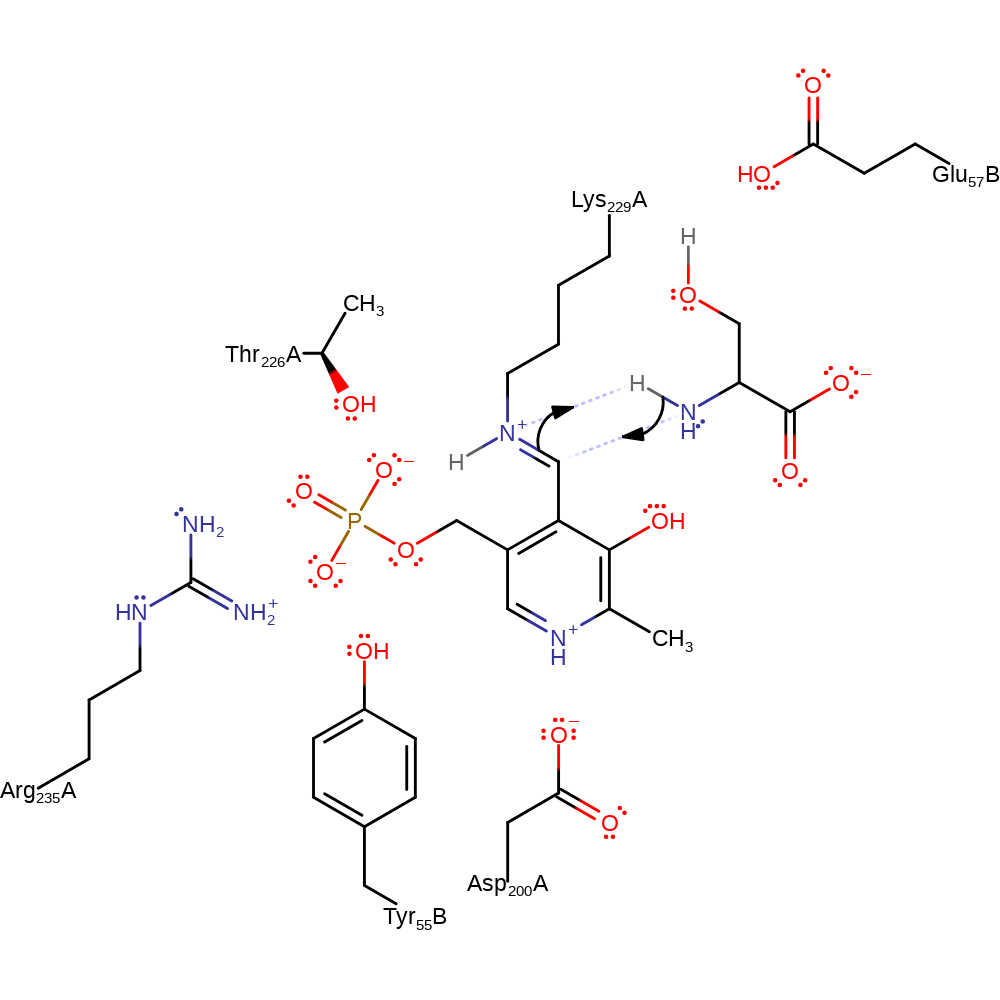
Step 1. The amine of the substrate L-serine attacks the PLP cofactor in a nucleophilic addition and the bound Lys229 deprotonates the newly attached amine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | covalently attached |
| Glu57(74)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Lys229(256)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation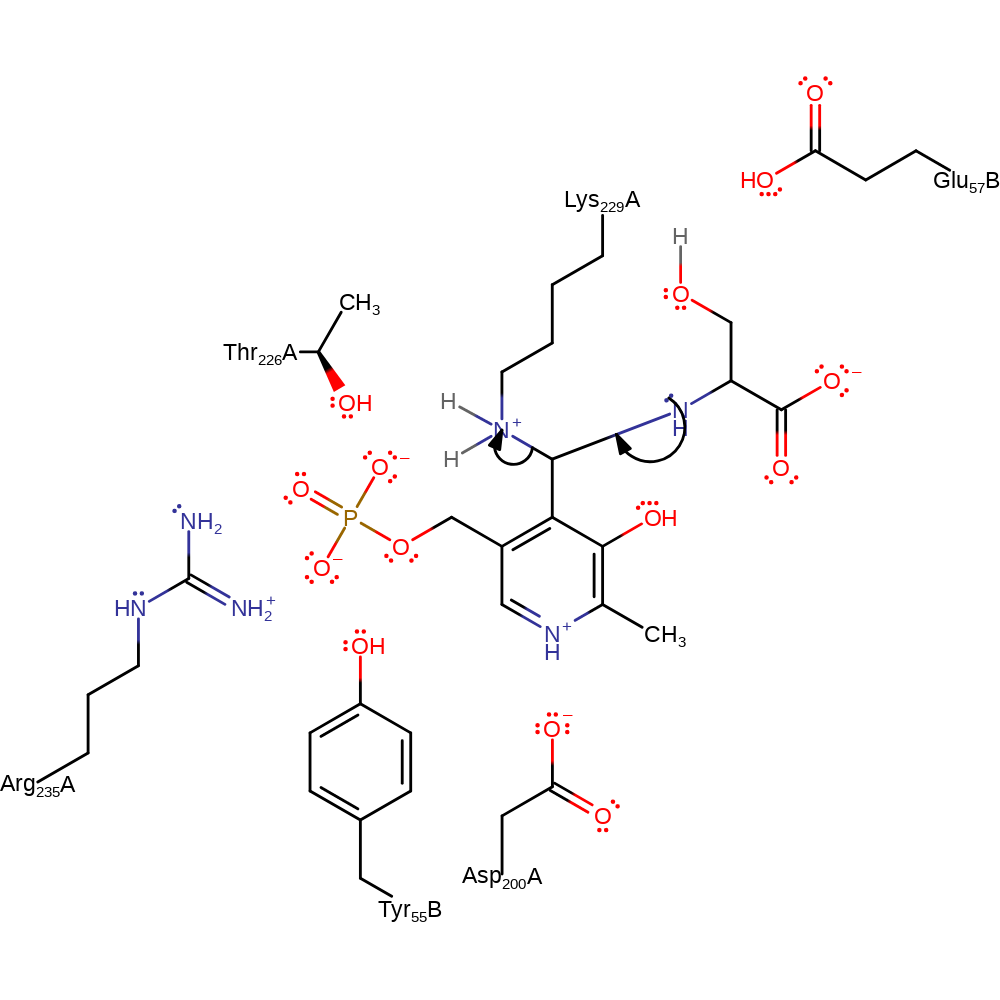
Step 2. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound lysine, resulting in free PLP and lysine in a neutral state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu57(74)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation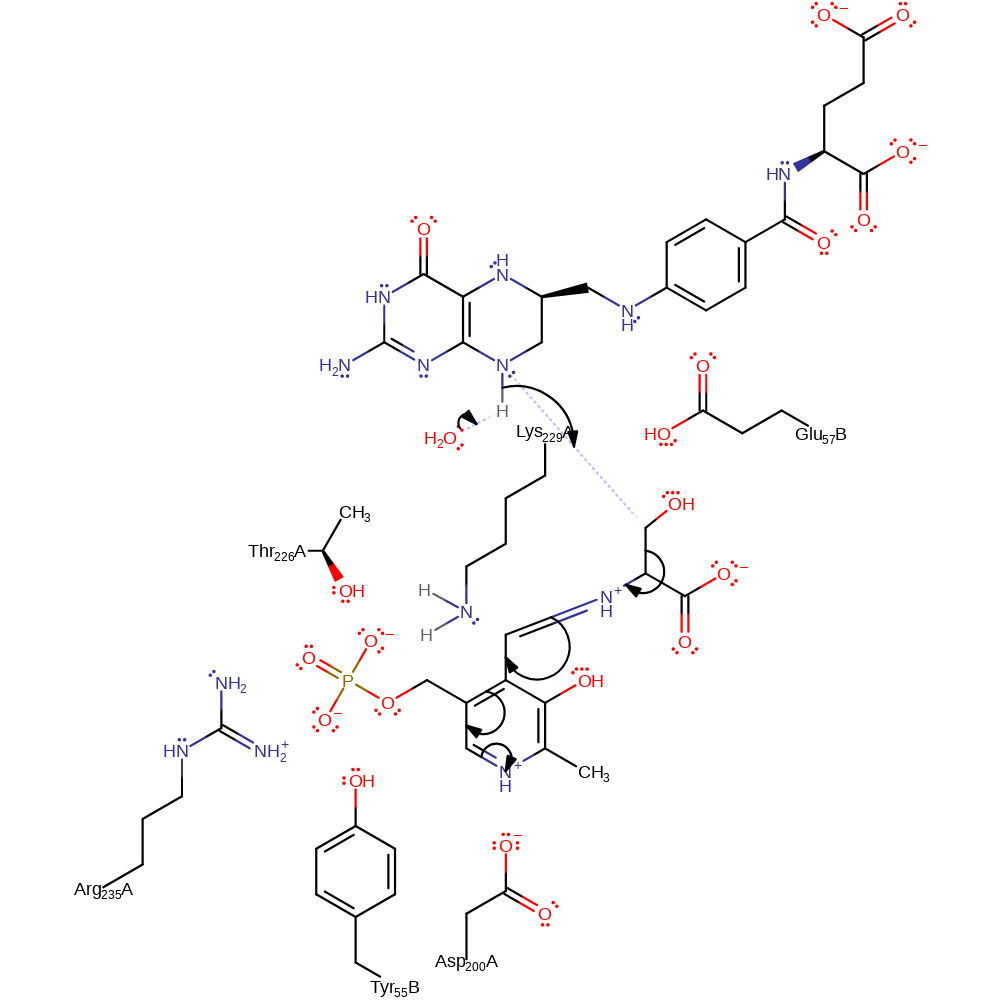
Step 3. Water deprotonates the second substrate (tetrahydrofolate), which attacks the L-serine-PLP complex, transferring the Me-OH group the tetrahydrofolate. PLP acts as an electron sink ofr this nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu57(74)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation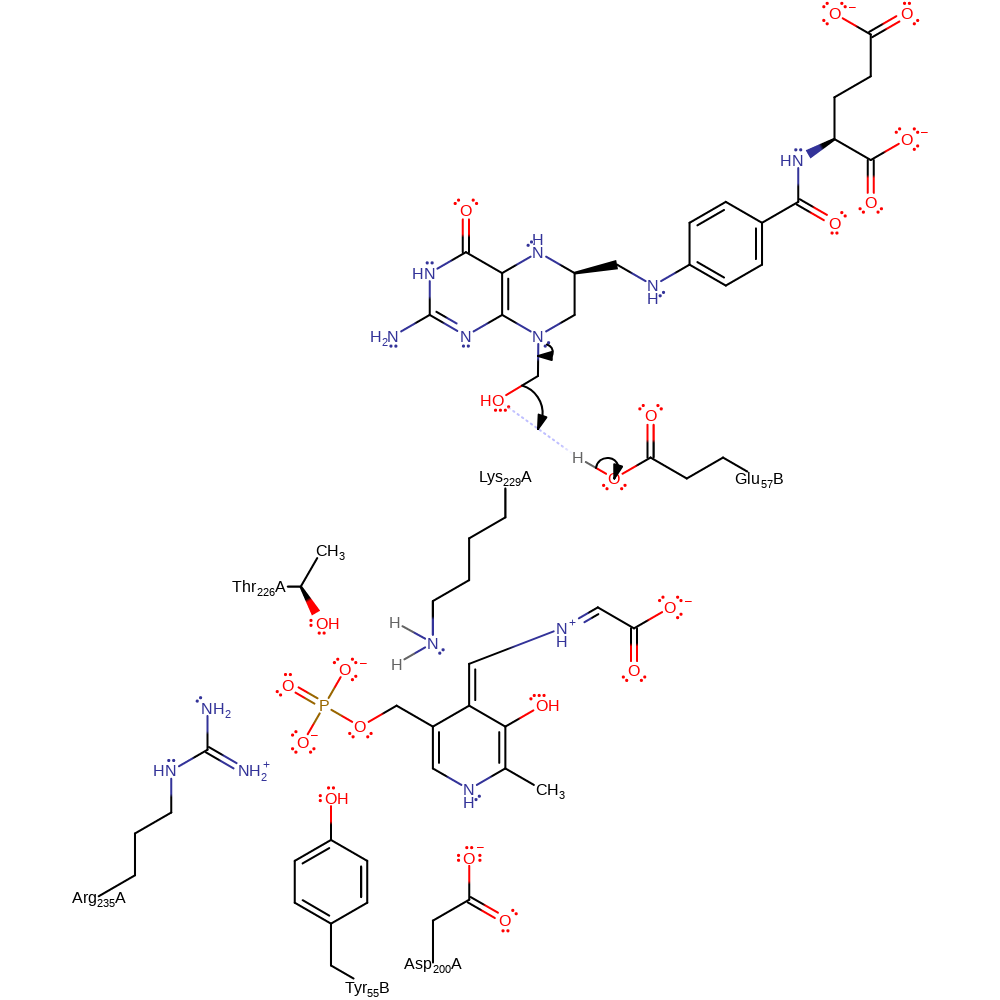
Step 4. The methoxylated nitrogen of the tetrahydrofolate intermediate initiates an elimination of the hydroxide group, which reprotonates from Glu57B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu57(74)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Glu57(74)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed, dehydration
Step 5. Glu57B deprotonates the methylated tetrahydrofolate intermediate at the secondary amine, which forms an intramolecular nucleophilic addition to the added carbon, forming 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys229(256)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu57(74)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Glu57(74)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, intermediate formation, overall product formed, cyclisation
Step 6. The amine of Lys229 attacks the PLP in a nucleophilic addition reaction, the secondary amine of the attached substrate protonates from the bound Lys229.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Lys229(256)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation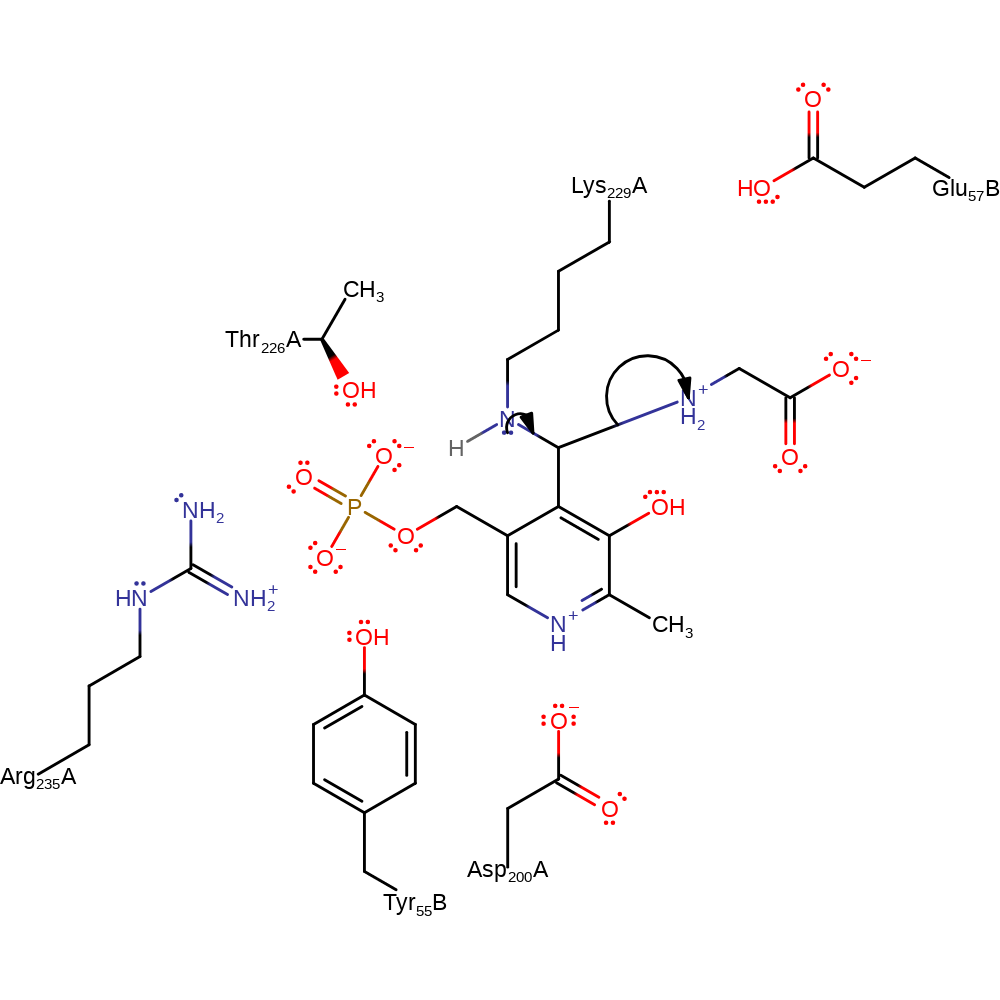
Step 7. The secondary amine that results from the initial attack initiates an elimination of the covalently bound product, resulting in glycine and the regenerated PLP cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr226(253)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | covalently attached |
| Tyr55(72)B | steric locator |
| Asp200(227)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg235(262)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys229(256)A | electron pair donor |





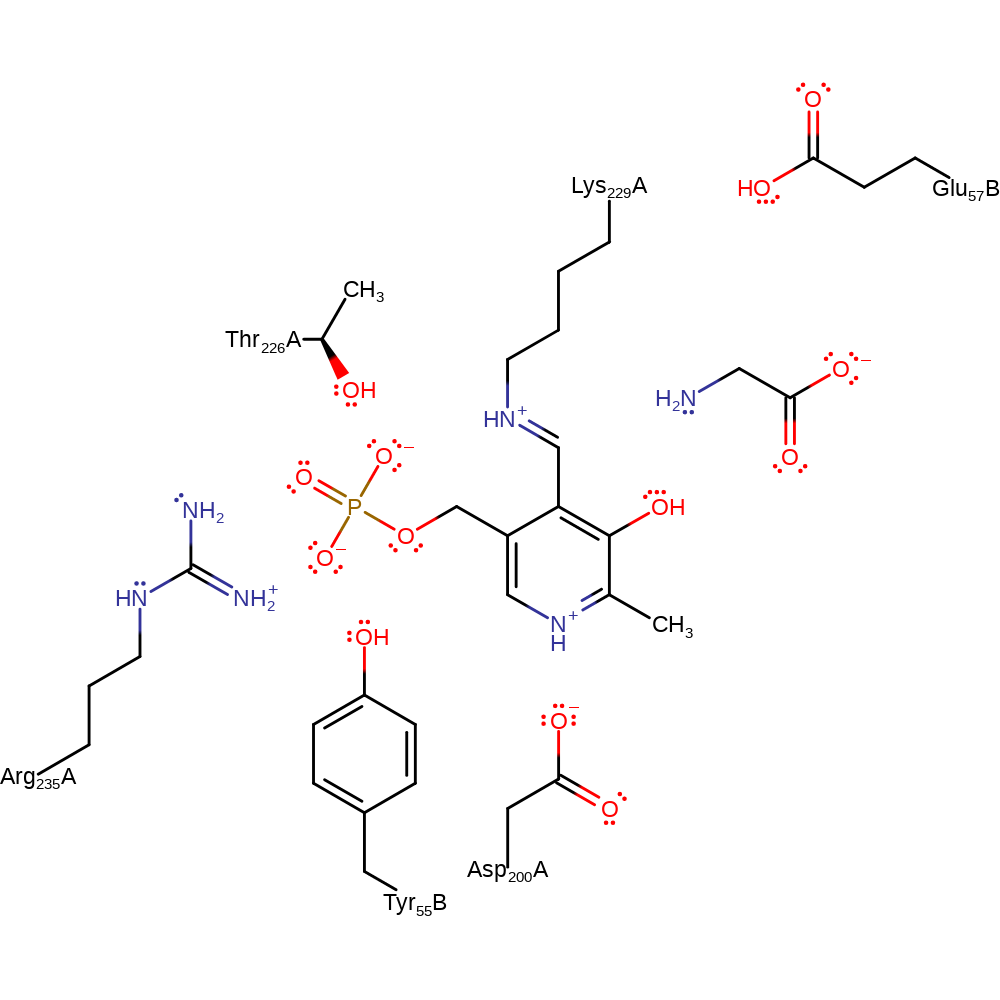 Download:
Download: