Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase
Tyrosine hydroxylase, sourced from Rattus norvegicus belongs to a family of tetrameric, biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases found in metazoans. It catalyses the hydroxylation of the aromatic group of tyrosine. Tyrosine hydroxylase is found in the central nervous system and the adrenal gland where it's role is to catalyse the production of dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) - the rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of catecholamine neurotransmitters.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P04177
 (1.14.16.2)
(1.14.16.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
2toh
- TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE CATALYTIC AND TETRAMERIZATION DOMAINS FROM RAT
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.800.10
 (see all for 2toh)
(see all for 2toh)
- Cofactors
- Iron(3+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.16.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Fe(II) binds to the oxygen molecule, to give Fe(II)O2. This undergoes an irreversible step involving single electron transfer from pterin to the oxygen to form Fe(II)O2- and a pterin cation radical. Radical collapse occurs and intermediate Fe(II) u-peroxypterin is formed. Heterolytic cleavage of the O-O bond of the intermediate results in the hydroxypterin product and an electrophilic Fe(IV)O species. The Fe(IV)O species is stabilised by ligand His 331. His 331 is stabilised electrostatically by Ser 395. Electrophilic aromatic substitution takes place. The aromatic ring of tyrosine becomes hydroxylated.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2toh) | ||
| Ser395 | Ser395(240)A | Ser 395 electrostatically stabilises and places His 331. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| His331, Ser395 | His331(176)A, Ser395(240)A | Residue is positioned appropriately (ligand position known). | hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His336, Glu376 | His336(181)A, Glu376(221)A | Forms part of the iron binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular homolytic addition, redox reaction, radical formation, overall reactant used, cofactor used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, aromatic bimolecular electrophilic addition, electron transfer, radical termination, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, hydride transfer, coordination, heterolysis, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Fitzpatrick PF (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 14083-14091. Mechanism of Aromatic Amino Acid Hydroxylation†. DOI:10.1021/bi035656u. PMID:14640675.
- Zhang S et al. (2014), J Mol Biol, 426, 1483-1497. The solution structure of the regulatory domain of tyrosine hydroxylase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.12.015. PMID:24361276.
- Roberts KM et al. (2013), IUBMB Life, 65, 350-357. Mechanisms of tryptophan and tyrosine hydroxylase. DOI:10.1002/iub.1144. PMID:23441081.
- Krzyaniak MD et al. (2013), Biochemistry, 52, 8430-8441. Pulsed EPR study of amino acid and tetrahydropterin binding in a tyrosine hydroxylase nitric oxide complex: evidence for substrate rearrangements in the formation of the oxygen-reactive complex. DOI:10.1021/bi4010914. PMID:24168553.
- Olsson E et al. (2011), Chemistry, 17, 3746-3758. Formation of the iron-oxo hydroxylating species in the catalytic cycle of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. DOI:10.1002/chem.201002910. PMID:21351297.
- Eser BE et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 645-652. Measurement of intrinsic rate constants in the tyrosine hydroxylase reaction. DOI:10.1021/bi901874e. PMID:20025246.
- Chow MS et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 7685-7698. Spectroscopy and kinetics of wild-type and mutant tyrosine hydroxylase: mechanistic insight into O2 activation. DOI:10.1021/ja810080c. PMID:19489646.
- Pavon JA et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 11030-11037. Insights into the catalytic mechanisms of phenylalanine and tryptophan hydroxylase from kinetic isotope effects on aromatic hydroxylation. DOI:10.1021/bi0607554. PMID:16953590.
- Ellis HR et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 4174-4181. Mutation of Serine 395 of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Decouples Oxygen−Oxygen Bond Cleavage and Tyrosine Hydroxylation†. DOI:10.1021/bi9928546. PMID:10747809.
- Goodwill KE et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 13437-13445. Crystal structure of tyrosine hydroxylase with bound cofactor analogue and iron at 2.3 A resolution: self-hydroxylation of Phe300 and the pterin-binding site. DOI:10.1021/bi981462g. PMID:9753429.
- Goodwill KE et al. (1997), Nat Struct Biol, 4, 578-585. Crystal structure of tyrosine hydroxylase at 2.3 A and its implications for inherited neurodegenerative diseases. PMID:9228951.
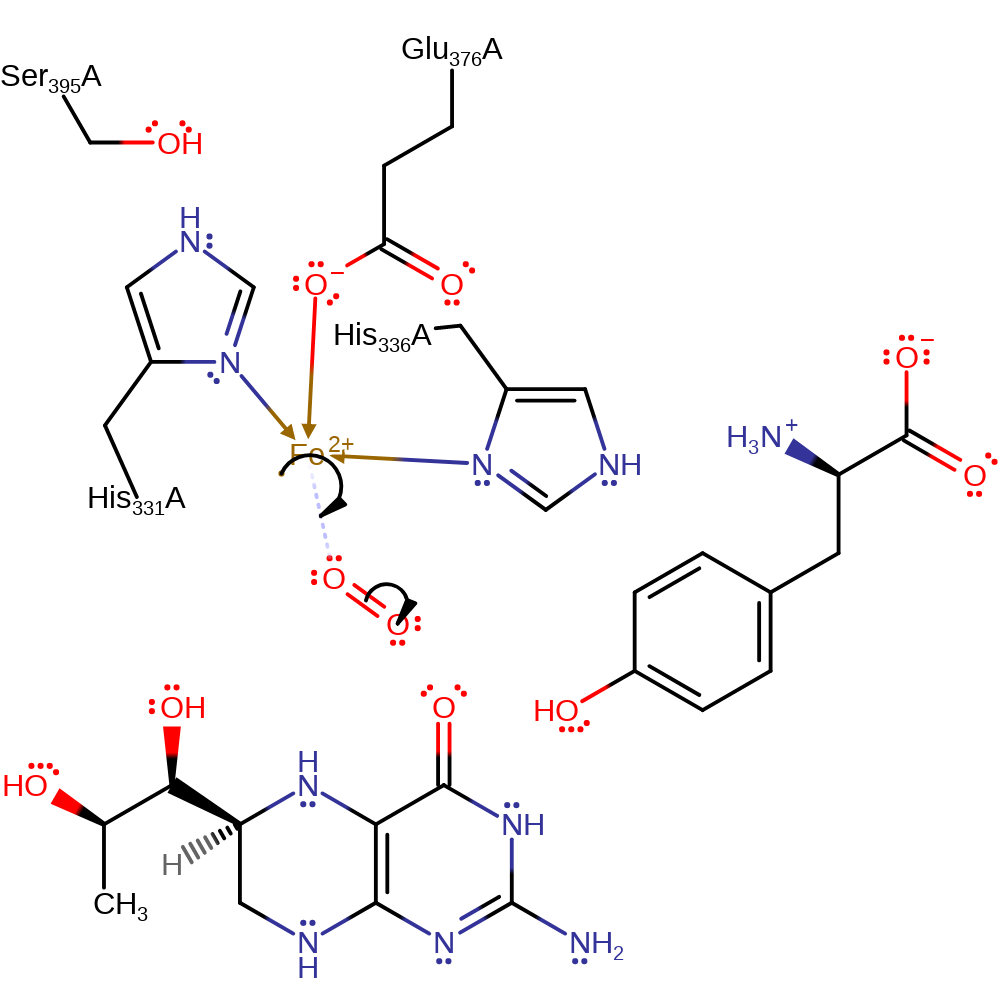
Step 1. The Fe(II) centre donates a single electron to the dioxygen molecule in a homolytic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
| Ser395(240)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, redox reaction, radical formation, overall reactant used, cofactor used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation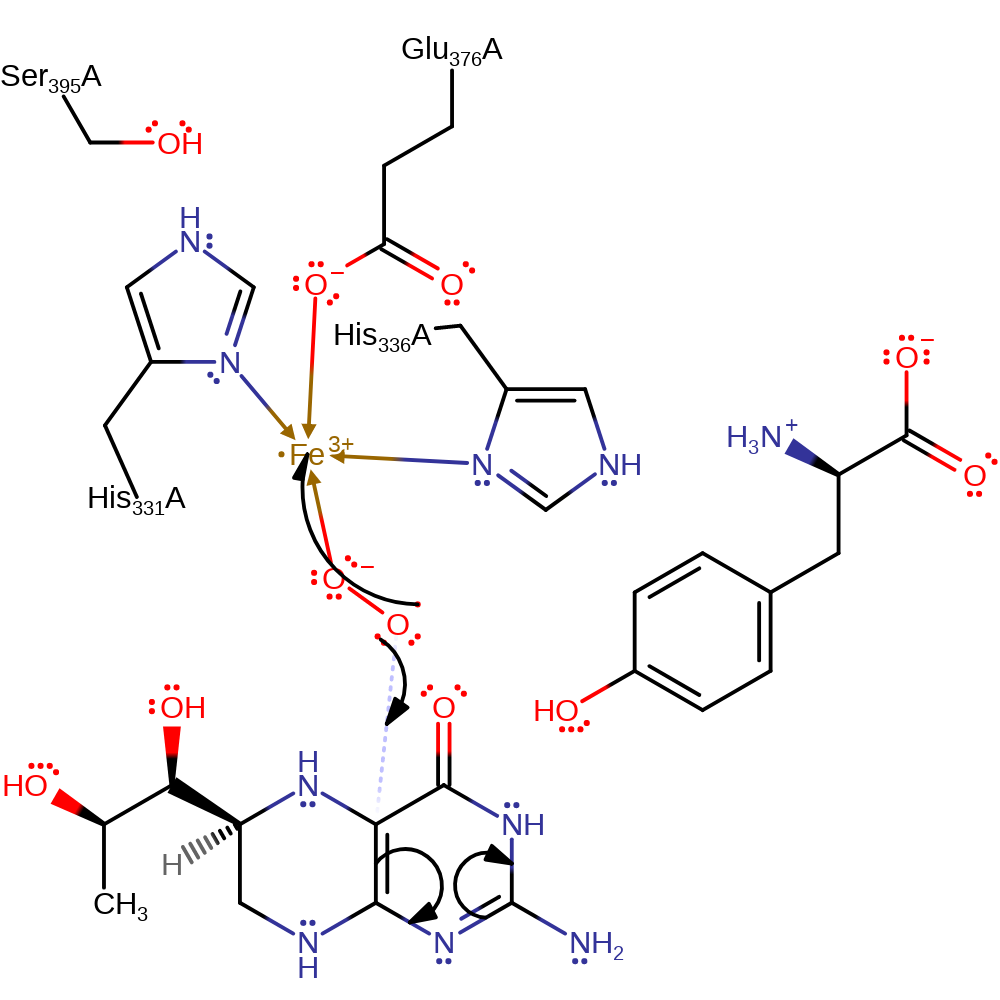
Step 2. The bound dioxygen radical initiates an electrophilic addition to the aromatic tetrahydrobiopterin which causes a single electron to be transferred back to the Fe(III) centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser395(240)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular electrophilic addition, electron transfer, radical termination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation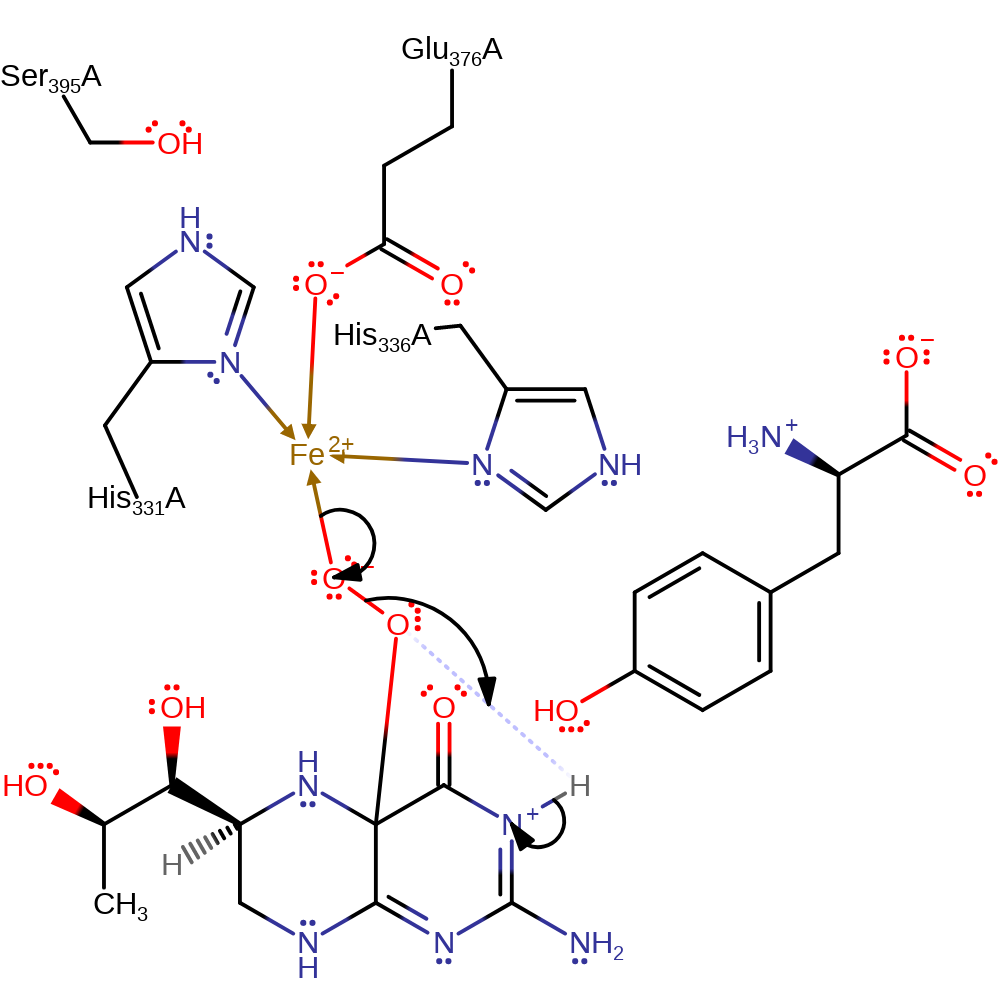
Step 3. The Fe(II) centre donates an electron pair to the oxygen bound directly to the Fe ion, eliminating the 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin product by cleaving the peroxo bond. The product undergoes an internal proton transfer to generate the final state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed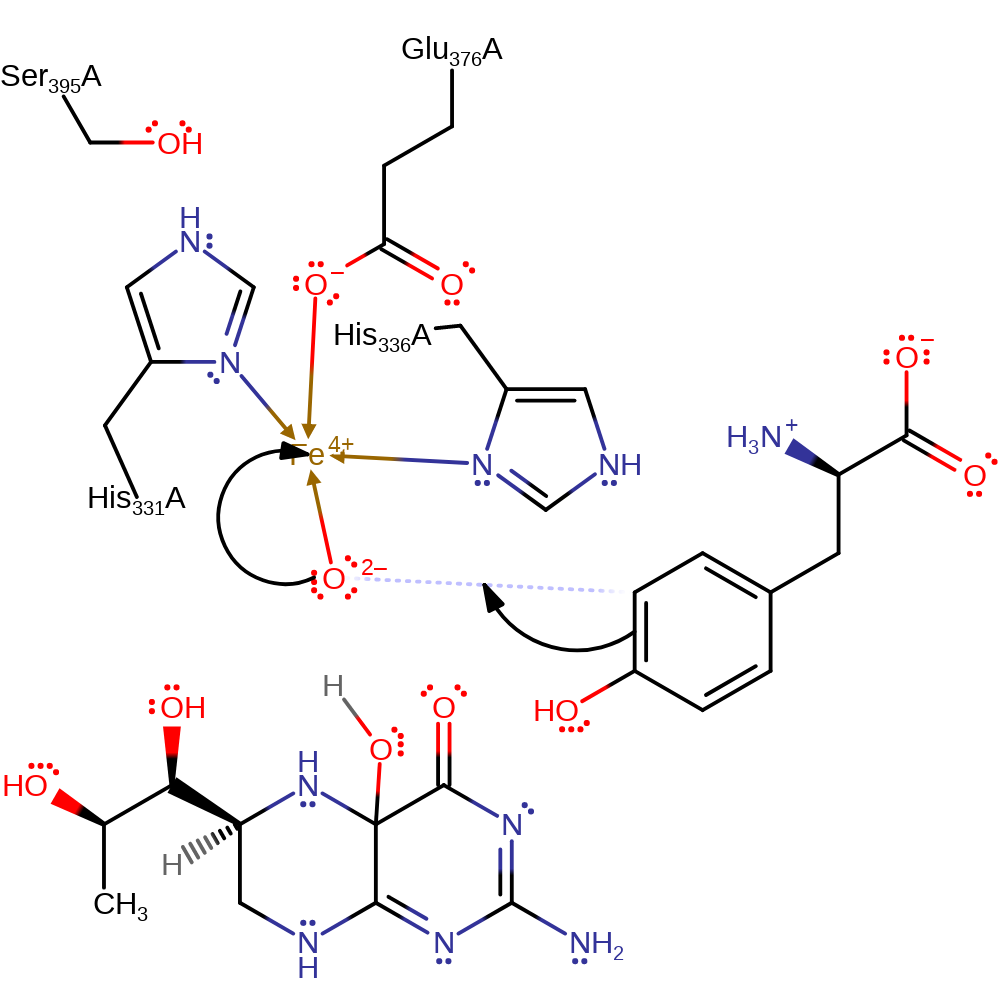
Step 4. Tyrosine initiates an electrophilic addition to the bound iron-bound oxo group, causing the iron centre to accept two electrons.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular electrophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation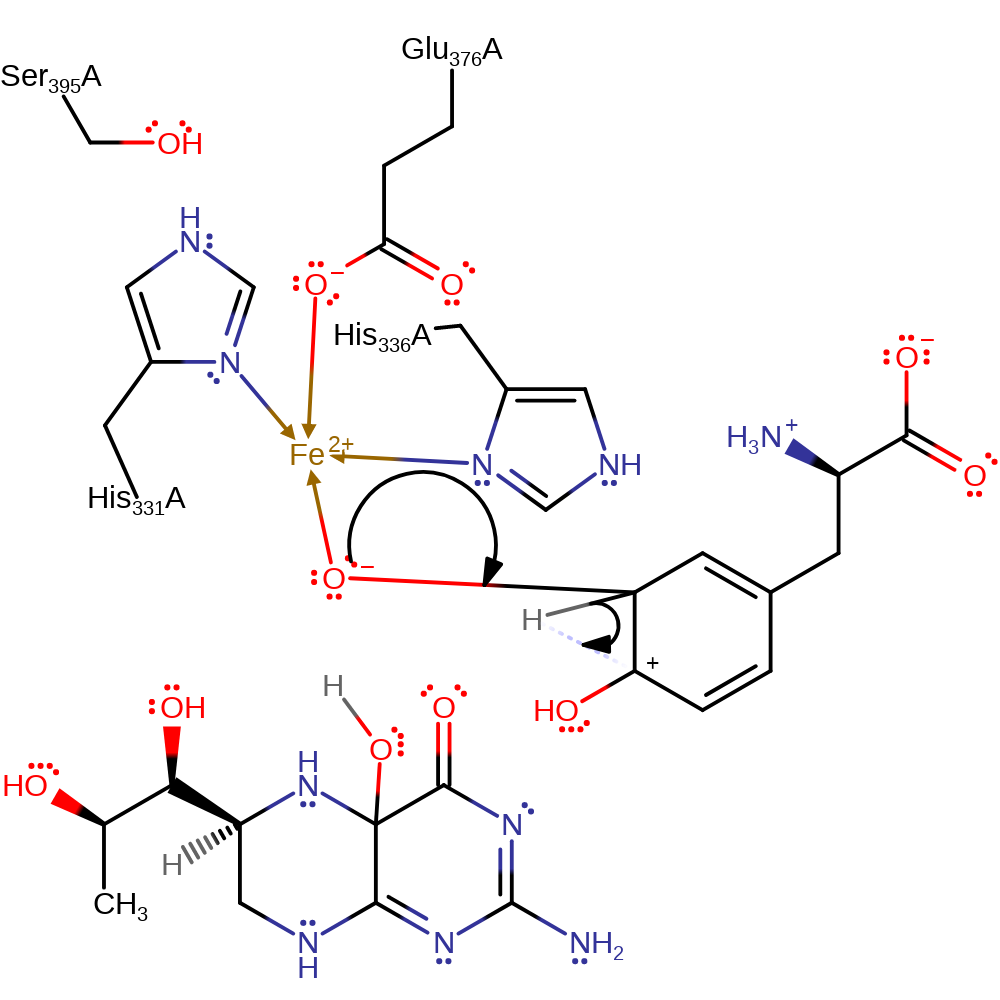
Step 5. In an NIH shift, the alkoxide group forms a ketone group, initiating an internal hydride transfer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
| Ser395(240)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, coordination, heterolysis, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated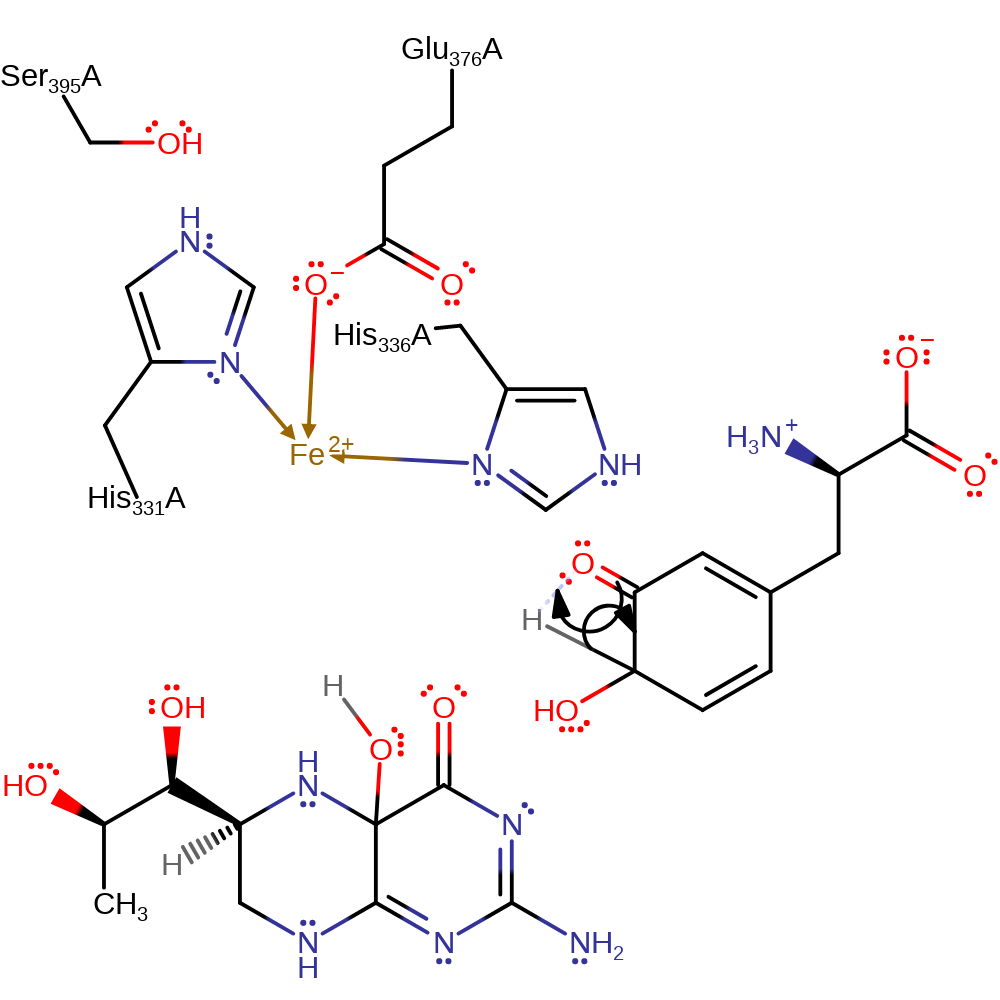
Step 6. The intermediate undergoes a keto-enol tautomerisation forming the 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine tautomer of the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His331(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser395(240)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His331(176)A | metal ligand |
| His336(181)A | metal ligand |
| Glu376(221)A | metal ligand |
| Ser395(240)A | electrostatic stabiliser |





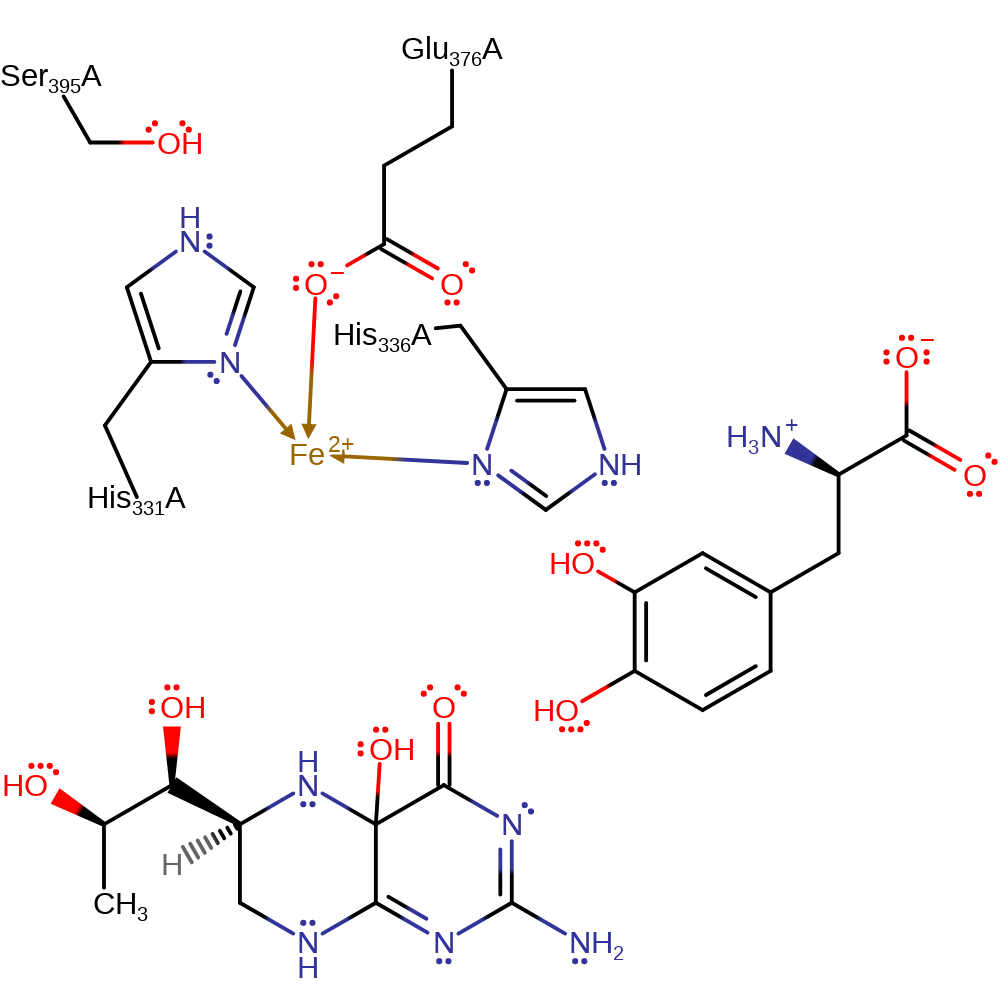 Download:
Download: