 |
PDBsum entry 6snh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Membrane protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6snh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 479 a.a.
479 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 225 a.a.
225 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 214 a.a.
214 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Membrane protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Cryo-em structure of yeast alg6 in complex with 6ag9 fab and dol25-p- glc
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Dolichyl pyrophosphate man9glcnac2 alpha-1,3- glucosyltransferase. Chain: x. Synonym: asparagine-linked glycosylation protein 6,dol-p-glc:man(9) glcnac(2)-pp-dol alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase,dolichyl-p- glc:man9glcnac2-pp-dolichyl glucosyltransferase. Engineered: yes. 6ag9 fab heavy chain. Chain: h.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Baker's yeast. Organism_taxid: 4932. Gene: alg6, yor002w, una544. Expressed in: spodoptera frugiperda. Expression_system_taxid: 7108. Synthetic construct. Organism_taxid: 32630. Expressed in: escherichia coli 'bl21-gold(de3)plyss ag'.
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.S.Bloch,G.Pesciullesi,J.Boilevin,K.Nosol,R.N.Irobalieva,T.Darbre, M.Aebi,A.A.Kossiakoff,J.L.Reymond,K.P.Locher
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.S.Bloch
et al.
(2020).
Structure and mechanism of the ER-based glucosyltransferase ALG6.
Nature,
579,
443-447.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Aug-19
|
Release date:
|
11-Mar-20
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q12001
(ALG6_YEAST) -
Dolichyl pyrophosphate Man9GlcNAc2 alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
544 a.a.
479 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain X:
E.C.2.4.1.267
- dolichyl-P-Glc:Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol alpha-1,3-glucosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man- (1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha- D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNAc- diphospho-di-trans,poly-cis-dolichol + a di-trans,poly-cis-dolichyl beta- D-glucosyl phosphate = an alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D- Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)- [alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man- (1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNAc-diphospho-di-trans,poly- cis-dolichol + a di-trans,poly-cis-dolichyl phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
dolichyl beta-D-glucosyl phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man- (1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha- D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)- beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNAc-diphosphodolichol
|
=
|
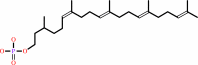 dolichyl phosphate
dolichyl phosphate
|
+
|
alpha-D-Glc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->2)- alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man- (1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D- GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-D-GlcNAc-diphosphodolichol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nature
579:443-447
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and mechanism of the ER-based glucosyltransferase ALG6.
|
|
J.S.Bloch,
G.Pesciullesi,
J.Boilevin,
K.Nosol,
R.N.Irobalieva,
T.Darbre,
M.Aebi,
A.A.Kossiakoff,
J.L.Reymond,
K.P.Locher.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In eukaryotic protein N-glycosylation, a series of glycosyltransferases catalyse
the biosynthesis of a dolichylpyrophosphate-linked oligosaccharide before its
transfer onto acceptor proteins1. The final seven steps occur in the
lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and require dolichylphosphate-activated
mannose and glucose as donor substrates2. The responsible
enzymes-ALG3, ALG9, ALG12, ALG6, ALG8 and ALG10-are glycosyltransferases of the
C-superfamily (GT-Cs), which are loosely defined as containing membrane-spanning
helices and processing an isoprenoid-linked carbohydrate donor
substrate3,4. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure
of yeast ALG6 at 3.0 Å resolution, which reveals a previously undescribed
transmembrane protein fold. Comparison with reported GT-C structures suggests
that GT-C enzymes contain a modular architecture with a conserved module and a
variable module, each with distinct functional roles. We used synthetic
analogues of dolichylphosphate-linked and dolichylpyrophosphate-linked sugars
and enzymatic glycan extension to generate donor and acceptor substrates using
purified enzymes of the ALG pathway to recapitulate the activity of ALG6 in
vitro. A second cryo-electron microscopy structure of ALG6 bound to an analogue
of dolichylphosphate-glucose at 3.9 Å resolution revealed the active site of
the enzyme. Functional analysis of ALG6 variants identified a catalytic
aspartate residue that probably acts as a general base. This residue is
conserved in the GT-C superfamily. Our results define the architecture of
ER-luminal GT-C enzymes and provide a structural basis for understanding their
catalytic mechanisms.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

