 |
PDBsum entry 6f4m

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6f4m
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.73
- [protein]-arginine 3-hydroxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-arginyl-[protein] + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = (3R)-3-hydroxy-L-arginyl- [protein] + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-arginyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
(3R)-3-hydroxy-L-arginyl- [protein]
|
+
|
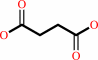 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.4.-.-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Commun
9:1180
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase.
|
|
S.E.Wilkins,
S.Islam,
J.M.Gannon,
S.Markolovic,
R.J.Hopkinson,
W.Ge,
C.J.Schofield,
R.Chowdhury.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Oxygenase-catalysed post-translational modifications of basic protein residues,
including lysyl hydroxylations and Nε-methyl lysyl demethylations,
have important cellular roles. Jumonji-C (JmjC) domain-containing protein 5
(JMJD5), which genetic studies reveal is essential in animal development, is
reported as a histone Nε-methyl lysine demethylase (KDM). Here we
report how extensive screening with peptides based on JMJD5 interacting proteins
led to the finding that JMJD5 catalyses stereoselective C-3 hydroxylation of
arginine residues in sequences from human regulator of chromosome condensation
domain-containing protein 1 (RCCD1) and ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6).
High-resolution crystallographic analyses reveal overall fold, active site and
substrate binding/product release features supporting the assignment of JMJD5 as
an arginine hydroxylase rather than a KDM. The results will be useful in the
development of selective oxygenase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer and
genetic diseases.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

