 |
PDBsum entry 5teb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5teb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Signaling protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the tir domain from the arabidopsis thaliana disease resistance protein rpp1
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Recognition of peronospora parasitica 1. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana. Mouse-ear cress. Organism_taxid: 3702. Gene: rpp1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.220
|
R-free:
|
0.269
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.R.Bentham,X.Zhang,T.Croll,S.Williams,B.Kobe
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
X.Zhang
et al.
(2017).
Multiple functional self-association interfaces in plant TIR domains.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
114,
E2046.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
20-Sep-16
|
Release date:
|
01-Feb-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
D9IW02
(D9IW02_ARATH) -
ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase from Arabidopsis thaliana
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1154 a.a.
166 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.2.6
- ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + H2O = ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
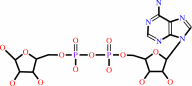 ADP-D-ribose
ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
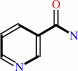 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
114:E2046
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Multiple functional self-association interfaces in plant TIR domains.
|
|
X.Zhang,
M.Bernoux,
A.R.Bentham,
T.E.Newman,
T.Ve,
L.W.Casey,
T.M.Raaymakers,
J.Hu,
T.I.Croll,
K.J.Schreiber,
B.J.Staskawicz,
P.A.Anderson,
K.H.Sohn,
S.J.Williams,
P.N.Dodds,
B.Kobe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The self-association of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR)
domains has been implicated in signaling in plant and animal immunity receptors.
Structure-based studies identified different TIR-domain dimerization interfaces
required for signaling of the plant nucleotide-binding oligomerization
domain-like receptors (NLRs) L6 from flax and disease resistance protein RPS4
from Arabidopsis Here we show that the crystal structure of the TIR domain from
the Arabidopsis NLR suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1 (SNC1) contains both an
L6-like interface involving helices αD and αE (DE interface) and an RPS4-like
interface involving helices αA and αE (AE interface). Mutations in either the
AE- or DE-interface region disrupt cell-death signaling activity of SNC1, L6,
and RPS4 TIR domains and full-length L6 and RPS4. Self-association of L6 and
RPS4 TIR domains is affected by mutations in either region, whereas only
AE-interface mutations affect SNC1 TIR-domain self-association. We further show
two similar interfaces in the crystal structure of the TIR domain from the
Arabidopsis NLR recognition of Peronospora parasitica 1 (RPP1). These data
demonstrate that both the AE and DE self-association interfaces are
simultaneously required for self-association and cell-death signaling in diverse
plant NLRs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

