 |
PDBsum entry 4z68

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Protein binding
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4z68
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Protein binding
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Hybrid structural analysis of the arp2/3 regulator arpin identifies its acidic tail as a primary binding epitope
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Tankyrase-2. Chain: a. Fragment: ankyrin repeats domain, unp residues 490-644. Synonym: tank2,adp-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 6,artd6, poly [adp-ribose] polymerase 5b,tnks-2,trf1-interacting ankyrin- related adp-ribose polymerase 2,tankyrase ii,tankyrase-like protein, tankyrase-related protein. Engineered: yes. Glu-ile-arg-glu-gln-gly-asp-gly-ala-glu-asp-glu.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: tnks2, parp5b, tank2, tnkl. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: rosetta plyss. Synthetic: yes. Organism_taxid: 9606
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.86Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.175
|
R-free:
|
0.217
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.K.Fetics,V.Campanacci,I.Dang,A.Gautreau,J.Cherfils
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.Fetics
et al.
(2016).
Hybrid Structural Analysis of the Arp2/3 Regulator Arpin Identifies Its Acidic Tail as a Primary Binding Epitope.
Structure,
24,
252-260.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Apr-15
|
Release date:
|
30-Dec-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.4.2.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.4.2.30
- NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
NAD+ + (ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor = nicotinamide + (ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
(ADP-D-ribosyl)n-acceptor
|
=
|
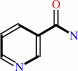 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
(ADP-D- ribosyl)n+1-acceptor
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
24:252-260
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Hybrid Structural Analysis of the Arp2/3 Regulator Arpin Identifies Its Acidic Tail as a Primary Binding Epitope.
|
|
S.Fetics,
A.Thureau,
V.Campanacci,
M.Aumont-Nicaise,
I.Dang,
A.Gautreau,
J.Pérez,
J.Cherfils.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Arpin is a newly discovered regulator of actin polymerization at the cell
leading edge, which steers cell migration by exerting a negative control on the
Arp2/3 complex. Arpin proteins have an acidic tail homologous to the acidic
motif of the VCA domain of nucleation-promoting factors (NPFs). This tail is
predicted to compete with the VCA of NPFs for binding to the Arp2/3 complex,
thereby mitigating activation and/or tethering of the complex to sites of actin
branching. Here, we investigated the structure of full-length Arpin using
synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering, and of its acidic tail in complex with
an ankyrin repeats domain using X-ray crystallography. The data were combined in
a hybrid model in which the acidic tail extends from the globular core as a
linear peptide and forms a primary epitope that is readily accessible in unbound
Arpin and suffices to tether Arpin to interacting proteins with high affinity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

