 |
PDBsum entry 4k44
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.11
- phosphoinositide phospholipase C.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
myo-Inositol Phosphate Metabolism
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate) + H2O = 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
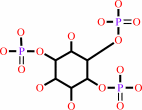 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
|
+
|
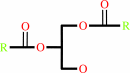 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
52:4810-4819
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Autoinhibition and phosphorylation-induced activation of phospholipase C-γ isozymes.
|
|
N.Hajicek,
T.H.Charpentier,
J.R.Rush,
T.K.Harden,
J.Sondek.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Multiple extracellular stimuli, such as growth factors and antigens, initiate
signaling cascades through tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of
phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ) isozymes. Like most other PLCs, PLC-γ1 is basally
autoinhibited by its X-Y linker, which separates the X- and Y-boxes of the
catalytic core. The C-terminal SH2 (cSH2) domain within the X-Y linker is the
critical determinant for autoinhibition of phospholipase activity. Release of
autoinhibition requires an intramolecular interaction between the cSH2 domain
and a phosphorylated tyrosine, Tyr783, also located within the X-Y linker. The
molecular mechanisms that mediate autoinhibition and phosphorylation-induced
activation have not been defined. Here, we describe structures of the cSH2
domain both alone and bound to a PLC-γ1 peptide encompassing phosphorylated
Tyr783. The cSH2 domain remains largely unaltered by peptide engagement. Point
mutations in the cSH2 domain located at the interface with the peptide were
sufficient to constitutively activate PLC-γ1, suggesting that peptide
engagement directly interferes with the capacity of the cSH2 domain to block the
lipase active site. This idea is supported by mutations in a complementary
surface of the catalytic core that also enhanced phospholipase activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

