 |
PDBsum entry 3f9c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human plasma platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase covalently inhibited by diisopropylfluorophosphate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: unp residues 47-429. Synonym: paf acetylhydrolase, paf 2-acylhydrolase, ldl-associated phospholipase a2, ldl-pla(2), 2-acetyl-1-alkylglycerophosphocholine esterase, 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pla2g7, pafah. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.199
|
R-free:
|
0.261
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
U.Samanta,B.J.Bahnson
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
U.Samanta
et al.
(2009).
Crystal structures of human group-VIIA phospholipase A2 inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents exhibit non-aged complexes.
Biochem Pharmacol,
78,
420-429.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Nov-08
|
Release date:
|
23-Jun-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q13093
(PAFA_HUMAN) -
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
441 a.a.
372 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.47
- 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + acetate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
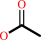 acetate
acetate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochem Pharmacol
78:420-429
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of human group-VIIA phospholipase A2 inhibited by organophosphorus nerve agents exhibit non-aged complexes.
|
|
U.Samanta,
S.D.Kirby,
P.Srinivasan,
D.M.Cerasoli,
B.J.Bahnson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The enzyme group-VIIA phospholipase A2 (gVIIA-PLA2) is bound to lipoproteins in
human blood and hydrolyzes the ester bond at the sn-2 position of phospholipid
substrates with a short sn-2 chain. The enzyme belongs to a serine hydrolase
superfamily of enzymes, which react with organophosphorus (OP) nerve agents. OPs
ultimately exert their toxicity by inhibiting human acetycholinesterase at nerve
synapses, but may additionally have detrimental effects through inhibition of
other serine hydrolases. We have solved the crystal structures of gVIIA-PLA2
following inhibition with the OPs diisopropylfluorophosphate, sarin, soman and
tabun. The sarin and soman complexes displayed a racemic mix of P(R) and P(S)
stereoisomers at the P-chiral center. The tabun complex displayed only the P(R)
stereoisomer in the crystal. In all cases, the crystal structures contained
intact OP adducts that had not aged. Aging refers to a secondary process OP
complexes can go through, which dealkylates the nerve agent adduct and results
in a form that is highly resistant to either spontaneous or oxime-mediated
reactivation. Non-aged OP complexes of the enzyme were corroborated by trypsin
digest and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry of
OP-enzyme complexes. The lack of stereoselectivity of sarin reaction was
confirmed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry using a chiral column to
separate and quantitate the unbound stereoisomers of sarin following incubation
with enzyme. The structural details and characterization of nascent reactivity
of several toxic nerve agents is discussed with a long-term goal of developing
gVIIA-PLA2 as a catalytic bioscavenger of OP nerve agents.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

