 |
PDBsum entry 1e3v

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.1
- steroid Delta-isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 3-oxo-Delta5-steroid = a 3-oxo-Delta4-steroid
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-oxo-Delta(5)-steroid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 71.43% similarity
|
=
|
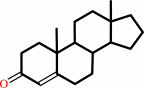 3-oxo-Delta(4)-steroid
3-oxo-Delta(4)-steroid
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
275:41100-41106
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Detection of large pKa perturbations of an inhibitor and a catalytic group at an enzyme active site, a mechanistic basis for catalytic power of many enzymes.
|
|
N.C.Ha,
M.S.Kim,
W.Lee,
K.Y.Choi,
B.H.Oh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Delta(5)-3-Ketosteroid isomerase catalyzes cleavage and formation of a C-H bond
at a diffusion-controlled limit. By determining the crystal structures of the
enzyme in complex with each of three different inhibitors and by nuclear
magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic investigation, we evidenced the
ionization of a hydroxyl group (pK(a) approximately 16.5) of an inhibitor, which
forms a low barrier hydrogen bond (LBHB) with a catalytic residue Tyr(14) (pK(a)
approximately 11.5), and the protonation of the catalytic residue Asp(38) with
pK(a) of approximately 4.5 at pH 6.7 in the interaction with a carboxylate group
of an inhibitor. The perturbation of the pK(a) values in both cases arises from
the formation of favorable interactions between inhibitors and catalytic
residues. The results indicate that the pK(a) difference between catalytic
residue and substrate can be significantly reduced in the active site
environment as a result of the formation of energetically favorable interactions
during the course of enzyme reactions. The reduction in the pK(a) difference
should facilitate the abstraction of a proton and thereby eliminate a large
fraction of activation energy in general acid/base enzyme reactions. The pK(a)
perturbation provides a mechanistic ground for the fast reactivity of many
enzymes and for the understanding of how some enzymes are able to extract a
proton from a C-H group with a pK(a) value as high as approximately 30.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Dimeric structure, enzymatic reaction mechanism,
and competitive inhibitors of PI. a, the dimeric structure of
KSI in complex with equilenin is shown with the three critical
active site residues and equilenin in a ball-and-stick model. b,
the enzyme mechanism of KSI proceeding through a dienolic
intermediate is shown with the catalytic residues. The H-bond
between the Tyr14 OH and the oxyanion of the intermediate is
indicated in a conventional way to denote a LBHB formation, the
proton being in the middle of the two heavy atoms. c, the three
competitive inhibitors used in this study are shown along with
their markedly different pK[a] values.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Interaction of DC with PI. a, stereoview of the
bound inhibitor and the three catalytic residues is shown along
with the 2F[o]  F[c]
electron density map at 2.0 Å resolution contoured at 1.0 F[c]
electron density map at 2.0 Å resolution contoured at 1.0
 . The
H-bonds and their distances are indicated. b, four possible
ionization states in the interaction of DC with the catalytic
residues. Whereas the first binding mode results in three
charged H-bonds, the rest of the binding modes result in one
charged and two neutral H-bonds. . The
H-bonds and their distances are indicated. b, four possible
ionization states in the interaction of DC with the catalytic
residues. Whereas the first binding mode results in three
charged H-bonds, the rest of the binding modes result in one
charged and two neutral H-bonds.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2000,
275,
41100-41106)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.Hotta,
X.Chen,
R.S.Paton,
A.Minami,
H.Li,
K.Swaminathan,
I.I.Mathews,
K.Watanabe,
H.Oikawa,
K.N.Houk,
and
C.Y.Kim
(2012).
Enzymatic catalysis of anti-Baldwin ring closure in polyether biosynthesis.
|
| |
Nature,
483,
355-358.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Pápai,
A.Hamza,
P.M.Pihko,
and
R.K.Wierenga
(2011).
Stereoelectronic requirements for optimal hydrogen-bond-catalyzed enolization.
|
| |
Chemistry,
17,
2859-2866.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Maurer,
and
R.Iftimie
(2010).
Combining ab initio quantum mechanics with a dipole-field model to describe acid dissociation reactions in water: first-principles free energy and entropy calculations.
|
| |
J Chem Phys,
132,
074112.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Li,
K.E.Roege,
and
W.L.Kelly
(2009).
Analysis of the indanomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces antibioticus NRRL 8167.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
1064-1072.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.K.Chakravorty,
A.V.Soudackov,
and
S.Hammes-Schiffer
(2009).
Hybrid quantum/classical molecular dynamics simulations of the proton transfer reactions catalyzed by ketosteroid isomerase: analysis of hydrogen bonding, conformational motions, and electrostatics.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
10608-10619.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Schwans,
D.A.Kraut,
and
D.Herschlag
(2009).
Determining the catalytic role of remote substrate binding interactions in ketosteroid isomerase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
14271-14275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Bakirci,
A.L.Koner,
T.Schwarzlose,
and
W.M.Nau
(2006).
Analysis of host-assisted guest protonation exemplified for p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene--towards enzyme-mimetic pKa shifts.
|
| |
Chemistry,
12,
4799-4807.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Shokhen,
and
A.Albeck
(2004).
Is there a weak H-bond --> LBHB transition on tetrahedral complex formation in serine proteases?
|
| |
Proteins,
54,
468-477.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

