 |
PDBsum entry 6qu7

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6qu7
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.3.5.2
- dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-dihydroorotate + a quinone = orotate + a quinol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(S)-dihydroorotate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
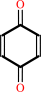 quinone
quinone
|
=
|
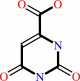 orotate
orotate
|
+
|
quinol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FMN
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FMN)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Leukemia
33:2403-2415
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The novel dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitor BAY 2402234 triggers differentiation and is effective in the treatment of myeloid malignancies.
|
|
S.Christian,
C.Merz,
L.Evans,
S.Gradl,
H.Seidel,
A.Friberg,
A.Eheim,
P.Lejeune,
K.Brzezinka,
K.Zimmermann,
S.Ferrara,
H.Meyer,
R.Lesche,
D.Stoeckigt,
M.Bauser,
A.Haegebarth,
D.B.Sykes,
D.T.Scadden,
J.A.Losman,
A.Janzer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a devastating disease, with the majority of
patients dying within a year of diagnosis. For patients with relapsed/refractory
AML, the prognosis is particularly poor with currently available treatments.
Although genetically heterogeneous, AML subtypes share a common differentiation
arrest at hematopoietic progenitor stages. Overcoming this differentiation
arrest has the potential to improve the long-term survival of patients, as is
the case in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), which is characterized by a
chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene.
Treatment of APL with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) induces terminal
differentiation and apoptosis of leukemic promyelocytes, resulting in cure rates
of over 80%. Unfortunately, similarly efficacious differentiation therapies
have, to date, been lacking outside of APL. Inhibition of dihydroorotate
dehydrogenase (DHODH), a key enzyme in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway,
was recently reported to induce differentiation of diverse AML subtypes. In this
report we describe the discovery and characterization of BAY 2402234 - a novel,
potent, selective and orally bioavailable DHODH inhibitor that shows monotherapy
efficacy and differentiation induction across multiple AML subtypes. Herein, we
present the preclinical data that led to initiation of a phase I evaluation of
this inhibitor in myeloid malignancies.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

