 |
PDBsum entry 6leh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|

|

|

|
 _ZN
×2 _ZN
×2
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 _CA _CA
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 _NA _NA
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 __K __K
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 _CL
×2 _CL
×2
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.39
- alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine + H2O = a 1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphate + ethanolamine + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
1-O-alkyl- sn-glycero-3-phosphate
|
+
|
ethanolamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.4
- phospholipase D.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero- 3-phosphate + choline + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero- 3-phosphate
|
+
|
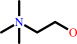 choline
choline
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
63:3188-3204
(2020)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification of Potent In Vivo Autotaxin Inhibitors that Bind to Both Hydrophobic Pockets and Channels in the Catalytic Domain.
|
|
M.Kawaguchi,
T.Okabe,
S.Okudaira,
K.Hama,
K.Kano,
H.Nishimasu,
H.Nakagawa,
R.Ishitani,
H.Kojima,
O.Nureki,
J.Aoki,
T.Nagano.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Autotaxin (ATX, also known as ENPP2) is a predominant lysophosphatidic acid
(LPA)-producing enzyme in the body, and LPA regulates various physiological
functions, such as angiogenesis and wound healing, as well as pathological
functions, including proliferation, metastasis, and fibrosis, via specific LPA
receptors. Therefore, the ATX-LPA axis is a promising therapeutic target for
dozens of diseases, including cancers, pulmonary and liver fibroses, and
neuropathic pain. Previous structural studies revealed that the catalytic domain
of ATX has a hydrophobic pocket and a hydrophobic channel; these serve to
recognize the substrate, lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and deliver generated
LPA to LPA receptors on the plasma membrane. Most reported ATX inhibitors bind
to either the hydrophobic pocket or the hydrophobic channel. Herein, we present
a unique ATX inhibitor that binds mainly to the hydrophobic pocket and also
partly to the hydrophobic channel, inhibiting ATX activity with high potency and
selectivity in vitro and in vivo. Notably, our inhibitor can
rescue the cardia bifida (two hearts) phenotype in ATX-overexpressing zebrafish
embryos.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

