 |
PDBsum entry 5cec

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Protein binding
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5cec
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.3.4.16.4
- serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-alanyl-D-alanine + H2O = 2 D-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
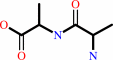
|
+
|
|
=
|
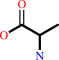 2
×
2
×
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
6:8884
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Ankyrin-mediated self-protection during cell invasion by the bacterial predator Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.
|
|
C.Lambert,
I.T.Cadby,
R.Till,
N.K.Bui,
T.R.Lerner,
W.S.Hughes,
D.J.Lee,
L.J.Alderwick,
W.Vollmer,
R.E.Sockett,
E.R.Sockett,
A.L.Lovering.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Predatory Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus are natural antimicrobial organisms,
killing other bacteria by whole-cell invasion. Self-protection against
prey-metabolizing enzymes is important for the evolution of predation. Initial
prey entry involves the predator's peptidoglycan DD-endopeptidases, which
decrosslink cell walls and prevent wasteful entry by a second predator. Here we
identify and characterize a self-protection protein from B. bacteriovorus,
Bd3460, which displays an ankyrin-based fold common to intracellular pathogens
of eukaryotes. Co-crystal structures reveal Bd3460 complexation of dual targets,
binding a conserved epitope of each of the Bd3459 and Bd0816 endopeptidases.
Complexation inhibits endopeptidase activity and cell wall decrosslinking in
vitro. Self-protection is vital - ΔBd3460 Bdellovibrio deleteriously
decrosslink self-peptidoglycan upon invasion, adopt a round morphology, and lose
predatory capacity and cellular integrity. Our analysis provides the first
mechanistic examination of self-protection in Bdellovibrio, documents
protection-multiplicity for products of two different genomic loci, and reveals
an important evolutionary adaptation to an invasive predatory bacterial
lifestyle.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

