 |
PDBsum entry 5bpp

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5bpp
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.3.2.6
- leukotriene-A4 hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
leukotriene A4 + H2O = leukotriene B4
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
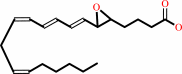 leukotriene A4
leukotriene A4
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
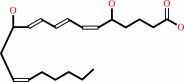 leukotriene B4
leukotriene B4
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.4.11.4
- tripeptide aminopeptidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
Release of a N-terminal residue from a tripeptide.
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Sci Rep
6:25298
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Bufexamac ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by targeting LTA4H.
|
|
Q.Xiao,
N.Dong,
X.Yao,
D.Wu,
Y.Lu,
F.Mao,
J.Zhu,
J.Li,
J.Huang,
A.Chen,
L.Huang,
X.Wang,
G.Yang,
G.He,
Y.Xu,
W.Lu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Neutrophils play an important role in the occurrence and development of acute
lung injury (ALI). Leukotriene B4 (LTB4), a hydrolysis product of epoxide
leukotriene A4 (LTA4) catalyzed by LTA4 hydrolase (LTA4H), is one of the most
potent chemoattractants for neutrophil. Bufexamac is a drug widely used as an
anti-inflammatory agent on the skin, however, the mechanism of action is still
not fully understood. In this study, we found bufexamac was capable of
specifically inhibiting LTA4H enzymatic activity and revealed the mode of
interaction of bufexamac and LTA4H using X-ray crystallography. Moreover,
bufexamac significantly prevented the production of LTB4 in neutrophil and
inhibited the fMLP-induced neutrophil migration through inhibition of LTA4H.
Finally, bufexamac significantly attenuated lung inflammation as reflected by
reduced LTB4 levels and weakened neutrophil infiltration in bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid from a lipopolysaccharide-induced ALI mouse model. In summary, our
study indicates that bufexamac acts as an inhibitor of LTB4 biosynthesis and may
have potential clinical applications for the treatment of ALI.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

