 |
PDBsum entry 4x7r
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.70
- poly(ribitol-phosphate) alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
4-O-[(D-ribitylphospho)(n)-di{(2R)-glycerylphospho}]-N-acetyl-beta-D- mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + n UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine = 4-O- ([2-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-1-D-ribitylphospho](n)-di{[2R]-1- glycerylphospho})-N-acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D- glucosaminyl di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + n UDP + n H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
4-O-[(D-ribitylphospho)(n)-di{(2R)-glycerylphospho}]-N-acetyl-beta-D- mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
n
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine
|
=
|
4-O- ([2-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-1-D-ribitylphospho](n)-di{[2R]-1- glycerylphospho})-N-acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D- glucosaminyl di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
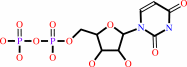 n
UDP
n
UDP
|
+
|
n
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
112:E576
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus TarM, the wall teichoic acid α-glycosyltransferase.
|
|
S.Sobhanifar,
L.J.Worrall,
R.J.Gruninger,
G.A.Wasney,
M.Blaukopf,
L.Baumann,
E.Lameignere,
M.Solomonson,
E.D.Brown,
S.G.Withers,
N.C.Strynadka.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Unique to Gram-positive bacteria, wall teichoic acids are anionic glycopolymers
cross-stitched to a thick layer of peptidoglycan. The polyol phosphate subunits
of these glycopolymers are decorated with GlcNAc sugars that are involved in
phage binding, genetic exchange, host antibody response, resistance, and
virulence. The search for the enzymes responsible for GlcNAcylation in
Staphylococcus aureus has recently identified TarM and TarS with respective α-
and β-(1-4) glycosyltransferase activities. The stereochemistry of the GlcNAc
attachment is important in balancing biological processes, such that the
interplay of TarM and TarS is likely important for bacterial pathogenicity and
survival. Here we present the crystal structure of TarM in an unusual
ternary-like complex consisting of a polymeric acceptor substrate analog, UDP
from a hydrolyzed donor, and an α-glyceryl-GlcNAc product formed in situ. These
structures support an internal nucleophilic substitution-like mechanism, lend
new mechanistic insight into the glycosylation of glycopolymers, and reveal a
trimerization domain with a likely role in acceptor substrate scaffolding.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

