 |
PDBsum entry 4rfc
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Human carbonic anhydrase ii in complex with tert-butyl 4-(4- sulfamoylphenoxy)butylcarbamate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: carbonate dehydratase ii, carbonic anhydrasE C, cac, carbonic anhydrase ii, ca-ii. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ca2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.65Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.226
|
R-free:
|
0.260
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Bozdag,M.A.Pinard,F.Carta,E.Masini,A.Scozzafava,R.Mckenna, C.T.Supuran
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Bozdag
et al.
(2014).
A class of 4-sulfamoylphenyl-ω-aminoalkyl ethers with effective carbonic anhydrase inhibitory action and antiglaucoma effects.
J Med Chem,
57,
9673-9686.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-Sep-14
|
Release date:
|
15-Apr-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
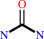 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
57:9673-9686
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A class of 4-sulfamoylphenyl-ω-aminoalkyl ethers with effective carbonic anhydrase inhibitory action and antiglaucoma effects.
|
|
M.Bozdag,
M.Pinard,
F.Carta,
E.Masini,
A.Scozzafava,
R.McKenna,
C.T.Supuran.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We report a series of 4-sulfamoylphenyl-ω-aminoalkyl ethers as carbonic
anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1) inhibitors. The structure-activity relationship was
drawn for the inhibition of four physiologically relevant isoforms: hCA I, II,
IX, and XII. Many of these compounds were highly effective, low nanomolar
inhibitors of all CA isoforms, whereas several isoform-selective were also
identified. X-ray crystal structures of two new sulfonamides bound to the
physiologically dominant CA II isoform showed the tails of these derivatives
bound within the hydrophobic half of the enzyme active site through van der
Waals contacts with Val135, Leu198, Leu204, Trp209, Pro201, and Pro202 amino
acids. One of the highly water-soluble compound (as trifluoroacetate salt)
showed effective IOP lowering properties in an animal model of glaucoma. Several
fluorescent sulfonamides incorporating either the fluorescein-thiourea (7a-c) or
tetramethylrhodamine-thiourea (9a,b) moieties were also obtained and showed
interesting CA inhibitory properties for the tumor-associated isoforms CA IX and
XII.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

