 |
PDBsum entry 4nfs

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4nfs
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
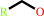 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
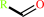 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
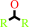 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
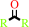 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
53:881-894
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Effects of cavities at the nicotinamide binding site of liver alcohol dehydrogenase on structure, dynamics and catalysis.
|
|
A.Yahashiri,
J.K.Rubach,
B.V.Plapp.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A role for protein dynamics in enzymatic catalysis of hydrogen transfer has
received substantial scientific support, but the connections between protein
structure and catalysis remain to be established. Valine residues 203 and 207
are at the binding site for the nicotinamide ring of the coenzyme in liver
alcohol dehydrogenase and have been suggested to facilitate catalysis with
"protein-promoting vibrations" (PPV). We find that the V207A
substitution has small effects on steady-state kinetic constants and the rate of
hydrogen transfer; the introduced cavity is empty and is tolerated with minimal
effects on structure (determined at 1.2 Å for the complex with NAD(+) and
2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl alcohol). Thus, no evidence is found to support a
role for Val-207 in the dynamics of catalysis. The protein structures and ligand
geometries (including donor-acceptor distances) in the V203A enzyme complexed
with NAD(+) and 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl alcohol or 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol
(determined at 1.1 Å) are very similar to those for the wild-type enzyme,
except that the introduced cavity accommodates a new water molecule that
contacts the nicotinamide ring. The structures of the V203A enzyme complexes
suggest, in contrast to previous studies, that the diminished tunneling and
decreased rate of hydride transfer (16-fold, relative to that of the wild-type
enzyme) are not due to differences in ground-state ligand geometries. The V203A
substitution may alter the PPV and the reorganization energy for hydrogen
transfer, but the protein scaffold and equilibrium thermal motions within the
Michaelis complex may be more significant for enzyme catalysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

