 |
PDBsum entry 4c4z
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human bifunctional epoxide hydroxylase 2 complexed with a8
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2. Chain: a, b. Fragment: epoxide hydroxylase domain residues 230-555. Synonym: bifunctional epoxide hydroxylase 2, cytosolic epoxide hydrolase 2, ceh, epoxide hydratase, soluble epoxide hydrolase, seh, lipid-phosphate phosphatase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.06Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.222
|
R-free:
|
0.253
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Pilger,A.Mazur,P.Monecke,H.Schreuder,B.Elshorst,T.Langer, A.Schiffer,I.Krimm,M.Wegstroth,D.Lee,G.Hessler,K.-U.Wendt,S.Becker, C.Griesinger
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Pilger
et al.
(2015).
A combination of spin diffusion methods for the determination of protein-ligand complex structural ensembles.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
54,
6511-6515.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
01-Oct-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P34913
(HYES_HUMAN) -
Bifunctional epoxide hydrolase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
555 a.a.
318 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.3.76
- lipid-phosphate phosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(9S,10S)-10-hydroxy-9-(phosphooxy)octadecanoate + H2O = (9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(9S,10S)-10-hydroxy-9-(phosphooxy)octadecanoate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
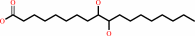 (9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate
(9S,10S)-9,10- dihydroxyoctadecanoate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.3.3.2.10
- soluble epoxide hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an epoxide + H2O = an ethanediol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
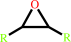 epoxide
epoxide
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
ethanediol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
54:6511-6515
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A combination of spin diffusion methods for the determination of protein-ligand complex structural ensembles.
|
|
J.Pilger,
A.Mazur,
P.Monecke,
H.Schreuder,
B.Elshorst,
S.Bartoschek,
T.Langer,
A.Schiffer,
I.Krimm,
M.Wegstroth,
D.Lee,
G.Hessler,
K.U.Wendt,
S.Becker,
C.Griesinger.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Structure-based drug design (SBDD) is a powerful and widely used approach to
optimize affinity of drug candidates. With the recently introduced INPHARMA
method, the binding mode of small molecules to their protein target can be
characterized even if no spectroscopic information about the protein is known.
Here, we show that the combination of the spin-diffusion-based NMR methods
INPHARMA, trNOE, and STD results in an accurate scoring function for docking
modes and therefore determination of protein-ligand complex structures.
Applications are shown on the model system protein kinase A and the drug
targets glycogen phosphorylase and soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). Multiplexing
of several ligands improves the reliability of the scoring function further. The
new score allows in the case of sEH detecting two binding modes of the ligand in
its binding site, which was corroborated by X-ray analysis.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

