 |
PDBsum entry 3wcf
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
The complex structure of hssqs wtih ligand,bph1218
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Squalene synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Fragment: unp residues 31-370. Synonym: sqs, ss, fpp, fpp farnesyltransferase, farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: fdft1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.22Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.204
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
N.Shang,Q.Li,T.P.Ko,H.C.Chan,C.H.Huang,F.Ren,Y.Zheng,Z.Zhu,C.C.Chen, R.T.Guo
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
N.Shang
et al.
(2014).
Squalene synthase as a target for Chagas disease therapeutics.
Plos Pathog,
10,
e1004114.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
27-May-13
|
Release date:
|
18-Jun-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P37268
(FDFT_HUMAN) -
Squalene synthase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
417 a.a.
334 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 4 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.21
- squalene synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Squalene and Phytoene Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
2 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + NADPH + H+ = squalene + 2 diphosphate + NADP+
|
|
2.
|
2 (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate + NADH + H+ = squalene + 2 diphosphate + NAD+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
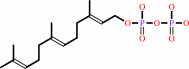 2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 squalene
squalene
|
+
|
 2
×
diphosphate
2
×
diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
2
×
(2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 squalene
squalene
|
+
|
 2
×
diphosphate
2
×
diphosphate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+) or Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Plos Pathog
10:e1004114
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Squalene synthase as a target for Chagas disease therapeutics.
|
|
N.Shang,
Q.Li,
T.P.Ko,
H.C.Chan,
J.Li,
Y.Zheng,
C.H.Huang,
F.Ren,
C.C.Chen,
Z.Zhu,
M.Galizzi,
Z.H.Li,
C.A.Rodrigues-Poveda,
D.Gonzalez-Pacanowska,
P.Veiga-Santos,
T.M.de Carvalho,
W.de Souza,
J.A.Urbina,
A.H.Wang,
R.Docampo,
K.Li,
Y.L.Liu,
E.Oldfield,
R.T.Guo.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Trypanosomatid parasites are the causative agents of many neglected tropical
diseases and there is currently considerable interest in targeting endogenous
sterol biosynthesis in these organisms as a route to the development of novel
anti-infective drugs. Here, we report the first x-ray crystallographic
structures of the enzyme squalene synthase (SQS) from a trypanosomatid parasite,
Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease. We obtained five
structures of T. cruzi SQS and eight structures of human SQS with four classes
of inhibitors: the substrate-analog S-thiolo-farnesyl diphosphate, the
quinuclidines E5700 and ER119884, several lipophilic bisphosphonates, and the
thiocyanate WC-9, with the structures of the two very potent quinuclidines
suggesting strategies for selective inhibitor development. We also show that the
lipophilic bisphosphonates have low nM activity against T. cruzi and inhibit
endogenous sterol biosynthesis and that E5700 acts synergistically with the
azole drug, posaconazole. The determination of the structures of trypanosomatid
and human SQS enzymes with a diverse set of inhibitors active in cells provides
insights into SQS inhibition, of interest in the context of the development of
drugs against Chagas disease.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

